使用子类与超类引用来引用子类对象
先决条件:继承
在Java中,所有非静态方法都基于底层对象的运行时类型,而不是指向该对象的引用类型。因此,无论您在对象声明中使用哪种类型,行为都是相同的。
如何引用子类对象
有两种方法可以引用子类对象。两者都有一些优点/缺点。声明影响在编译时可见的方法上可见。
- 第一种方法(使用超类引用进行引用):超类的引用变量可用于引用从该超类派生的任何子类对象。如果方法存在于 SuperClass 中,但被 SubClass 覆盖,则将执行被覆盖的方法。
- 第二种方法(使用子类引用进行引用):子类引用可用于引用其对象。
考虑一个解释这两种方法的示例。
// Java program to illustrate
// referring to a subclass
// base class
class Bicycle
{
// the Bicycle class has two fields
public int gear;
public int speed;
// the Bicycle class has one constructor
public Bicycle(int gear, int speed)
{
this.gear = gear;
this.speed = speed;
}
// the Bicycle class has three methods
public void applyBrake(int decrement)
{
speed -= decrement;
}
public void speedUp(int increment)
{
speed += increment;
}
// toString() method to print info of Bicycle
public String toString()
{
return("No of gears are "+gear
+"\n"
+ "speed of bicycle is "+speed);
}
}
// derived class
class MountainBike extends Bicycle
{
// the MountainBike subclass adds one more field
public int seatHeight;
// the MountainBike subclass has one constructor
public MountainBike(int gear,int speed,
int startHeight)
{
// invoking base-class(Bicycle) constructor
super(gear, speed);
seatHeight = startHeight;
}
// the MountainBike subclass adds one more method
public void setHeight(int newValue)
{
seatHeight = newValue;
}
// overriding toString() method
// of Bicycle to print more info
@Override
public String toString()
{
return (super.toString()+
"\nseat height is "+seatHeight);
}
}
// driver class
public class Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// using superclass reference
// first approach
Bicycle mb2 = new MountainBike(4, 200, 20);
// using subclass reference( )
// second approach
MountainBike mb1 = new MountainBike(3, 100, 25);
System.out.println("seat height of first bicycle is "
+ mb1.seatHeight);
// In case of overridden methods
// always subclass
// method will be executed
System.out.println(mb1.toString());
System.out.println(mb2.toString());
/* The following statement is invalid because Bicycle
does not define a seatHeight.
// System.out.println("seat height of second bicycle is "
+ mb2.seatHeight); */
/* The following statement is invalid because Bicycle
does not define setHeight() method.
mb2.setHeight(21);*/
}
}
输出:
seat height of first bicycle is 25
No of gears are 3
speed of bicycle is 100
seat height is 25
No of gears are 4
speed of bicycle is 200
seat height is 20
上述程序说明:
- MountainBike 类的对象是通过使用子类引用“mb1”来引用的。使用这个引用,我们将可以访问由超类或子类定义的对象的两个部分(方法和变量)。请参阅下图以获得清晰的理解。
MountainBike mb1 = new MountainBike(3, 100, 25);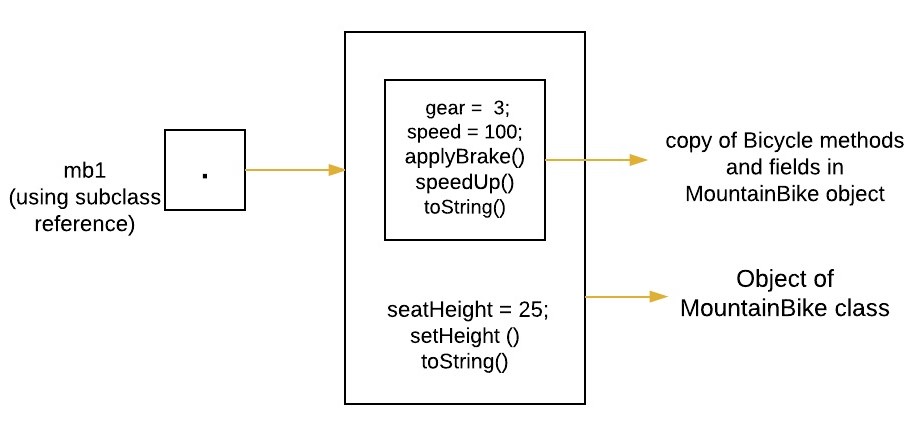
- 现在我们再次创建 MountainBike 类的对象,但这次它是通过使用超类 Bicycle 引用“mb2”来引用的。使用这个引用,我们将只能访问由超类定义的对象的那些部分(方法和变量)。
Bicycle mb2 = new MountainBike(4, 200, 20);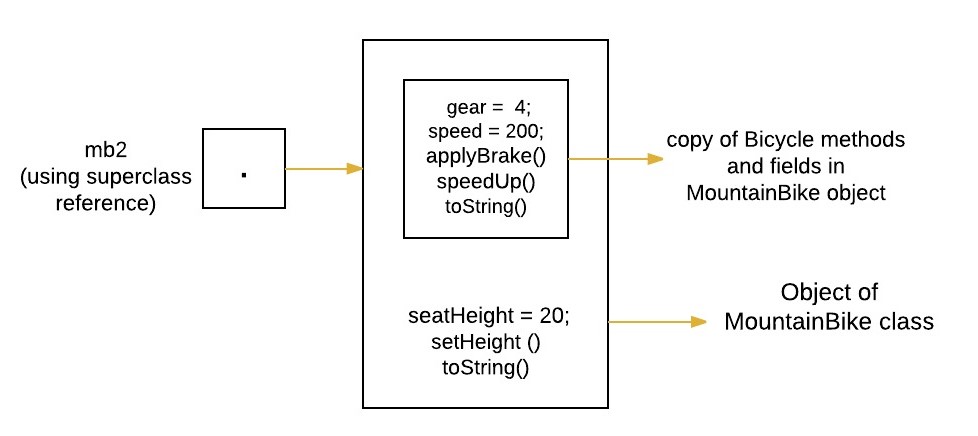
- 由于引用'mb1'可以访问字段'seatHeight',所以我们在控制台上打印它。
System.out.println("seat height of first bicycle is " + mb1.seatHeight); - 如果超类中存在方法,但被子类覆盖,并且如果创建了子类的对象,那么无论我们使用什么引用(子类或超类),它将始终是子类中被覆盖的方法将被执行。所以下面两条语句会调用 MountainBike 类的 toString() 方法。
System.out.println(mb1.toString()); System.out.println(mb2.toString()); - 由于 'mb2' 的引用是 Bicycle 类型,所以我们会在下面的语句中得到编译时错误。
System.out.println("seat height of second bicycle is " + mb2.seatHeight); - 'mb2' 再次引用的类型是 Bicycle ,所以我们将在下面的语句中得到编译时错误。
mb2.setHeight(21);类型转换的使用
在上面的例子中,我们已经看到,通过使用 Bicycle 类型的引用“mb2”,我们无法调用子类特定的方法或访问子类字段。这个问题可以使用Java中的类型转换来解决。例如,我们可以声明另一个引用,比如 MountainBike 类型的“mb3”,并使用类型转换将其分配给“mb2”。
// declaring MountainBike reference MountainBike mb3; // assigning mb3 to mb2 using typecasting. mb3 = (MountainBike)mb2;所以,现在以下陈述是有效的。
System.out.println("seat height of second bicycle is " + mb3.seatHeight); mb3.setHeight(21);
何时采用第一种方法(使用超类引用进行引用)
如果我们不知道对象的确切运行时类型,那么我们应该使用这种方法。例如,考虑在不同索引处包含不同对象的 ArrayList。现在,当我们尝试使用ArrayList.get(int index)方法获取数组列表的元素时,我们必须使用对象引用,因为在这种情况下,我们不知道对象的确切运行时类型。例如 :
/* Java program to illustrate referring to a subclass
using superclass reference variable */
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
ArrayList al = new ArrayList(2);
// adding String object to al
al.add(new String("GeeksForGeeks"));
// adding Integer object to al
al.add(new Integer(5));
// getting all elements using Object reference
for (Object object : al)
{
System.out.println(object);
}
}
}
输出:
GeeksForGeeks
5
优点:我们可以使用超类引用来保存从它派生的任何子类对象。
缺点:通过使用超类引用,我们将只能访问由超类定义的对象的那些部分(方法和变量)。例如,在上面的第一个示例中,我们不能使用 Bicycle 引用访问seatHeight变量或调用setHeight(int newValue)方法。这是因为它们是在子类中而不是在超类中定义的。
何时采用第二种方法(使用子类引用进行引用)
如果我们知道对象的确切运行时类型,那么这种方法会更好。使用这种方法,我们还可以调用特定对象的特定方法。例如 :
/* Java program to illustrate referring to a subclass
using subclass reference variable */
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
ArrayList al = new ArrayList(2);
// adding String objects to al
al.add(new String("GeeksForGeeks"));
al.add(new String("for java archives"));
// getting elements using String reference
String str1 = (String)al.get(0);
String str2 = (String)al.get(1);
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str2);
// using String class specific method
System.out.println(str1.length());
System.out.println(str2.substring(4,8));
}
}
输出:
GeeksForGeeks
for java archives
13
java
优点:通过使用子类引用,我们将可以访问由超类或子类定义的对象的两个部分(方法和变量)。例如,我们可以使用上面第一个示例中的 MountainBike 引用调用setHeight(int newValue)方法或speedUp(int increment)方法。
缺点:我们可以使用子类引用仅保留特定的子类对象。
参考:堆栈溢出