使用Java实现校验和
校验和是一种错误检测技术,可应用于任何长度的消息。它主要用于 TCP/IP 协议套件的网络和传输层。
在这里,我们考虑了发送方使用套接字编程向接收方发送的十进制数据。此处将数据划分的段数取决于发送数据的长度。如果正在发送的数据长度是“x”,那么段数也是“x”,这意味着每个段都有单个数据。在这里,我们基本上处理十进制数据。这个概念对于字符串数据也是一致的,因为字符串的每个字符都可以用其等效的 ASCII 码表示,因此再次给我们留下了十进制数据。
先决条件: Java中的套接字编程 |校验和
例子 :
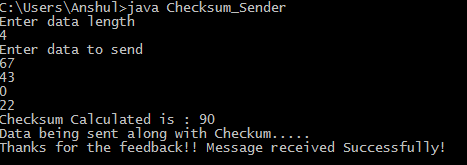
At sender side :
Enter data length
4
Enter data to send
67
43
0
22
Checksum Calculated is : 90
Data being sent along with Checksum.....
Thanks for the feedback!!
Message received Successfully!
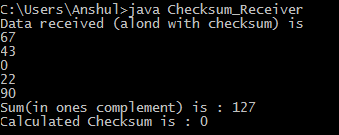
At receiver side :
Data received (alond with checksum) is
67
43
0
22
90
Sum(in ones complement) is : 127
Calculated Checksum is : 0
Here the checksum calculated at
the receiver side was 0. Hence,
it indicates a successful data transfer.方法 :
在发送方:
- 首先,询问要发送的数据长度,以确定段数。
- 然后对正在输入的每个数据执行一个补充,同时添加它们。这意味着这笔款项将不需要再次补充。
- 然后将数据连同计算的校验和一起发送到服务器。
- 然后根据从服务器收到的反馈报告消息传输是否成功。
在接收方:
- 接收方等待发送方的数据到达。
- 一旦从发送方接收到数据和校验和,接收方就会对接收到的内容进行补充,同时继续添加它们。
- 最后,接收方对上述和进行补全,检查结果是否为零,并将结果报告给发送方。零表示数据传输成功,其他任何值都表示接收到的数据有错误。
最后,所有连接都被双方关闭。
以下是上述方法的实现。
这里使用“localhost”作为建立连接的IP,打开端口号5000进行连接。发送方应先开始运行并等待接收方。
Java
// Java code for Checksum_Sender
package checksum_sender;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Checksum_Sender
{
// Setting maximum data length
private int MAX = 100;
// initialize socket and I/O streams
private Socket socket = null;
private ServerSocket servsock = null;
private DataInputStream dis = null;
private DataOutputStream dos = null;
public Checksum_Sender(int port) throws IOException
{
servsock = new ServerSocket(port);
// Used to block until a client connects to the server
socket = servsock.accept();
dis = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
dos = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
while (true)
{
int i, l, sum = 0, nob;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter data length");
l = sc.nextInt();
// Array to hold the data being entered
int data[] = new int[MAX];
// Array to hold the complement of each data
int c_data[] = new int[MAX];
System.out.println("Enter data to send");
for (i = 0; i < l; i++)
{
data[i] = sc.nextInt();
// Complementing the entered data
// Here we find the number of bits required to represent
// the data, like say 8 requires 1000, i.e 4 bits
nob = (int)(Math.floor(Math.log(data[i]) / Math.log(2))) + 1;
// Here we do a XOR of the data with the number 2^n -1,
// where n is the nob calculated in previous step
c_data[i] = ((1 << nob) - 1) ^ data[i];
// Adding the complemented data and storing in sum
sum += c_data[i];
}
// The sum(i.e checksum) is also sent along with the data
data[i] = sum;
l += 1;
System.out.println("Checksum Calculated is : " + sum);
System.out.println("Data being sent along with Checksum.....");
// Sends the data length to receiver
dos.writeInt(l);
// Sends the data one by one to receiver
for (int j = 0; j < l; j++)
dos.writeInt(data[j]);
// Displaying appropriate message depending on feedback received
if (dis.readUTF().equals("success"))
{
System.out.println("Thanks for the feedback!! Message received
Successfully!");
break;
}
else if (dis.readUTF().equals("failure"))
{
System.out.println("Message was not received successfully!");
break;
}
}
// Closing all connections
dis.close();
dos.close();
socket.close();
}
// Driver Method
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
Checksum_Sender cs = new Checksum_Sender(45678);
}
}Java
// Java code for Checksum_Receiver
package checksum_sender;
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Checksum_Receiver {
// Initialize socket and I/O streams
private Socket s = null;
private DataInputStream dis = null;
private DataOutputStream dos = null;
// Constructor to put ip address and port
public Checksum_Receiver(InetAddress ip,int port)throws IOException
{
// Opens a socket for connection
s = new Socket(ip,port);
dis = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());
dos = new DataOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
while (true)
{ Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int i, l, nob, sum = 0, chk_sum;
// Reads the data length sent by sender
l = dis.readInt();
// Initializes the arrays based on data length received
int c_data[] = new int[l];
int data[] = new int[l];
System.out.println("Data received (alond with checksum) is");
for(i = 0; i< data.length; i++)
{
// Reading the data being sent one by one
data[i] = dis.readInt();
System.out.println(data[i]);
// Complementing the data being received
nob = (int)(Math.floor(Math.log(data[i]) / Math.log(2))) + 1;
c_data[i] = ((1 << nob) - 1) ^ data[i];
// Adding the complemented data
sum += c_data[i];
}
System.out.println("Sum(in ones complement) is : "+sum);
// Complementing the sum
nob = (int)(Math.floor(Math.log(sum) / Math.log(2))) + 1;
sum = ((1 << nob) - 1) ^ sum;
System.out.println("Calculated Checksum is : "+sum);
// Checking whether final result is 0 or something else
// and sending feedback accordingly
if(sum == 0)
{
dos.writeUTF("success");
break;
}
else
{
dos.writeUTF("failure");
break;
}
}
// Closing all connections
dis.close();
dos.close();
s.close();
}
// Driver Method
public static void main(String args[])throws IOException
{
// Getting ip address on which the receiver is running
// Here, it is "localhost"
InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
Checksum_Receiver cr = new Checksum_Receiver(ip,5000);
}
}Java
// Java code for Checksum_Receiver
package checksum_sender;
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Checksum_Receiver {
// Initialize socket and I/O streams
private Socket s = null;
private DataInputStream dis = null;
private DataOutputStream dos = null;
// Constructor to put ip address and port
public Checksum_Receiver(InetAddress ip,int port)throws IOException
{
// Opens a socket for connection
s = new Socket(ip,port);
dis = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());
dos = new DataOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
while (true)
{ Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int i, l, nob, sum = 0, chk_sum;
// Reads the data length sent by sender
l = dis.readInt();
// Initializes the arrays based on data length received
int c_data[] = new int[l];
int data[] = new int[l];
System.out.println("Data received (alond with checksum) is");
for(i = 0; i< data.length; i++)
{
// Reading the data being sent one by one
data[i] = dis.readInt();
System.out.println(data[i]);
// Complementing the data being received
nob = (int)(Math.floor(Math.log(data[i]) / Math.log(2))) + 1;
c_data[i] = ((1 << nob) - 1) ^ data[i];
// Adding the complemented data
sum += c_data[i];
}
System.out.println("Sum(in ones complement) is : "+sum);
// Complementing the sum
nob = (int)(Math.floor(Math.log(sum) / Math.log(2))) + 1;
sum = ((1 << nob) - 1) ^ sum;
System.out.println("Calculated Checksum is : "+sum);
// Checking whether final result is 0 or something else
// and sending feedback accordingly
if(sum == 0)
{
dos.writeUTF("success");
break;
}
else
{
dos.writeUTF("failure");
break;
}
}
// Closing all connections
dis.close();
dos.close();
s.close();
}
// Driver Method
public static void main(String args[])throws IOException
{
// Getting ip address on which the receiver is running
// Here, it is "localhost"
InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
Checksum_Receiver cr = new Checksum_Receiver(ip,5000);
}
}
输出: