Dijkstra 的最短路径算法使用 STL 的 priority_queue
给定一个图和图中的一个源顶点,找到从源到给定图中所有顶点的最短路径。
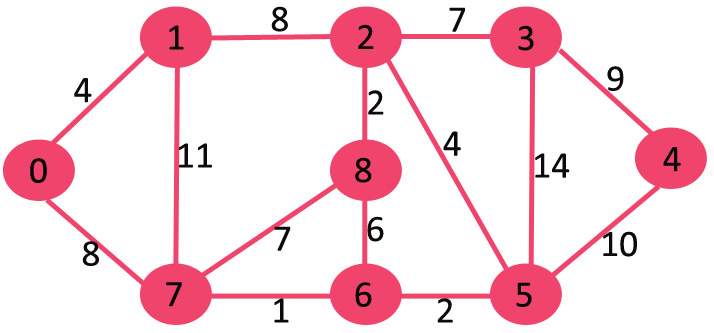 输入:源 = 0 输出:到源的顶点距离 0 0 1 4 2 12 3 19 4 21 5 11 6 9 7 8 8 14
输入:源 = 0 输出:到源的顶点距离 0 0 1 4 2 12 3 19 4 21 5 11 6 9 7 8 8 14
我们已经讨论了 Dijkstra 的最短路径实现。
- Dijkstra 的邻接矩阵表示算法(在 C/C++ 中,时间复杂度为 O(v 2 )
- Dijkstra 的邻接表表示算法(在 C 语言中,时间复杂度为 O(ELogV))
- Dijkstra 在 STL 中使用集合的最短路径算法(在 C++ 中,时间复杂度为 O(ELogV))
第二种实现在时间复杂度方面更好,但确实很复杂,因为我们已经实现了自己的优先级队列。
第三种实现更简单,因为它使用 STL。第三种实现的问题是,它使用 set 反过来使用自平衡二叉搜索树。对于 Dijkstra 算法,始终建议使用堆(或优先级队列),因为所需的操作(提取最小值和减少键)与堆(或优先级队列)的特性相匹配。但是,问题是,priority_queue 不支持减少键。要解决此问题,请不要更新密钥,而是再插入一份。所以我们允许优先级队列中相同顶点的多个实例。这种方法不需要减少键操作,并且具有以下重要属性。
- 每当一个顶点的距离减少时,我们就会在priority_queue 中再添加一个顶点实例。即使有多个实例,我们也只考虑距离最小的实例而忽略其他实例。
- 时间复杂度仍然为 O(ELogV)),因为优先级队列中最多有 O(E) 个顶点,并且 O(Log E) 与 O(Log V) 相同
下面是基于上述思想的算法。
1) Initialize distances of all vertices as infinite.
2) Create an empty priority_queue pq. Every item
of pq is a pair (weight, vertex). Weight (or
distance) is used used as first item of pair
as first item is by default used to compare
two pairs
3) Insert source vertex into pq and make its
distance as 0.
4) While either pq doesn't become empty
a) Extract minimum distance vertex from pq.
Let the extracted vertex be u.
b) Loop through all adjacent of u and do
following for every vertex v.
// If there is a shorter path to v
// through u.
If dist[v] > dist[u] + weight(u, v)
(i) Update distance of v, i.e., do
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight(u, v)
(ii) Insert v into the pq (Even if v is
already there)
5) Print distance array dist[] to print all shortest
paths.
下面是上述想法的 C++ 实现。
// Program to find Dijkstra's shortest path using
// priority_queue in STL
#include
using namespace std;
# define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
// iPair ==> Integer Pair
typedef pair iPair;
// This class represents a directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
// In a weighted graph, we need to store vertex
// and weight pair for every edge
list< pair > *adj;
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int u, int v, int w);
// prints shortest path from s
void shortestPath(int s);
};
// Allocates memory for adjacency list
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list [V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v, int w)
{
adj[u].push_back(make_pair(v, w));
adj[v].push_back(make_pair(u, w));
}
// Prints shortest paths from src to all other vertices
void Graph::shortestPath(int src)
{
// Create a priority queue to store vertices that
// are being preprocessed. This is weird syntax in C++.
// Refer below link for details of this syntax
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/implement-min-heap-using-stl/
priority_queue< iPair, vector , greater > pq;
// Create a vector for distances and initialize all
// distances as infinite (INF)
vector dist(V, INF);
// Insert source itself in priority queue and initialize
// its distance as 0.
pq.push(make_pair(0, src));
dist[src] = 0;
/* Looping till priority queue becomes empty (or all
distances are not finalized) */
while (!pq.empty())
{
// The first vertex in pair is the minimum distance
// vertex, extract it from priority queue.
// vertex label is stored in second of pair (it
// has to be done this way to keep the vertices
// sorted distance (distance must be first item
// in pair)
int u = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
// 'i' is used to get all adjacent vertices of a vertex
list< pair >::iterator i;
for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i)
{
// Get vertex label and weight of current adjacent
// of u.
int v = (*i).first;
int weight = (*i).second;
// If there is shorted path to v through u.
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight)
{
// Updating distance of v
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
pq.push(make_pair(dist[v], v));
}
}
}
// Print shortest distances stored in dist[]
printf("Vertex Distance from Source\n");
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
printf("%d \t\t %d\n", i, dist[i]);
}
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
int main()
{
// create the graph given in above figure
int V = 9;
Graph g(V);
// making above shown graph
g.addEdge(0, 1, 4);
g.addEdge(0, 7, 8);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 8);
g.addEdge(1, 7, 11);
g.addEdge(2, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(2, 8, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 5, 4);
g.addEdge(3, 4, 9);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 14);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 10);
g.addEdge(5, 6, 2);
g.addEdge(6, 7, 1);
g.addEdge(6, 8, 6);
g.addEdge(7, 8, 7);
g.shortestPath(0);
return 0;
}
输出:
Vertex Distance from Source
0 0
1 4
2 12
3 19
4 21
5 11
6 9
7 8
8 14
使用加权图的对向量表示的更快实现:
// Program to find Dijkstra's shortest path using
// priority_queue in STL
#include
using namespace std;
# define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
// iPair ==> Integer Pair
typedef pair iPair;
// To add an edge
void addEdge(vector > adj[], int u,
int v, int wt)
{
adj[u].push_back(make_pair(v, wt));
adj[v].push_back(make_pair(u, wt));
}
// Prints shortest paths from src to all other vertices
void shortestPath(vector > adj[], int V, int src)
{
// Create a priority queue to store vertices that
// are being preprocessed. This is weird syntax in C++.
// Refer below link for details of this syntax
// http://geeksquiz.com/implement-min-heap-using-stl/
priority_queue< iPair, vector , greater > pq;
// Create a vector for distances and initialize all
// distances as infinite (INF)
vector dist(V, INF);
// Insert source itself in priority queue and initialize
// its distance as 0.
pq.push(make_pair(0, src));
dist[src] = 0;
/* Looping till priority queue becomes empty (or all
distances are not finalized) */
while (!pq.empty())
{
// The first vertex in pair is the minimum distance
// vertex, extract it from priority queue.
// vertex label is stored in second of pair (it
// has to be done this way to keep the vertices
// sorted distance (distance must be first item
// in pair)
int u = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
// Get all adjacent of u.
for (auto x : adj[u])
{
// Get vertex label and weight of current adjacent
// of u.
int v = x.first;
int weight = x.second;
// If there is shorted path to v through u.
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight)
{
// Updating distance of v
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
pq.push(make_pair(dist[v], v));
}
}
}
// Print shortest distances stored in dist[]
printf("Vertex Distance from Source\n");
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
printf("%d \t\t %d\n", i, dist[i]);
}
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
int main()
{
int V = 9;
vector adj[V];
// making above shown graph
addEdge(adj, 0, 1, 4);
addEdge(adj, 0, 7, 8);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2, 8);
addEdge(adj, 1, 7, 11);
addEdge(adj, 2, 3, 7);
addEdge(adj, 2, 8, 2);
addEdge(adj, 2, 5, 4);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4, 9);
addEdge(adj, 3, 5, 14);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5, 10);
addEdge(adj, 5, 6, 2);
addEdge(adj, 6, 7, 1);
addEdge(adj, 6, 8, 6);
addEdge(adj, 7, 8, 7);
shortestPath(adj, V, 0);
return 0;
}
输出:
Vertex Distance from Source
0 0
1 4
2 12
3 19
4 21
5 11
6 9
7 8
8 14
进一步优化
我们可以使用一个标志数组来存储从优先级队列中提取的所有顶点。这样我们可以避免更新已经提取的项目的权重。请参阅此以优化实施。