Java Java类
Java.io.ByteArrayInputStream类包含所有缓冲区,包含要从输入流中读取的字节。在 ByteArrayInputStream 类方法的情况下没有 IO 异常。这个类的方法即使关闭Stream也可以调用,对类方法没有影响。
宣言 :
public class ByteArrayInputStream
extends InputStream字段
- protected byte[] buf:由流的创建者提供的字节数组。
- protected int count:比输入流缓冲区中最后一个有效字符大一的索引。
- protected int mark:流中当前标记的位置。
- protected int pos:这是要从输入流缓冲区读取的下一个字符的索引。
构造函数:
- ByteArrayInputStream(byte[] buffer) :创建 ByteArrayInputStream 以使用缓冲区数组——“buffer”。
- ByteArrayInputStream(byte[] buf, int offset, int length) :创建使用“缓冲区”的某些部分的 ByteArrayInputStream,即缓冲区数组
方法:
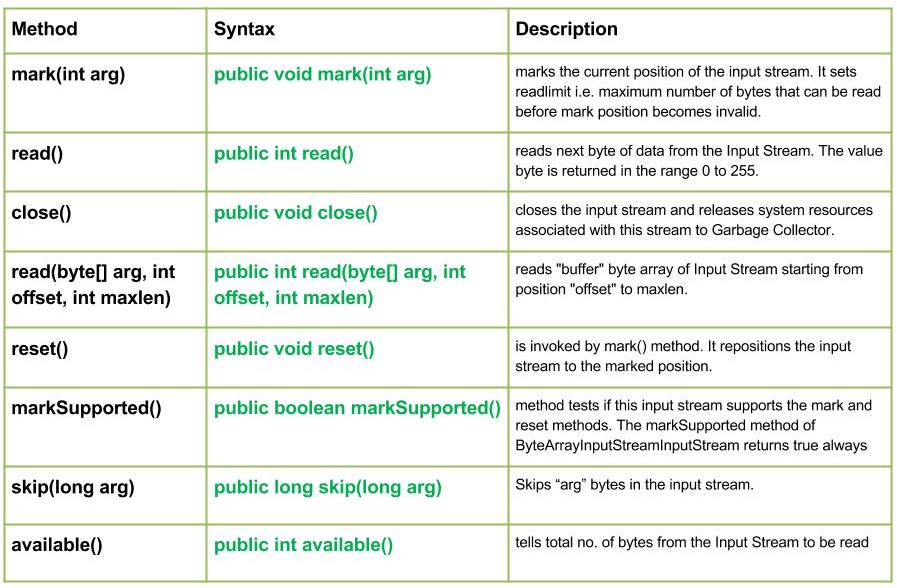
- mark(int arg) : Java.io.ByteArrayInputStream.mark(int arg)标记输入流的当前位置。它设置readlimit,即在标记位置无效之前可以读取的最大字节数。
句法 :
public void mark(int arg)
Parameters :
arg : integer specifying the read limit of the input Stream
Return :
void- read() : Java.io.ByteArrayInputStream.read()从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节。返回值字节在 0 到 255 的范围内。如果由于已到达流的末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回值 -1。方法不阻塞
句法 :
public int read()
Parameters :
------
Return :
Reads next data else, -1 i.e. when end of file is reached.
Exception :
-> IOException : If I/O error occurs.- close() : Java.io.ByteArrayInputStream.close()关闭输入流并将与该流关联的系统资源释放到垃圾收集器。
句法 :
public void close()
Parameters :
------
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : If I/O error occurs.- read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen) : Java.io.ByteArrayInputStream.read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen)从位置“offset”到maxlen读取输入流的“buffer”字节数组.
句法 :
public int read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen)
Parameters :
arg : array whose number of bytes to be read
offset : starting position in buffer from where to read
maxlen : maximum no. of bytes to be read
Return :
reads number of bytes and return to the buffer else, -1 i.e. when end of file is reached.
Exception :
-> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
-> NullPointerException : if arg is null.- reset() : Java.io.ByteArrayInputStream.reset()由 mark() 方法调用。它将输入流重新定位到标记的位置。
句法 :
public void reset()
Parameters :
----
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : If I/O error occurs.- markSupported() : Java.io.ByteArrayInputStream.markSupported()方法测试此输入流是否支持标记和重置方法。 ByteArrayInputStreamInputStream 的 markSupported 方法总是返回 true
句法 :
public boolean markSupported()
Parameters :
-------
Return :
true if input stream supports the mark() and reset() method else,false- skip(long arg) : Java.io.ByteArrayInputStream.skip(long arg)跳过输入流中的arg字节。
句法 :
public long skip(long arg)
Parameters :
arg : no. of bytes to be skipped
Return :
skip bytes.
Exception :
-> IOException : If I/O error occurs.- available() : Java.io.ByteArrayInputStream.available()告诉总数。输入流中要读取的字节数
句法 :
public int available()
Parameters :
-----------
Return :
total no. of bytes to be read
Exception :
-----------解释 ByteArrayInputStream 类方法的Java程序:
Java
// Java program illustrating the working of ByteArrayInputStream method
// mark(), read(), skip(), available()
// markSupported(), close(), reset()
import java.io.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
byte[] buffer = {71, 69, 69, 75, 83};
ByteArrayInputStream geek = null;
try
{
geek = new ByteArrayInputStream(buffer);
// Use of available() method : telling the no. of bytes to be read
int number = geek.available();
System.out.println("Use of available() method : " + number);
// Use of read() method : reading and printing Characters one by one
System.out.println("\nChar : "+(char)geek.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)geek.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)geek.read());
// Use of mark() :
geek.mark(0);
// Use of skip() : it results in skipping 'k' from "GEEKS"
geek.skip(1);
System.out.println("skip() method comes to play");
System.out.println("mark() method comes to play");
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)geek.read());
// Use of markSupported
boolean check = geek.markSupported();
System.out.println("\nmarkSupported() : " + check);
if(geek.markSupported())
{
// Use of reset() method : repositioning the stream to marked positions.
geek.reset();
System.out.println("\nreset() invoked");
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)geek.read());
System.out.println("Char : "+(char)geek.read());
}
else
{
System.out.println("reset() method not supported.");
}
System.out.println("geek.markSupported() supported reset() : "+check);
}
catch(Exception except)
{
// in case of I/O error
except.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
// releasing the resources back to the GarbageCollector when closes
if(geek!=null)
{
// Use of close() : closing the file and releasing resources
geek.close();
}
}
}
}输出 :
Use of available() method : 5
Char : G
Char : E
Char : E
skip() method comes to play
mark() method comes to play
Char : S
markSupported() : true
reset() invoked
Char : K
Char : S
geek.markSupported() supported reset() : true下一篇: Java中的io.ByteArrayOutputStream()类