Spring – 刻板印象注释
Spring 是最流行的Java EE 框架之一。它是一个开源轻量级框架,允许Java EE 7 开发人员构建简单、可靠且可扩展的企业应用程序。该框架主要侧重于提供各种方法来帮助您管理业务对象。现在谈论 Spring Annotation, Spring Annotation 是一种元数据形式,它提供有关程序的数据。注释用于提供有关程序的补充信息。它对他们注释的代码的操作没有直接影响。它不会改变编译程序的动作。
刻板印象注释
Spring Framework 为我们提供了一些特殊的注解。这些注解用于在应用程序上下文中自动创建 Spring bean。 @Component 注解是主要的 Stereotype 注解。有一些从@Component派生的 Stereotype 元注释,它们是
- @服务
- @Repository
- @控制器
1:@Service:我们用@Service 指定一个类来表明他们持有业务逻辑。该注解除了用于服务层外,没有其他特殊用途。实用程序类可以标记为服务类。
2:@Repository:我们用@Repository 指定一个类来表示他们正在处理CRUD 操作,通常,它与处理数据库表的DAO(数据访问对象)或Repository 实现一起使用。
3:@Controller:我们用@Controller 指定一个类,表示它们是前端控制器,负责处理用户请求并返回适当的响应。它主要用于 REST Web 服务。
So the stereotype annotations in spring are @Component, @Service, @Repository, and @Controller.

@Component 注解
@Component 是一个类级别的注解。它用于将类表示为组件。我们可以在整个应用程序中使用 @Component 将 bean 标记为 Spring 的托管组件。一个组件负责一些操作。
说明:让我们创建一个非常简单的 Spring 启动应用程序来展示 Spring 组件注解的使用以及 Spring 如何通过基于注解的配置和类路径扫描自动检测它。
第 1 步:创建一个简单的 Spring Boot 项目。极客,您需要创建和设置 Spring Boot 项目的先决条件
参考这篇文章在 Eclipse IDE 中创建和设置 Spring Boot 项目并创建一个简单的 Spring Boot 项目。
第 2 步:在 pom.xml 文件中添加 spring-context 依赖项。转到项目中的 pom.xml 文件并添加以下 spring-context 依赖项。
XML
org.springframework
spring-context
5.3.13
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Component class
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// Annotation
@Component
// Class
public class ComponentDemo {
// Method
public void demoFunction()
{
// Print statement when method is called
System.out.println("Hello GeeksForGeeks");
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Application class
// Importing package here
package com.example.demo;
// Importing required classes
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
// Annotation
@SpringBootApplication
// Class
public class DemoApplication {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Annotation based spring context
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.scan("com.example.demo");
context.refresh();
// Getting the Bean from the component class
ComponentDemo componentDemo = context.getBean(ComponentDemo.class);
componentDemo.demoFunction();
// Closing the context
// using close() method
context.close();
}
}XML
org.springframework
spring-context
5.3.13
Java
package com.example.demo.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MyServiceClass {
// Simple program for
// factorial of a number
public int factorial(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
return n*factorial(n-1);
}
}Java
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.service.MyServiceClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.scan("com.example.demo");
context.refresh();
MyServiceClass myServiceClass = context.getBean(MyServiceClass.class);
// Testing the factorial method
int factorialOf5 = myServiceClass.factorial(5);
System.out.println("Factorial of 5 is: " + factorialOf5);
// close the spring context
context.close();
}
}XML
org.springframework
spring-context
5.3.13
Java
package com.example.demo.entity;
public class Student {
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(Long id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}Java
// Java Program to illustrate DemoRepository File
package com.example.demo.repository;
public interface DemoRepository {
// Save method
public void save(T t);
// Find a student by its id
public T findStudentById(Long id);
} Java
// Java Program to illustrate StudentRepository File
package com.example.demo.repository;
import com.example.demo.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Repository
public class StudentRepository implements DemoRepository {
// Using an in-memory Map
// to store the object data
private Map repository;
public StudentRepository() {
this.repository = new HashMap<>();
}
// Implementation for save method
@Override
public void save(Student student) {
repository.put(student.getId(), student);
}
// Implementation for findStudentById method
@Override
public Student findStudentById(Long id) {
return repository.get(id);
}
} Java
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.entity.Student;
import com.example.demo.repository.StudentRepository;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.scan("com.example.demo");
context.refresh();
StudentRepository repository = context.getBean(StudentRepository.class);
// testing the store method
repository.save(new Student(1L, "Anshul", 25));
repository.save(new Student(2L, "Mayank", 23));
// testing the retrieve method
Student student = repository.findStudentById(1L);
System.out.println(student);
// close the spring context
context.close();
}
}XML
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
Java
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class DemoController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public String helloGFG()
{
return "Hello GeeksForGeeks";
}
}Java
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}第三步:创建一个简单的组件类
转到src > main > Java > your package name > 右键单击 > New > Java Class并创建您的组件类并用@Component注释标记它。
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Component class
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// Annotation
@Component
// Class
public class ComponentDemo {
// Method
public void demoFunction()
{
// Print statement when method is called
System.out.println("Hello GeeksForGeeks");
}
}
第 4 步:创建基于注释的 spring 上下文
现在转到您的应用程序(@SpringBootApplication)文件,并在此文件中创建一个基于注释的 spring 上下文并从中获取 ComponentDemo bean。
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Application class
// Importing package here
package com.example.demo;
// Importing required classes
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
// Annotation
@SpringBootApplication
// Class
public class DemoApplication {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Annotation based spring context
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.scan("com.example.demo");
context.refresh();
// Getting the Bean from the component class
ComponentDemo componentDemo = context.getBean(ComponentDemo.class);
componentDemo.demoFunction();
// Closing the context
// using close() method
context.close();
}
}
输出:
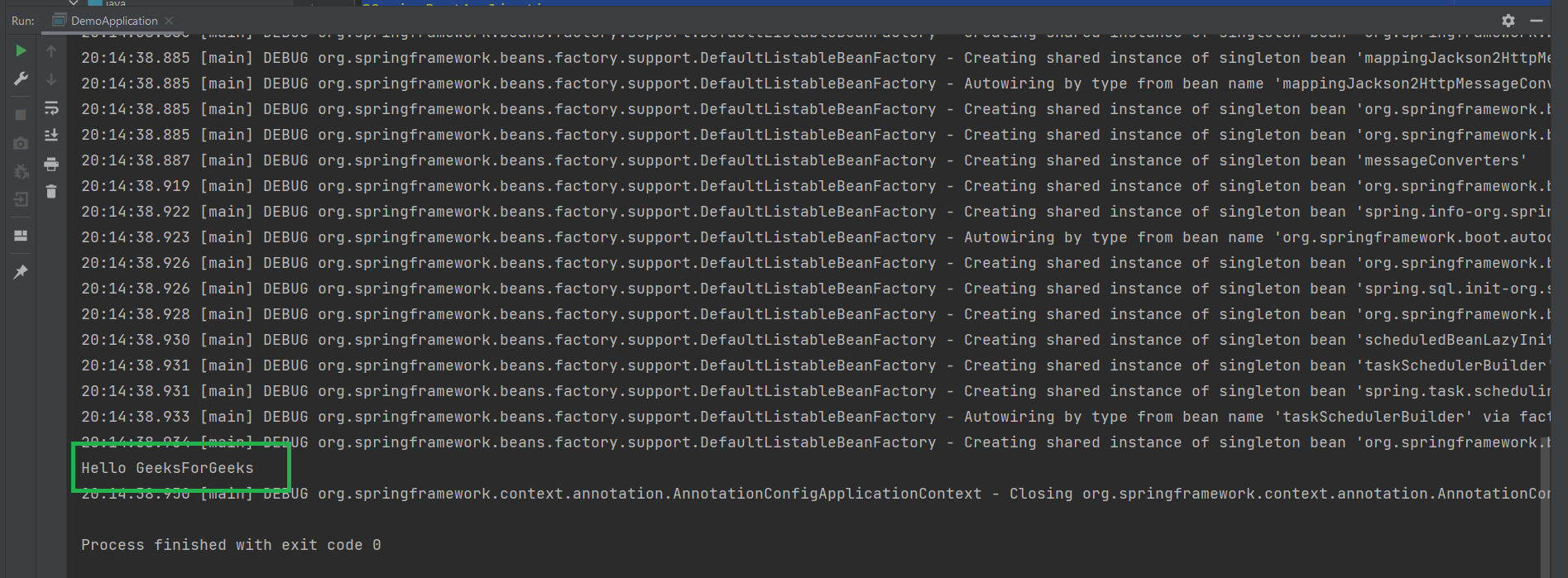
所以你可以看到@Component注解的威力,我们不需要做任何事情来将我们的组件注入到spring上下文中。
@Service注解
在应用程序中,业务逻辑位于服务层中,因此我们使用@Service 注解来指示一个类属于该层。它也是@Component Annotation的一个特化,就像@Repository Annotation一样。 @Service 注解最重要的一点是它只能应用于类。它用于将类标记为服务提供者。因此,整体 @Service 注释与提供一些业务功能的类一起使用。当使用基于注释的配置和类路径扫描时,Spring 上下文将自动检测这些类。
例子
第 1 步:创建一个简单的 Spring Boot 项目
参考这篇文章在 Eclipse IDE 中创建和设置 Spring Boot 项目并创建一个简单的 Spring Boot 项目。
第 2 步:在 pom.xml 文件中添加 spring-context 依赖项。转到项目中的 pom.xml 文件并添加以下 spring-context 依赖项。
XML
org.springframework
spring-context
5.3.13
第 3 步:在您的项目中创建一个包并将包命名为“服务”。在服务包中创建一个类并将其命名为MyServiceClass 。这将是我们最终的项目结构。

下面是MyServiceClass 的代码。 Java文件。
Java
package com.example.demo.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MyServiceClass {
// Simple program for
// factorial of a number
public int factorial(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
return n*factorial(n-1);
}
}
请注意,在这段代码中,它是一个简单的Java类,提供了计算数字的阶乘的功能。所以我们可以称它为服务提供者。我们使用 @Service 注释对其进行了注释,以便 spring-context 可以自动检测它,并且我们可以从上下文中获取它的实例。
第 4 步: Spring 存储库测试
所以现在我们的 Spring Repository 已经准备好了,让我们测试一下。转到演示应用程序。 Java文件并参考下面的代码。
Java
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.service.MyServiceClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.scan("com.example.demo");
context.refresh();
MyServiceClass myServiceClass = context.getBean(MyServiceClass.class);
// Testing the factorial method
int factorialOf5 = myServiceClass.factorial(5);
System.out.println("Factorial of 5 is: " + factorialOf5);
// close the spring context
context.close();
}
}
输出:
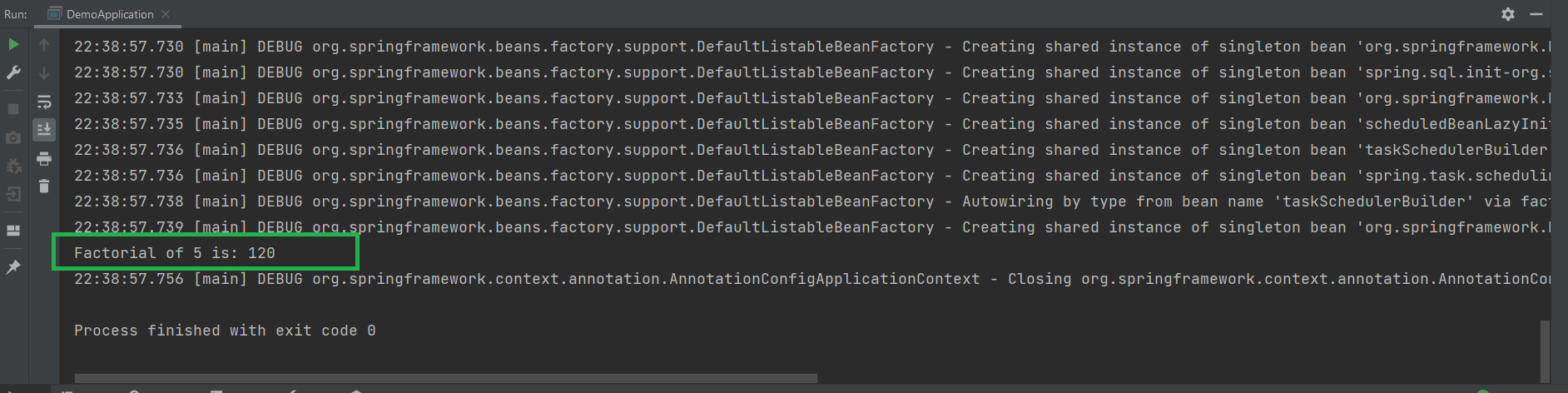
@Repository 注解
@Repository 注解是@Component注解的一种特殊化,用于表示该类提供了对对象进行存储、检索、更新、删除和搜索操作的机制。虽然它是 @Component 注解的特化,所以 Spring Repository 类是由 Spring 框架通过类路径扫描自动检测到的。这个注解是一个通用的原型注解,它非常接近 DAO 模式,其中 DAO 类负责在数据库表上提供 CRUD 操作。
例子
第 1 步:创建一个简单的 Spring Boot 项目
参考这篇文章在 Eclipse IDE 中创建和设置 Spring Boot 项目并创建一个简单的 Spring Boot 项目。
第 2 步:在 pom.xml 文件中添加 spring-context 依赖项。转到项目中的 pom.xml 文件并添加以下 spring-context 依赖项。
XML
org.springframework
spring-context
5.3.13
第 3 步:在您的项目中创建两个包,并将包命名为“实体”和“存储库”。在实体包中创建一个类,将其命名为 Student。在存储库中,包创建一个通用接口,将其命名为 DemoRepository,并将一个类命名为 StudentRepository。这将是我们最终的项目结构。

第 4 步:创建一个实体类,我们将为其实现一个 spring 存储库。这里我们的实体类是Student。下面是学生的代码。 Java文件。这是Java中的一个简单POJO (Plain Old Java Object)类。
Java
package com.example.demo.entity;
public class Student {
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(Long id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
第 5 步:在实现 Repository 类之前,我们创建了一个通用的 DemoRepository 接口来为我们的存储库类提供要实现的契约。下面是DemoRepository 的代码。 Java文件。
Java
// Java Program to illustrate DemoRepository File
package com.example.demo.repository;
public interface DemoRepository {
// Save method
public void save(T t);
// Find a student by its id
public T findStudentById(Long id);
}
第 6 步:现在让我们看看 StudentRepository 类的实现。
Java
// Java Program to illustrate StudentRepository File
package com.example.demo.repository;
import com.example.demo.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Repository
public class StudentRepository implements DemoRepository {
// Using an in-memory Map
// to store the object data
private Map repository;
public StudentRepository() {
this.repository = new HashMap<>();
}
// Implementation for save method
@Override
public void save(Student student) {
repository.put(student.getId(), student);
}
// Implementation for findStudentById method
@Override
public Student findStudentById(Long id) {
return repository.get(id);
}
}
在这个StudentRepository 中。在Java文件中,可以注意到我们添加了@Repository注解,表示该类提供了对对象进行存储、检索、更新、删除和搜索操作的机制。
Note: Here we have used an in-memory Map to store the object data, you can use any other mechanisms too. In the real world, we use Databases to store object data.
第 7 步: Spring 存储库测试
所以现在我们的 Spring Repository 已经准备好了,让我们测试一下。转到演示应用程序。 Java文件并参考下面的代码。
Java
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.entity.Student;
import com.example.demo.repository.StudentRepository;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.scan("com.example.demo");
context.refresh();
StudentRepository repository = context.getBean(StudentRepository.class);
// testing the store method
repository.save(new Student(1L, "Anshul", 25));
repository.save(new Student(2L, "Mayank", 23));
// testing the retrieve method
Student student = repository.findStudentById(1L);
System.out.println(student);
// close the spring context
context.close();
}
}
输出:最后,运行您的应用程序,您应该得到如下输出,如下所示:
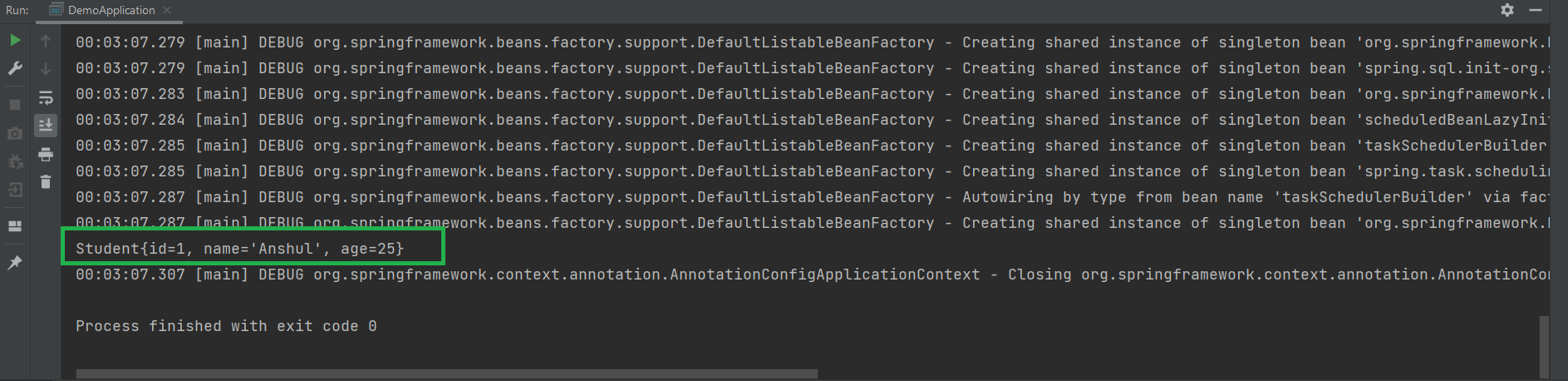
@控制器注解
Spring @Controller 注解也是@Component注解的一种特化。 @Controller 注释表明一个特定的类充当控制器的角色。 Spring Controller 注解通常与基于@RequestMapping注解的注解处理程序方法结合使用。它只能应用于类。它用于将类标记为 Web 请求处理程序。它主要用于 Spring MVC 应用程序。这个注解充当被注解类的原型,表明它的作用。调度程序扫描这些带注释的类以查找映射方法并检测@RequestMapping注释。让我们通过例子来理解所有这些。
例子
第 1 步:创建一个简单的 Spring Boot 项目
参考这篇文章在 Eclipse IDE 中创建和设置 Spring Boot 项目并创建一个简单的 Spring Boot 项目。
第 2 步:在 pom.xml 文件中添加 spring-web 依赖项。转到项目中的 pom.xml 文件并添加以下 spring-web 依赖项。
XML
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
第 3 步:在您的项目中创建一个包并将该包命名为“控制器”。在控制器包中创建一个类并将其命名为DemoController 。这将是我们最终的项目结构。
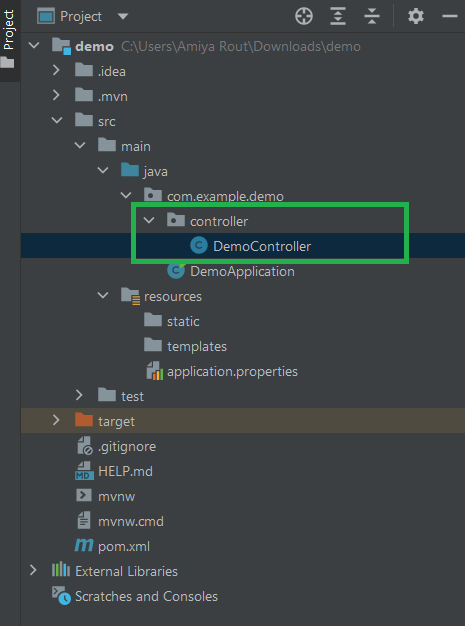
下面是DemoController 的代码。 Java文件。
Java
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class DemoController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public String helloGFG()
{
return "Hello GeeksForGeeks";
}
}
我们在控制器层中使用了以下注释。在此示例中,URI 路径为/hello 。
- @Controller:用于指定控制器。
- @RequestMapping:用于映射到 Spring MVC 控制器方法。
- @ResponseBody:用于将 HTTP 响应正文与返回类型中的域对象绑定。

现在,我们的控制器已准备就绪。让我们在DemoApplication 中运行我们的应用程序。 Java文件。无需更改DemoApplication 内部的任何内容。 Java文件。
Java
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
输出:

试试这个运行在http://localhost:8989/hello上的 Tomcat URL
