请参阅Proto Van Emde Boas树上的先前文章以正确理解这些内容。
插入步骤:
- 基本案例:如果Proto-VEB的大小为2,则将true分配给位数组(在此代码中,由于递归结构,我们分配了Proto-VEB(1),因此现在它不是nullptr,它作为true)键的位置。
- 在达到基本情况之前,我们将递归调用包含键的群集上的插入,现在我们还将键用作键在该群集中的位置,而不是查询键。
- 我们将对摘要执行相同的过程,该过程将根据插入的键将true赋值。
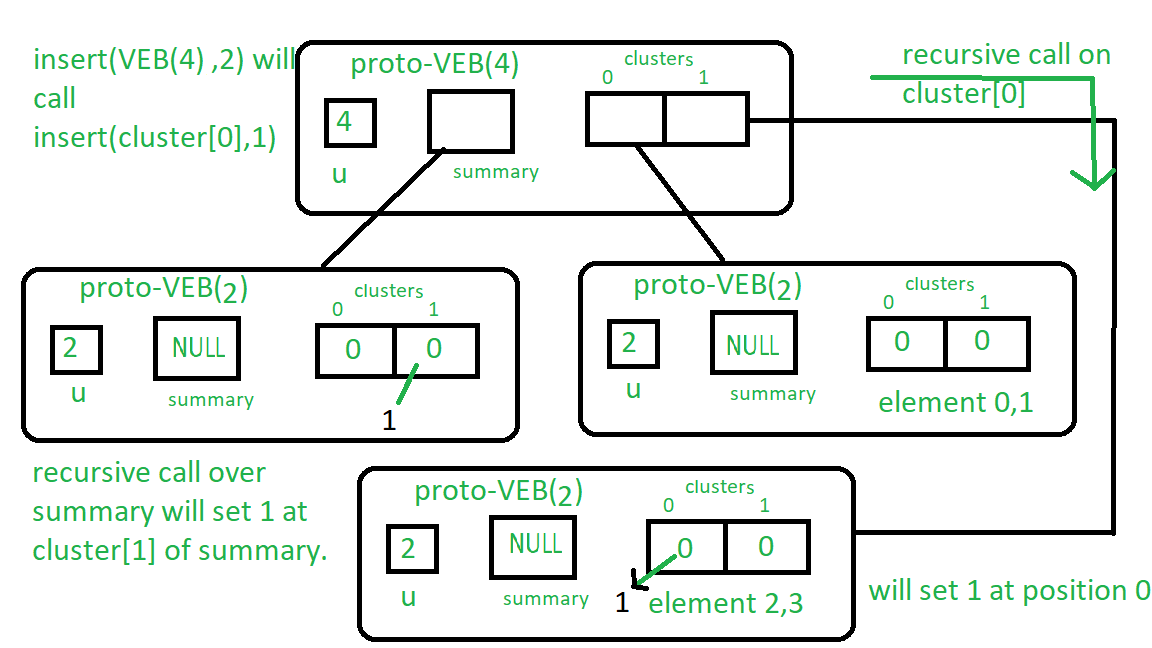
示例:让我们将2插入Proto-VEB(u = 4):从插入过程开始,因为Proto-VEB的大小大于2,所以将开始递归,因此我们递归地调用簇2 /上的insert() ![]() 这是1,它的位置是2%
这是1,它的位置是2% ![]() 它是0,所以递归调用将是insert(cluster [1],0)。
它是0,所以递归调用将是insert(cluster [1],0)。
并且cluster [1]的大小为2个Proto-VEB,我们在基本情况下达到了,因此它将在代码Proto-VEB(1)中将true分配给true [ c ] cluster [1] 0位。
同样,我们将对摘要执行相同的过程。
请参见下图,以获取更多清晰度:
请按照从上至下在方框附近写的说明进行操作。
isMember过程:该过程根据密钥是否存在于Proto-VEB中返回布尔值。了解上面的图片以了解它是非常琐碎的。
- 基本情况:如果Proto-VEB大小为2,则检查键位置的位数组值是否为true,并相应地返回值。 (在代码中,我们检查键位置处的指针是否为nullptr。)
- 递归:我们对包含键的集群进行递归调用,直到达到基本情况为止。
以上算法的实现:
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
class Proto_Van_Emde_Boas {
public:
// Total number of keys
int universe_size;
// Summary
Proto_Van_Emde_Boas* summary;
// Clusters array of Proto-VEB pointers
vector clusters;
int root(int u)
{
return int(sqrt(u));
}
// Function to return cluster numbers
// in which key is present
int high(int x)
{
return x / root(universe_size);
}
// Function to return position of x in cluster
int low(int x)
{
return x % root(universe_size);
}
// Function to return the index from
// cluster number and position
int generate_index(int cluster, int position)
{
return cluster * root(universe_size) + position;
}
// Constructor
Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(int size)
{
universe_size = size;
// Base case
if (size <= 2) {
// Set summary to nullptr as there is no
// more summary for size 2
summary = nullptr;
// Vector of two pointers
// nullptr in starting
clusters = vector(size, nullptr);
}
else {
// Assiging Proto-VEB(sqrt(u)) to summary
summary = new Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(root(size));
// Creating array of Proto-VEB Tree pointers of size sqrt(u)
// first all nullptrs are going to assign
clusters = vector(root(size), nullptr);
// Assigning Proto-VEB(sqrt(u)) to all its clusters
for (int i = 0; i < root(size); i++) {
clusters[i] = new Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(root(size));
}
}
}
};
// Function that returns true if the
// key is present in the tree
bool isMember(Proto_Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key)
{
// If key is greater then universe_size then
// returns false
if (key >= helper->universe_size)
return false;
// If we reach at base case
// the just return whether
// pointer is nullptr then false
// else return true
if (helper->universe_size == 2) {
return helper->clusters[key];
}
else {
// Recursively go deep into the
// level of Proto-VEB tree using its
// cluster index and its position
return isMember(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)],
helper->low(key));
}
}
// Function to insert a key in the tree
void insert(Proto_Van_Emde_Boas*& helper, int key)
{
// If we reach at base case
// then assign Proto-VEB(1) in place
// of nullptr
if (helper->universe_size == 2) {
helper->clusters[key] = new Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(1);
}
else {
// Recursively using index of cluster and its
// position in cluster
insert(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)],
helper->low(key));
// Also do the same recusion in summary VEB
insert(helper->summary, helper->high(key));
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Proto_Van_Emde_Boas* hello = new Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(4);
cout << isMember(hello, 3);
insert(hello, 3);
cout << isMember(hello, 3);
}
插入算法复杂度递归:
T(u)= 2T( ![]() )+ O(1)
)+ O(1)
该算法在O(log2(u))最坏的情况下运行。
isMember算法复杂度递归:
T(u)= T( ![]() )+ O(1)
)+ O(1)
该算法在O(log2(log2(u)))最坏的情况下运行。