二叉树的对角遍历
考虑在节点之间通过的斜率 -1 线。给定一棵二叉树,打印二叉树中属于同一行的所有对角线元素。
Input : Root of below tree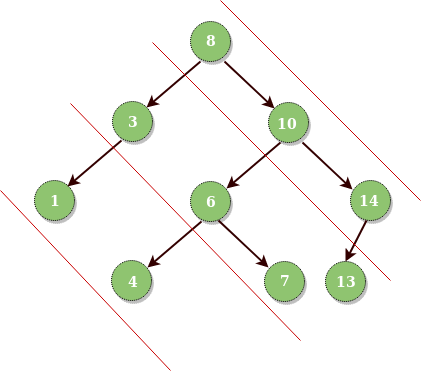
Output :
Diagonal Traversal of binary tree :
8 10 14
3 6 7 13
1 4
Observation : root and root->right values will be prioritized over all root->left values.这个想法是使用地图。我们使用不同的坡度距离并将它们用作地图中的关键。地图中的值是节点的向量(或动态数组)。我们遍历树以将值存储在地图中。一旦地图建立,我们打印它的内容。
下面是上述思想的实现。
C++
// C++ program for diagonal
// traversal of Binary Tree
#include
using namespace std;
// Tree node
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
/* root - root of the binary tree
d - distance of current line from rightmost
-topmost slope.
diagonalPrint - multimap to store Diagonal
elements (Passed by Reference) */
void diagonalPrintUtil(Node* root, int d,
map> &diagonalPrint)
{
// Base case
if (!root)
return;
// Store all nodes of same
// line together as a vector
diagonalPrint[d].push_back(root->data);
// Increase the vertical
// distance if left child
diagonalPrintUtil(root->left,
d + 1, diagonalPrint);
// Vertical distance remains
// same for right child
diagonalPrintUtil(root->right,
d, diagonalPrint);
}
// Print diagonal traversal
// of given binary tree
void diagonalPrint(Node* root)
{
// create a map of vectors
// to store Diagonal elements
map > diagonalPrint;
diagonalPrintUtil(root, 0, diagonalPrint);
cout << "Diagonal Traversal of binary tree : \n";
for (auto it :diagonalPrint)
{
vector v=it.second;
for(auto it:v)
cout<data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(8);
root->left = newNode(3);
root->right = newNode(10);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right->right->left = newNode(13);
root->left->right->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right->right = newNode(7);
/* Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(9);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->left = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left->left = newNode(12);
root->left->right->left = newNode(11);
root->left->left->right = newNode(10);*/
diagonalPrint(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for diagonal
// traversal of Binary Tree
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Vector;
public class DiagonalTraversalBTree
{
// Tree node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
//constructor
Node(int data)
{
this.data=data;
left = null;
right =null;
}
}
/* root - root of the binary tree
d - distance of current line from rightmost
-topmost slope.
diagonalPrint - HashMap to store Diagonal
elements (Passed by Reference) */
static void diagonalPrintUtil(Node root,int d,
TreeMap> diagonalPrint)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
// get the list at the particular d value
Vector k = diagonalPrint.get(d);
// k is null then create a
// vector and store the data
if (k == null)
{
k = new Vector<>();
k.add(root.data);
}
// k is not null then update the list
else
{
k.add(root.data);
}
// Store all nodes of same line
// together as a vector
diagonalPrint.put(d,k);
// Increase the vertical distance
// if left child
diagonalPrintUtil(root.left,
d + 1, diagonalPrint);
// Vertical distance remains
// same for right child
diagonalPrintUtil(root.right,
d, diagonalPrint);
}
// Print diagonal traversal
// of given binary tree
static void diagonalPrint(Node root)
{
// create a map of vectors
// to store Diagonal elements
TreeMap>
diagonalPrint = new TreeMap<>();
diagonalPrintUtil(root, 0, diagonalPrint);
System.out.println("Diagonal Traversal of Binary Tree");
for (Entry> entry :
diagonalPrint.entrySet())
{
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
}
}
// Driver program
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.left.right = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.left.right.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right.right = new Node(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sumit Ghosh Python3
# Python program for diagonal
# traversal of Binary Tree
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a
# new binary tree node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
""" root - root of the binary tree
d - distance of current line from rightmost
-topmost slope.
diagonalPrint - multimap to store Diagonal
elements (Passed by Reference) """
def diagonalPrintUtil(root, d, diagonalPrintMap):
# Base Case
if root is None:
return
# Store all nodes of same line
# together as a vector
try :
diagonalPrintMap[d].append(root.data)
except KeyError:
diagonalPrintMap[d] = [root.data]
# Increase the vertical distance
# if left child
diagonalPrintUtil(root.left,
d+1, diagonalPrintMap)
# Vertical distance remains
# same for right child
diagonalPrintUtil(root.right,
d, diagonalPrintMap)
# Print diagonal traversal of given binary tree
def diagonalPrint(root):
# Create a dict to store diagonal elements
diagonalPrintMap = dict()
# Find the diagonal traversal
diagonalPrintUtil(root, 0, diagonalPrintMap)
print ("Diagonal Traversal of binary tree : ")
for i in diagonalPrintMap:
for j in diagonalPrintMap[i]:
print (j,end=" ")
print()
# Driver Program
root = Node(8)
root.left = Node(3)
root.right = Node(10)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(14)
root.right.right.left = Node(13)
root.left.right.left = Node(4)
root.left.right.right = Node(7)
diagonalPrint(root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)Python3
from collections import deque
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a
# new binary tree node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def diagonal(root):
out = []
node = root
# queue to store left nodes
left_q = deque()
while node:
# append data to output array
out.append(node.data)
# if left available add it to the queue
if node.left:
left_q.appendleft(node.left)
# if right is available change the node
if node.right:
node = node.right
else:
# else pop the left_q
if len(left_q) >= 1:
node = left_q.pop()
else:
node = None
return out
# Driver Code
root = Node(8)
root.left = Node(3)
root.right = Node(10)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(14)
root.right.right.left = Node(13)
root.left.right.left = Node(4)
root.left.right.right = Node(7)
print(diagonal(root))C++14
#include
using namespace std;
// Tree node
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
vector diagonal(Node* root)
{
vector diagonalVals;
if (!root)
return diagonalVals;
// The leftQueue will be a queue which will store all
// left pointers while traversing the tree, and will be
// utilized when at any point right pointer becomes NULL
queue leftQueue;
Node* node = root;
while (node) {
// Add current node to output
diagonalVals.push_back(node->data);
// If left child available, add it to queue
if (node->left)
leftQueue.push(node->left);
// if right child, transfer the node to right
if (node->right)
node = node->right;
else {
// If left child Queue is not empty, utilize it
// to traverse further
if (!leftQueue.empty()) {
node = leftQueue.front();
leftQueue.pop();
}
else {
// All the right childs traversed and no
// left child left
node = NULL;
}
}
}
return diagonalVals;
}
// Utility method to create a new node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(8);
root->left = newNode(3);
root->right = newNode(10);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right->right->left = newNode(13);
root->left->right->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right->right = newNode(7);
/* Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(9);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->left = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left->left = newNode(12);
root->left->right->left = newNode(11);
root->left->left->right = newNode(10);*/
vector diagonalValues = diagonal(root);
for (int i = 0; i < diagonalValues.size(); i++) {
cout << diagonalValues[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
} C++
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
vector > result;
void diagonalPrint(Node* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
queue q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
vector answer;
while(size--)
{
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
// traversing each component;
while(temp)
{
answer.push_back(temp->data);
if(temp->left)
q.push(temp->left);
temp = temp->right;
}
}
result.push_back(answer);
}
}
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(8);
root->left = newNode(3);
root->right = newNode(10);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right->right->left = newNode(13);
root->left->right->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right->right = newNode(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
for(int i=0 ; i Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Tree node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
// Constructor
Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
static class TNode
{
Node node;
int level;
public TNode(Node n, int l)
{
this.node = n;
this.level = l;
}
}
public static void diagonalPrint(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
{
return;
}
TreeMap> map = new TreeMap>();
Queue q = new LinkedList();
q.add(new TNode(root, 0));
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
TNode curr = q.poll();
map.putIfAbsent(curr.level, new ArrayList<>());
map.get(curr.level).add(curr.node.data);
if (curr.node.left != null)
{
q.add(new TNode(curr.node.left,
curr.level + 1));
}
if (curr.node.right != null)
{
q.add(new TNode(curr.node.right,
curr.level));
}
}
for(Map.Entry>
entry : map.entrySet())
{
int k = entry.getKey();
List l = map.get(k);
int size = l.size();
for(int i = 0; i < l.size(); i++)
{
System.out.print(l.get(i));
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println("");
}
return;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.left.right = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.left.right.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right.right = new Node(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by abhinaygupta98 输出
Diagonal Traversal of binary tree :
8 10 14
3 6 7 13
1 4 该解的时间复杂度为O( N logN ) ,空间复杂度为O( N )
我们可以使用队列和迭代算法来解决同样的问题。
Python3
from collections import deque
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a
# new binary tree node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def diagonal(root):
out = []
node = root
# queue to store left nodes
left_q = deque()
while node:
# append data to output array
out.append(node.data)
# if left available add it to the queue
if node.left:
left_q.appendleft(node.left)
# if right is available change the node
if node.right:
node = node.right
else:
# else pop the left_q
if len(left_q) >= 1:
node = left_q.pop()
else:
node = None
return out
# Driver Code
root = Node(8)
root.left = Node(3)
root.right = Node(10)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(14)
root.right.right.left = Node(13)
root.left.right.left = Node(4)
root.left.right.right = Node(7)
print(diagonal(root))
C++14
#include
using namespace std;
// Tree node
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
vector diagonal(Node* root)
{
vector diagonalVals;
if (!root)
return diagonalVals;
// The leftQueue will be a queue which will store all
// left pointers while traversing the tree, and will be
// utilized when at any point right pointer becomes NULL
queue leftQueue;
Node* node = root;
while (node) {
// Add current node to output
diagonalVals.push_back(node->data);
// If left child available, add it to queue
if (node->left)
leftQueue.push(node->left);
// if right child, transfer the node to right
if (node->right)
node = node->right;
else {
// If left child Queue is not empty, utilize it
// to traverse further
if (!leftQueue.empty()) {
node = leftQueue.front();
leftQueue.pop();
}
else {
// All the right childs traversed and no
// left child left
node = NULL;
}
}
}
return diagonalVals;
}
// Utility method to create a new node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(8);
root->left = newNode(3);
root->right = newNode(10);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right->right->left = newNode(13);
root->left->right->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right->right = newNode(7);
/* Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(9);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->left = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left->left = newNode(12);
root->left->right->left = newNode(11);
root->left->left->right = newNode(10);*/
vector diagonalValues = diagonal(root);
for (int i = 0; i < diagonalValues.size(); i++) {
cout << diagonalValues[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
[8, 10, 14, 3, 6, 7, 13, 1, 4]该解的时间复杂度为O( N logN ) ,空间复杂度为O( N )
方法2:使用队列。
每个节点都将有助于生成下一个对角线。只有当它的左边可用时,我们才会将元素推送到队列中。我们将处理节点并向右移动。
代码:
C++
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
vector > result;
void diagonalPrint(Node* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
queue q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
vector answer;
while(size--)
{
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
// traversing each component;
while(temp)
{
answer.push_back(temp->data);
if(temp->left)
q.push(temp->left);
temp = temp->right;
}
}
result.push_back(answer);
}
}
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(8);
root->left = newNode(3);
root->right = newNode(10);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right->right->left = newNode(13);
root->left->right->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right->right = newNode(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
for(int i=0 ; i Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Tree node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
// Constructor
Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
static class TNode
{
Node node;
int level;
public TNode(Node n, int l)
{
this.node = n;
this.level = l;
}
}
public static void diagonalPrint(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
{
return;
}
TreeMap> map = new TreeMap>();
Queue q = new LinkedList();
q.add(new TNode(root, 0));
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
TNode curr = q.poll();
map.putIfAbsent(curr.level, new ArrayList<>());
map.get(curr.level).add(curr.node.data);
if (curr.node.left != null)
{
q.add(new TNode(curr.node.left,
curr.level + 1));
}
if (curr.node.right != null)
{
q.add(new TNode(curr.node.right,
curr.level));
}
}
for(Map.Entry>
entry : map.entrySet())
{
int k = entry.getKey();
List l = map.get(k);
int size = l.size();
for(int i = 0; i < l.size(); i++)
{
System.out.print(l.get(i));
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println("");
}
return;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.left.right = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.left.right.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right.right = new Node(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by abhinaygupta98
输出
8 10 14
3 6 7 13
1 4 时间复杂度: O(N) ,因为我们访问节点一次。
空间复杂度: O(N) ,因为我们使用的是队列。