Python列表
列表就像在其他语言中声明的动态大小的数组(C++ 中的向量和Java中的 ArrayList)。列表不必总是同质的,这使它成为Python中最强大的工具。单个列表可能包含数据类型,如整数、字符串以及对象。列表是可变的,因此即使在创建之后也可以更改。
Python中的列表是有序的并且有明确的计数。列表中的元素按照一定的顺序进行索引,列表的索引以 0 为第一个索引。列表中的每个元素在列表中都有其确定的位置,这允许复制列表中的元素,每个元素都有自己独特的位置和可信度。
Note-列表是保存数据序列并进一步迭代它的有用工具。
Table of content:
- Creating a List
- Knowing the size of List
- Adding Elements to a List:
- Using append() method
- Using insert() method
- Using extend() method
- Accessing elements from the List
- Removing Elements from the List:
- Using remove() method
- Using pop() method
- Slicing of a List
- List Comprehension
- Operations on List
- List Methods
创建列表
Python中的列表只需将序列放在方括号[] 内即可创建。与 Set 不同,列表不需要内置函数来创建列表。
注意 –与 Set 不同,列表可能包含可变元素。
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Creation of List
# Creating a List
List = []
print("Blank List: ")
print(List)
# Creating a List of numbers
List = [10, 20, 14]
print("\nList of numbers: ")
print(List)
# Creating a List of strings and accessing
# using index
List = ["Geeks", "For", "Geeks"]
print("\nList Items: ")
print(List[0])
print(List[2])
# Creating a Multi-Dimensional List
# (By Nesting a list inside a List)
List = [['Geeks', 'For'], ['Geeks']]
print("\nMulti-Dimensional List: ")
print(List)Python3
# Creating a List with
# the use of Numbers
# (Having duplicate values)
List = [1, 2, 4, 4, 3, 3, 3, 6, 5]
print("\nList with the use of Numbers: ")
print(List)
# Creating a List with
# mixed type of values
# (Having numbers and strings)
List = [1, 2, 'Geeks', 4, 'For', 6, 'Geeks']
print("\nList with the use of Mixed Values: ")
print(List)Python3
# Creating a List
List1 = []
print(len(List1))
# Creating a List of numbers
List2 = [10, 20, 14]
print(len(List2))Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Addition of elements in a List
# Creating a List
List = []
print("Initial blank List: ")
print(List)
# Addition of Elements
# in the List
List.append(1)
List.append(2)
List.append(4)
print("\nList after Addition of Three elements: ")
print(List)
# Adding elements to the List
# using Iterator
for i in range(1, 4):
List.append(i)
print("\nList after Addition of elements from 1-3: ")
print(List)
# Adding Tuples to the List
List.append((5, 6))
print("\nList after Addition of a Tuple: ")
print(List)
# Addition of List to a List
List2 = ['For', 'Geeks']
List.append(List2)
print("\nList after Addition of a List: ")
print(List)Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Addition of elements in a List
# Creating a List
List = [1,2,3,4]
print("Initial List: ")
print(List)
# Addition of Element at
# specific Position
# (using Insert Method)
List.insert(3, 12)
List.insert(0, 'Geeks')
print("\nList after performing Insert Operation: ")
print(List)Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Addition of elements in a List
# Creating a List
List = [1, 2, 3, 4]
print("Initial List: ")
print(List)
# Addition of multiple elements
# to the List at the end
# (using Extend Method)
List.extend([8, 'Geeks', 'Always'])
print("\nList after performing Extend Operation: ")
print(List)Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# accessing of element from list
# Creating a List with
# the use of multiple values
List = ["Geeks", "For", "Geeks"]
# accessing a element from the
# list using index number
print("Accessing a element from the list")
print(List[0])
print(List[2])
# Creating a Multi-Dimensional List
# (By Nesting a list inside a List)
List = [['Geeks', 'For'], ['Geeks']]
# accessing an element from the
# Multi-Dimensional List using
# index number
print("Accessing a element from a Multi-Dimensional list")
print(List[0][1])
print(List[1][0])Python3
List = [1, 2, 'Geeks', 4, 'For', 6, 'Geeks']
# accessing an element using
# negative indexing
print("Accessing element using negative indexing")
# print the last element of list
print(List[-1])
# print the third last element of list
print(List[-3])Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Removal of elements in a List
# Creating a List
List = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]
print("Initial List: ")
print(List)
# Removing elements from List
# using Remove() method
List.remove(5)
List.remove(6)
print("\nList after Removal of two elements: ")
print(List)
# Removing elements from List
# using iterator method
for i in range(1, 5):
List.remove(i)
print("\nList after Removing a range of elements: ")
print(List)Python3
List = [1,2,3,4,5]
# Removing element from the
# Set using the pop() method
List.pop()
print("\nList after popping an element: ")
print(List)
# Removing element at a
# specific location from the
# Set using the pop() method
List.pop(2)
print("\nList after popping a specific element: ")
print(List)Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Removal of elements in a List
# Creating a List
List = ['G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S', 'F',
'O', 'R', 'G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S']
print("Initial List: ")
print(List)
# Print elements of a range
# using Slice operation
Sliced_List = List[3:8]
print("\nSlicing elements in a range 3-8: ")
print(Sliced_List)
# Print elements from a
# pre-defined point to end
Sliced_List = List[5:]
print("\nElements sliced from 5th "
"element till the end: ")
print(Sliced_List)
# Printing elements from
# beginning till end
Sliced_List = List[:]
print("\nPrinting all elements using slice operation: ")
print(Sliced_List)Python3
# Creating a List
List = ['G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S', 'F',
'O', 'R', 'G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S']
print("Initial List: ")
print(List)
# Print elements from beginning
# to a pre-defined point using Slice
Sliced_List = List[:-6]
print("\nElements sliced till 6th element from last: ")
print(Sliced_List)
# Print elements of a range
# using negative index List slicing
Sliced_List = List[-6:-1]
print("\nElements sliced from index -6 to -1")
print(Sliced_List)
# Printing elements in reverse
# using Slice operation
Sliced_List = List[::-1]
print("\nPrinting List in reverse: ")
print(Sliced_List)Python3
# Python program to demonstrate list
# comprehension in Python
# below list contains square of all
# odd numbers from range 1 to 10
odd_square = [x ** 2 for x in range(1, 11) if x % 2 == 1]
print(odd_square)Python3
# for understanding, above generation is same as,
odd_square = []
for x in range(1, 11):
if x % 2 == 1:
odd_square.append(x**2)
print(odd_square)Blank List:
[]
List of numbers:
[10, 20, 14]
List Items
Geeks
Geeks
Multi-Dimensional List:
[['Geeks', 'For'], ['Geeks']]创建具有多个不同或重复元素的列表
列表可能包含具有不同位置的重复值,因此,可以在创建列表时将多个不同或重复值作为序列传递。
Python3
# Creating a List with
# the use of Numbers
# (Having duplicate values)
List = [1, 2, 4, 4, 3, 3, 3, 6, 5]
print("\nList with the use of Numbers: ")
print(List)
# Creating a List with
# mixed type of values
# (Having numbers and strings)
List = [1, 2, 'Geeks', 4, 'For', 6, 'Geeks']
print("\nList with the use of Mixed Values: ")
print(List)
List with the use of Numbers:
[1, 2, 4, 4, 3, 3, 3, 6, 5]
List with the use of Mixed Values:
[1, 2, 'Geeks', 4, 'For', 6, 'Geeks']了解List的大小
Python3
# Creating a List
List1 = []
print(len(List1))
# Creating a List of numbers
List2 = [10, 20, 14]
print(len(List2))
0
3将元素添加到列表
使用 append() 方法
可以使用内置的append()函数将元素添加到列表中。使用 append() 方法一次只能将一个元素添加到列表中,对于使用 append() 方法添加多个元素,使用循环。也可以使用 append 方法将元组添加到列表中,因为元组是不可变的。与 Set 不同,List 也可以使用 append() 方法添加到现有列表中。
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Addition of elements in a List
# Creating a List
List = []
print("Initial blank List: ")
print(List)
# Addition of Elements
# in the List
List.append(1)
List.append(2)
List.append(4)
print("\nList after Addition of Three elements: ")
print(List)
# Adding elements to the List
# using Iterator
for i in range(1, 4):
List.append(i)
print("\nList after Addition of elements from 1-3: ")
print(List)
# Adding Tuples to the List
List.append((5, 6))
print("\nList after Addition of a Tuple: ")
print(List)
# Addition of List to a List
List2 = ['For', 'Geeks']
List.append(List2)
print("\nList after Addition of a List: ")
print(List)
Initial blank List:
[]
List after Addition of Three elements:
[1, 2, 4]
List after Addition of elements from 1-3:
[1, 2, 4, 1, 2, 3]
List after Addition of a Tuple:
[1, 2, 4, 1, 2, 3, (5, 6)]
List after Addition of a List:
[1, 2, 4, 1, 2, 3, (5, 6), ['For', 'Geeks']]使用 insert() 方法
append() 方法仅适用于在 List 末尾添加元素,对于在所需位置添加元素,使用 insert() 方法。与只接受一个参数的 append() 不同,insert() 方法需要两个参数(位置、值)。
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Addition of elements in a List
# Creating a List
List = [1,2,3,4]
print("Initial List: ")
print(List)
# Addition of Element at
# specific Position
# (using Insert Method)
List.insert(3, 12)
List.insert(0, 'Geeks')
print("\nList after performing Insert Operation: ")
print(List)
Initial List:
[1, 2, 3, 4]
List after performing Insert Operation:
['Geeks', 1, 2, 3, 12, 4]使用 extend() 方法
除了 append() 和 insert() 方法之外,还有一种添加元素的方法extend() ,该方法用于在列表末尾同时添加多个元素。
注意 – append() 和 extend() 方法只能在末尾添加元素。
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Addition of elements in a List
# Creating a List
List = [1, 2, 3, 4]
print("Initial List: ")
print(List)
# Addition of multiple elements
# to the List at the end
# (using Extend Method)
List.extend([8, 'Geeks', 'Always'])
print("\nList after performing Extend Operation: ")
print(List)
Initial List:
[1, 2, 3, 4]
List after performing Extend Operation:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 'Geeks', 'Always']访问列表中的元素
为了访问列表项,请参阅索引号。使用索引运算符[ ] 访问列表中的项目。索引必须是整数。使用嵌套索引访问嵌套列表。
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# accessing of element from list
# Creating a List with
# the use of multiple values
List = ["Geeks", "For", "Geeks"]
# accessing a element from the
# list using index number
print("Accessing a element from the list")
print(List[0])
print(List[2])
# Creating a Multi-Dimensional List
# (By Nesting a list inside a List)
List = [['Geeks', 'For'], ['Geeks']]
# accessing an element from the
# Multi-Dimensional List using
# index number
print("Accessing a element from a Multi-Dimensional list")
print(List[0][1])
print(List[1][0])
Accessing a element from the list
Geeks
Geeks
Accessing a element from a Multi-Dimensional list
For
Geeks负索引
在Python中,负序列索引表示从数组末尾开始的位置。不必像在 List[len(List)-3] 中那样计算偏移量,只需编写 List[-3] 就足够了。负索引表示从末尾开始,-1 指最后一项,-2 指倒数第二项,依此类推。
Python3
List = [1, 2, 'Geeks', 4, 'For', 6, 'Geeks']
# accessing an element using
# negative indexing
print("Accessing element using negative indexing")
# print the last element of list
print(List[-1])
# print the third last element of list
print(List[-3])
Accessing element using negative indexing
Geeks
For从列表中删除元素
使用 remove() 方法
可以使用内置的remove()函数从列表中删除元素,但如果列表中不存在该元素,则会出现错误。 Remove() 方法一次只删除一个元素,要删除一系列元素,使用迭代器。 remove() 方法删除指定的项目。
注意 – List 中的 Remove 方法只会删除第一次出现的搜索元素。
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Removal of elements in a List
# Creating a List
List = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]
print("Initial List: ")
print(List)
# Removing elements from List
# using Remove() method
List.remove(5)
List.remove(6)
print("\nList after Removal of two elements: ")
print(List)
# Removing elements from List
# using iterator method
for i in range(1, 5):
List.remove(i)
print("\nList after Removing a range of elements: ")
print(List)
Initial List:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]
List after Removal of two elements:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]
List after Removing a range of elements:
[7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]使用 pop() 方法
Pop()函数也可用于从列表中移除并返回一个元素,但默认情况下它只移除列表的最后一个元素,从列表的特定位置移除一个元素,传递元素的索引作为 pop() 方法的参数。
Python3
List = [1,2,3,4,5]
# Removing element from the
# Set using the pop() method
List.pop()
print("\nList after popping an element: ")
print(List)
# Removing element at a
# specific location from the
# Set using the pop() method
List.pop(2)
print("\nList after popping a specific element: ")
print(List)
List after popping an element:
[1, 2, 3, 4]
List after popping a specific element:
[1, 2, 4]列表切片
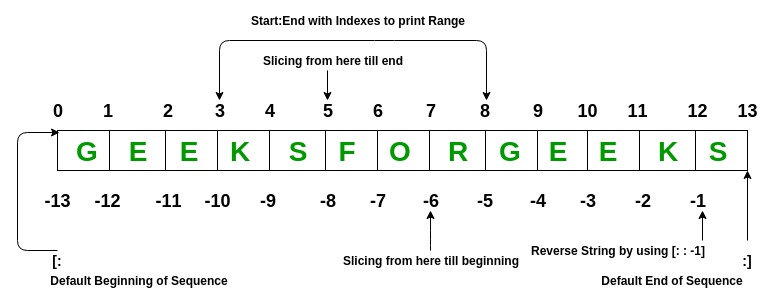
在Python List 中,有多种方法可以打印包含所有元素的整个 List,但要从列表中打印特定范围的元素,我们使用 Slice 操作。使用冒号(:) 对列表执行切片操作。要从开始到范围打印元素使用 [:Index],从最终使用 [:-Index] 打印元素,从特定索引到结束使用 [Index:] 打印元素,在范围内打印元素,使用[开始索引:结束索引]并使用切片操作打印整个列表,请使用[:]。此外,要以相反的顺序打印整个列表,请使用 [::-1]。
注意 –要从后端打印 List 的元素,请使用负索引。
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Removal of elements in a List
# Creating a List
List = ['G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S', 'F',
'O', 'R', 'G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S']
print("Initial List: ")
print(List)
# Print elements of a range
# using Slice operation
Sliced_List = List[3:8]
print("\nSlicing elements in a range 3-8: ")
print(Sliced_List)
# Print elements from a
# pre-defined point to end
Sliced_List = List[5:]
print("\nElements sliced from 5th "
"element till the end: ")
print(Sliced_List)
# Printing elements from
# beginning till end
Sliced_List = List[:]
print("\nPrinting all elements using slice operation: ")
print(Sliced_List)
Initial List:
['G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S', 'F', 'O', 'R', 'G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S']
Slicing elements in a range 3-8:
['K', 'S', 'F', 'O', 'R']
Elements sliced from 5th element till the end:
['F', 'O', 'R', 'G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S']
Printing all elements using slice operation:
['G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S', 'F', 'O', 'R', 'G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S']负索引列表切片
Python3
# Creating a List
List = ['G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S', 'F',
'O', 'R', 'G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S']
print("Initial List: ")
print(List)
# Print elements from beginning
# to a pre-defined point using Slice
Sliced_List = List[:-6]
print("\nElements sliced till 6th element from last: ")
print(Sliced_List)
# Print elements of a range
# using negative index List slicing
Sliced_List = List[-6:-1]
print("\nElements sliced from index -6 to -1")
print(Sliced_List)
# Printing elements in reverse
# using Slice operation
Sliced_List = List[::-1]
print("\nPrinting List in reverse: ")
print(Sliced_List)
Initial List:
['G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S', 'F', 'O', 'R', 'G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S']
Elements sliced till 6th element from last:
['G', 'E', 'E', 'K', 'S', 'F', 'O']
Elements sliced from index -6 to -1
['R', 'G', 'E', 'E', 'K']
Printing List in reverse:
['S', 'K', 'E', 'E', 'G', 'R', 'O', 'F', 'S', 'K', 'E', 'E', 'G']列表理解
列表推导用于从其他可迭代对象(如元组、字符串、数组、列表等)创建新列表。
列表推导式由包含表达式的括号组成,该表达式与 for 循环一起为每个元素执行以迭代每个元素。
句法:
newList = [ expression(element) for element in oldList if condition ]
例子:
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate list
# comprehension in Python
# below list contains square of all
# odd numbers from range 1 to 10
odd_square = [x ** 2 for x in range(1, 11) if x % 2 == 1]
print(odd_square)
输出:
[1, 9, 25, 49, 81]为了更好地理解,上面的代码类似于 -
Python3
# for understanding, above generation is same as,
odd_square = []
for x in range(1, 11):
if x % 2 == 1:
odd_square.append(x**2)
print(odd_square)
输出:
[1, 9, 25, 49, 81]请参阅以下文章以获取有关列表理解的详细信息。
- Python列表理解和切片
- Python中的嵌套列表理解
- Python中的列表理解和 ord()
列表操作
- 查找列表的长度
- 遍历Python中的列表
- 在Python中连接两个列表
- 列出成员资格测试
列出方法
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Append() | Add an element to the end of the list |
| Extend() | Add all elements of a list to another list |
| Insert() | Insert an item at the defined index |
| Remove() | Removes an item from the list |
| Pop() | Removes and returns an element at the given index |
| Clear() | Removes all items from the list |
| Index() | Returns the index of the first matched item |
| Count() | Returns the count of the number of items passed as an argument |
| Sort() | Sort items in a list in ascending order |
| Reverse() | Reverse the order of items in the list |
| copy() | Returns a copy of the list |
带有 List 的内置函数
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| reduce() | apply a particular function passed in its argument to all of the list elements stores the intermediate result and only returns the final summation value |
| sum() | Sums up the numbers in the list |
| ord() | Returns an integer representing the Unicode code point of the given Unicode character |
| cmp() | This function returns 1 if the first list is “greater” than the second list |
| max() | return maximum element of a given list |
| min() | return minimum element of a given list |
| all() | Returns true if all element is true or if the list is empty |
| any() | return true if any element of the list is true. if the list is empty, return false |
| len() | Returns length of the list or size of the list |
| enumerate() | Returns enumerate object of the list |
| accumulate() | apply a particular function passed in its argument to all of the list elements returns a list containing the intermediate results |
| filter() | tests if each element of a list is true or not |
| map() | returns a list of the results after applying the given function to each item of a given iterable |
| lambda() | This function can have any number of arguments but only one expression, which is evaluated and returned. |
最近关于列表的文章
More videos on Python Lists: Python List – Set 2
更多关于Python列表 -
- 创建 3D 列表
- 遍历Python中的列表
- 同时迭代多个列表
- Python中列表的内部工作
- Python切片
- Python列表理解与生成器表达式
- 列出Python中的方法 – 第 1 组 第 2 组
- Lambda 表达式和过滤函数
有用的链接:
- Python列表中的最新文章
- Python教程
- 列表中的Python输出程序:Set 6、Set 11、Set 12、Set 13
- 多项选择题
- Python分类中的所有文章