从给定的中序和前序遍历构造树
让我们考虑以下遍历:
中序序列:DBEAF C
预购序列:ABDECF
在 Preorder 序列中,最左边的元素是树的根。所以我们知道'A'是给定序列的根。通过在Inorder序列中搜索'A',我们可以发现'A'左侧的所有元素都在左子树中,而右侧的元素在右子树中。所以我们现在知道了下面的结构。
A
/ \
/ \
D B E F C我们递归地按照上面的步骤,得到下面的树。
A
/ \
/ \
B C
/ \ /
/ \ /
D E F算法:buildTree()
1) 从 Preorder 中选择一个元素。增加一个预排序索引变量(下面代码中的 preIndex)来选择下一个递归调用中的下一个元素。
2) 创建一个新的树节点 tNode ,将数据作为选取的元素。
3) 在 Inorder 中找到选取元素的索引。设索引为 inIndex。
4) 对inIndex之前的元素调用buildTree,将构建的树作为tNode的左子树。
5) inIndex 之后的元素调用buildTree,将构建的树作为tNode 的右子树。
6)返回tNode。
C++
/* C++ program to construct tree using
inorder and preorder traversals */
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
char data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
/* Prototypes for utility functions */
int search(char arr[], int strt, int end, char value);
node* newNode(char data);
/* Recursive function to construct binary
of size len from Inorder traversal in[]
and Preorder traversal pre[]. Initial values
of inStrt and inEnd should be 0 and len -1.
The function doesn't do any error checking
for cases where inorder and preorder do not
form a tree */
node* buildTree(char in[], char pre[], int inStrt, int inEnd)
{
static int preIndex = 0;
if (inStrt > inEnd)
return NULL;
/* Pick current node from Preorder
traversal using preIndex
and increment preIndex */
node* tNode = newNode(pre[preIndex++]);
/* If this node has no children then return */
if (inStrt == inEnd)
return tNode;
/* Else find the index of this node in Inorder traversal */
int inIndex = search(in, inStrt, inEnd, tNode->data);
/* Using index in Inorder traversal, construct left and
right subtress */
tNode->left = buildTree(in, pre, inStrt, inIndex - 1);
tNode->right = buildTree(in, pre, inIndex + 1, inEnd);
return tNode;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to find index of value in arr[start...end]
The function assumes that value is present in in[] */
int search(char arr[], int strt, int end, char value)
{
int i;
for (i = strt; i <= end; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == value)
return i;
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(char data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return (Node);
}
/* This function is here just to test buildTree() */
void printInorder(node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print the data of node */
cout<data<<" ";
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver code */
int main()
{
char in[] = { 'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C' };
char pre[] = { 'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F' };
int len = sizeof(in) / sizeof(in[0]);
node* root = buildTree(in, pre, 0, len - 1);
/* Let us test the built tree by
printing Inorder traversal */
cout << "Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is \n";
printInorder(root);
}
// This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
/* program to construct tree using inorder and preorder traversals */
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
char data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Prototypes for utility functions */
int search(char arr[], int strt, int end, char value);
struct node* newNode(char data);
/* Recursive function to construct binary of size len from
Inorder traversal in[] and Preorder traversal pre[]. Initial values
of inStrt and inEnd should be 0 and len -1. The function doesn't
do any error checking for cases where inorder and preorder
do not form a tree */
struct node* buildTree(char in[], char pre[], int inStrt, int inEnd)
{
static int preIndex = 0;
if (inStrt > inEnd)
return NULL;
/* Pick current node from Preorder traversal using preIndex
and increment preIndex */
struct node* tNode = newNode(pre[preIndex++]);
/* If this node has no children then return */
if (inStrt == inEnd)
return tNode;
/* Else find the index of this node in Inorder traversal */
int inIndex = search(in, inStrt, inEnd, tNode->data);
/* Using index in Inorder traversal, construct left and
right subtress */
tNode->left = buildTree(in, pre, inStrt, inIndex - 1);
tNode->right = buildTree(in, pre, inIndex + 1, inEnd);
return tNode;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to find index of value in arr[start...end]
The function assumes that value is present in in[] */
int search(char arr[], int strt, int end, char value)
{
int i;
for (i = strt; i <= end; i++) {
if (arr[i] == value)
return i;
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(char data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* This function is here just to test buildTree() */
void printInorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print the data of node */
printf("%c ", node->data);
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
char in[] = { 'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C' };
char pre[] = { 'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F' };
int len = sizeof(in) / sizeof(in[0]);
struct node* root = buildTree(in, pre, 0, len - 1);
/* Let us test the built tree by printing Inorder traversal */
printf("Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is \n");
printInorder(root);
getchar();
} Java
// Java program to construct a tree using inorder and preorder traversal
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class Node {
char data;
Node left, right;
Node(char item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
static int preIndex = 0;
/* Recursive function to construct binary of size len from
Inorder traversal in[] and Preorder traversal pre[].
Initial values of inStrt and inEnd should be 0 and len -1.
The function doesn't do any error checking for cases where
inorder and preorder do not form a tree */
Node buildTree(char in[], char pre[], int inStrt, int inEnd)
{
if (inStrt > inEnd)
return null;
/* Pick current node from Preorder traversal using preIndex
and increment preIndex */
Node tNode = new Node(pre[preIndex++]);
/* If this node has no children then return */
if (inStrt == inEnd)
return tNode;
/* Else find the index of this node in Inorder traversal */
int inIndex = search(in, inStrt, inEnd, tNode.data);
/* Using index in Inorder traversal, construct left and
right subtress */
tNode.left = buildTree(in, pre, inStrt, inIndex - 1);
tNode.right = buildTree(in, pre, inIndex + 1, inEnd);
return tNode;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to find index of value in arr[start...end]
The function assumes that value is present in in[] */
int search(char arr[], int strt, int end, char value)
{
int i;
for (i = strt; i <= end; i++) {
if (arr[i] == value)
return i;
}
return i;
}
/* This function is here just to test buildTree() */
void printInorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
// driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
char in[] = new char[] { 'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C' };
char pre[] = new char[] { 'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F' };
int len = in.length;
Node root = tree.buildTree(in, pre, 0, len - 1);
// building the tree by printing inorder traversal
System.out.println("Inorder traversal of constructed tree is : ");
tree.printInorder(root);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank JaiswalPython3
# Python program to construct tree using inorder and
# preorder traversals
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
"""Recursive function to construct binary of size len from
Inorder traversal in[] and Preorder traversal pre[]. Initial values
of inStrt and inEnd should be 0 and len -1. The function doesn't
do any error checking for cases where inorder and preorder
do not form a tree """
def buildTree(inOrder, preOrder, inStrt, inEnd):
if (inStrt > inEnd):
return None
# Pick current node from Preorder traversal using
# preIndex and increment preIndex
tNode = Node(preOrder[buildTree.preIndex])
buildTree.preIndex += 1
# If this node has no children then return
if inStrt == inEnd :
return tNode
# Else find the index of this node in Inorder traversal
inIndex = search(inOrder, inStrt, inEnd, tNode.data)
# Using index in Inorder Traversal, construct left
# and right subtrees
tNode.left = buildTree(inOrder, preOrder, inStrt, inIndex-1)
tNode.right = buildTree(inOrder, preOrder, inIndex + 1, inEnd)
return tNode
# UTILITY FUNCTIONS
# Function to find index of value in arr[start...end]
# The function assumes that value is present in inOrder[]
def search(arr, start, end, value):
for i in range(start, end + 1):
if arr[i] == value:
return i
def printInorder(node):
if node is None:
return
# first recur on left child
printInorder(node.left)
# then print the data of node
print (node.data,end=' ')
# now recur on right child
printInorder(node.right)
# Driver program to test above function
inOrder = ['D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C']
preOrder = ['A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F']
# Static variable preIndex
buildTree.preIndex = 0
root = buildTree(inOrder, preOrder, 0, len(inOrder)-1)
# Let us test the build tree by printing Inorder traversal
print ("Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is")
printInorder(root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// C# program to construct a tree using
// inorder and preorder traversal
using System;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer
to left child and a pointer to right child */
public class Node {
public char data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(char item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class GFG {
public Node root;
public static int preIndex = 0;
/* Recursive function to construct binary
of size len from Inorder traversal in[]
and Preorder traversal pre[]. Initial values
of inStrt and inEnd should be 0 and len -1.
The function doesn't do any error checking for
cases where inorder and preorder do not form a tree */
public virtual Node buildTree(char[] arr, char[] pre,
int inStrt, int inEnd)
{
if (inStrt > inEnd) {
return null;
}
/* Pick current node from Preorder traversal
using preIndex and increment preIndex */
Node tNode = new Node(pre[preIndex++]);
/* If this node has no children then return */
if (inStrt == inEnd) {
return tNode;
}
/* Else find the index of this
node in Inorder traversal */
int inIndex = search(arr, inStrt,
inEnd, tNode.data);
/* Using index in Inorder traversal,
construct left and right subtress */
tNode.left = buildTree(arr, pre, inStrt, inIndex - 1);
tNode.right = buildTree(arr, pre, inIndex + 1, inEnd);
return tNode;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to find index of value in arr[start...end]
The function assumes that value is present in in[] */
public virtual int search(char[] arr, int strt,
int end, char value)
{
int i;
for (i = strt; i <= end; i++) {
if (arr[i] == value) {
return i;
}
}
return i;
}
/* This function is here just to test buildTree() */
public virtual void printInorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null) {
return;
}
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
GFG tree = new GFG();
char[] arr = new char[] { 'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C' };
char[] pre = new char[] { 'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F' };
int len = arr.Length;
Node root = tree.buildTree(arr, pre, 0, len - 1);
// building the tree by printing inorder traversal
Console.WriteLine("Inorder traversal of "
+ "constructed tree is : ");
tree.printInorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13Javascript
C++
/* C++ program to construct tree using inorder
and preorder traversals */
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct Node {
char data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
struct Node* newNode(char data)
{
struct Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Recursive function to construct binary of size
len from Inorder traversal in[] and Preorder traversal
pre[]. Initial values of inStrt and inEnd should be
0 and len -1. The function doesn't do any error
checking for cases where inorder and preorder
do not form a tree */
struct Node* buildTree(char in[], char pre[], int inStrt,
int inEnd, unordered_map& mp)
{
static int preIndex = 0;
if (inStrt > inEnd)
return NULL;
/* Pick current node from Preorder traversal using preIndex
and increment preIndex */
char curr = pre[preIndex++];
struct Node* tNode = newNode(curr);
/* If this node has no children then return */
if (inStrt == inEnd)
return tNode;
/* Else find the index of this node in Inorder traversal */
int inIndex = mp[curr];
/* Using index in Inorder traversal, construct left and
right subtress */
tNode->left = buildTree(in, pre, inStrt, inIndex - 1, mp);
tNode->right = buildTree(in, pre, inIndex + 1, inEnd, mp);
return tNode;
}
// This function mainly creates an unordered_map, then
// calls buildTree()
struct Node* buldTreeWrap(char in[], char pre[], int len)
{
// Store indexes of all items so that we
// we can quickly find later
unordered_map mp;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
mp[in[i]] = i;
return buildTree(in, pre, 0, len - 1, mp);
}
/* This function is here just to test buildTree() */
void printInorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
printInorder(node->left);
printf("%c ", node->data);
printInorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
char in[] = { 'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C' };
char pre[] = { 'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F' };
int len = sizeof(in) / sizeof(in[0]);
struct Node* root = buldTreeWrap(in, pre, len);
/* Let us test the built tree by printing
Inorder traversal */
printf("Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is \n");
printInorder(root);
} Java
/* Java program to construct tree using inorder
and preorder traversals */
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class Node
{
char data;
Node left,right;
Node(char item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class Tree
{
public static Node root;
// Store indexes of all items so that we
// we can quickly find later
static HashMap mp = new HashMap<>();
static int preIndex = 0;
/* Recursive function to construct binary of size
len from Inorder traversal in[] and Preorder traversal
pre[]. Initial values of inStrt and inEnd should be
0 and len -1. The function doesn't do any error
checking for cases where inorder and preorder
do not form a tree */
public static Node buildTree(char[] in, char[] pre, int inStrt, int inEnd)
{
if(inStrt > inEnd)
{
return null;
}
/* Pick current node from Preorder traversal using preIndex
and increment preIndex */
char curr = pre[preIndex++];
Node tNode;
tNode = new Node(curr);
/* If this node has no children then return */
if (inStrt == inEnd)
{
return tNode;
}
/* Else find the index of this node in Inorder traversal */
int inIndex = mp.get(curr);
/* Using index in Inorder traversal, construct left and
right subtress */
tNode.left = buildTree(in, pre, inStrt, inIndex - 1);
tNode.right = buildTree(in, pre, inIndex + 1, inEnd);
return tNode;
}
// This function mainly creates an unordered_map, then
// calls buildTree()
public static Node buldTreeWrap(char[] in, char[] pre, int len)
{
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
mp.put(in[i], i);
}
return buildTree(in, pre, 0, len - 1);
}
/* This function is here just to test buildTree() */
static void printInorder(Node node)
{
if(node == null)
{
return;
}
printInorder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
printInorder(node.right);
}
/* Driver code */
public static void main (String[] args)
{
char[] in = {'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C'};
char[] pre = {'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F'};
int len = in.length;
Tree.root=buldTreeWrap(in, pre, len);
/* Let us test the built tree by printing
Inorder traversal */
System.out.println("Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is");
printInorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 Python3
# Python3 program to construct tree using inorder
# and preorder traversals
# A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
# and a pointer to right child
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Recursive function to construct binary of size
# len from Inorder traversal in[] and Preorder traversal
# pre[]. Initial values of inStrt and inEnd should be
# 0 and len -1. The function doesn't do any error
# checking for cases where inorder and preorder
# do not form a tree
def buildTree(inn, pre, inStrt, inEnd):
global preIndex, mp
if (inStrt > inEnd):
return None
# Pick current node from Preorder traversal
# using preIndex and increment preIndex
curr = pre[preIndex]
preIndex += 1
tNode = Node(curr)
# If this node has no children then return
if (inStrt == inEnd):
return tNode
# Else find the index of this
# node in Inorder traversal
inIndex = mp[curr]
# Using index in Inorder traversal,
# construct left and right subtress
tNode.left = buildTree(inn, pre, inStrt,
inIndex - 1)
tNode.right = buildTree(inn, pre, inIndex + 1,
inEnd)
return tNode
# This function mainly creates an
# unordered_map, then calls buildTree()
def buldTreeWrap(inn, pre, lenn):
global mp
# Store indexes of all items so that we
# we can quickly find later
# unordered_map mp;
for i in range(lenn):
mp[inn[i]] = i
return buildTree(inn, pre, 0, lenn - 1)
# This function is here just to test buildTree()
def prInorder(node):
if (node == None):
return
prInorder(node.left)
print(node.data, end = " ")
prInorder(node.right)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
mp = {}
preIndex = 0
inn = [ 'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C' ]
pre = [ 'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F' ]
lenn = len(inn)
root = buldTreeWrap(inn, pre,lenn)
# Let us test the built tree by printing
# Inorder traversal
print("Inorder traversal of "
"the constructed tree is")
prInorder(root)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29 C#
/* C# program to construct tree using inorder
and preorder traversals */
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
public class Node
{
public char data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(char d)
{
data = d;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class Tree
{
public static Node root;
// Store indexes of all items so that we
// we can quickly find later
static Dictionary mp = new Dictionary();
static int preIndex = 0;
/* Recursive function to construct binary of size
len from Inorder traversal in[] and Preorder traversal
pre[]. Initial values of inStrt and inEnd should be
0 and len -1. The function doesn't do any error
checking for cases where inorder and preorder
do not form a tree */
static Node buildTree(char[] In, char[] pre,
int inStrt, int inEnd)
{
if(inStrt > inEnd)
{
return null;
}
/* Pick current node from Preorder traversal using preIndex
and increment preIndex */
char curr = pre[preIndex++];
Node tNode;
tNode = new Node(curr);
/* If this node has no children then return */
if(inStrt == inEnd)
{
return tNode;
}
/* Else find the index of this node in Inorder traversal */
int inIndex = mp[curr];
/* Using index in Inorder traversal, construct left and
right subtress */
tNode.left = buildTree(In, pre, inStrt, inIndex - 1);
tNode.right = buildTree(In, pre, inIndex + 1, inEnd);
return tNode;
}
// This function mainly creates an unordered_map, then
// calls buildTree()
public static Node buldTreeWrap(char[] In, char[] pre, int len)
{
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
mp.Add(In[i], i);
}
return buildTree(In, pre, 0, len - 1);
}
/* This function is here just to test buildTree() */
static void printInorder(Node node)
{
if(node == null)
{
return;
}
printInorder(node.left);
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
printInorder(node.right);
}
/* Driver code */
static public void Main (){
char[] In = {'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C'};
char[] pre = {'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F'};
int len = In.Length;
Tree.root = buldTreeWrap(In, pre, len);
/* Let us test the built tree by printing
Inorder traversal */
Console.WriteLine("Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is");
printInorder(Tree.root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127 C++
// C++ program to construct a tree using
// inorder and preorder traversal
#include
using namespace std;
class TreeNode
{
public:
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
};
set s;
stack st;
// Function to build tree using given traversal
TreeNode* buildTree(int preorder[], int inorder[],int n)
{
TreeNode* root = NULL;
for (int pre = 0, in = 0; pre < n;)
{
TreeNode* node = NULL;
do
{
node = new TreeNode(preorder[pre]);
if (root == NULL)
{
root = node;
}
if (st.size() > 0)
{
if (s.find(st.top()) != s.end())
{
s.erase(st.top());
st.top()->right = node;
st.pop();
}
else
{
st.top()->left = node;
}
}
st.push(node);
} while (preorder[pre++] != inorder[in] && pre < n);
node = NULL;
while (st.size() > 0 && in < n &&
st.top()->val == inorder[in])
{
node = st.top();
st.pop();
in++;
}
if (node != NULL)
{
s.insert(node);
st.push(node);
}
}
return root;
}
// Function to print tree in Inorder
void printInorder(TreeNode* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print the data of node */
cout << node->val << " ";
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node->right);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int in[] = { 9, 8, 4, 2, 10, 5, 10, 1, 6, 3, 13, 12, 7 };
int pre[] = { 1, 2, 4, 8, 9, 5, 10, 10, 3, 6, 7, 12, 13 };
int len = sizeof(in)/sizeof(int);
TreeNode *root = buildTree(pre, in, len);
printInorder(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu Java
// Java program to construct a tree using inorder and preorder traversal
import java.util.*;
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
class BinaryTree {
static Set set = new HashSet<>();
static Stack stack = new Stack<>();
// Function to build tree using given traversal
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder)
{
TreeNode root = null;
for (int pre = 0, in = 0; pre < preorder.length;) {
TreeNode node = null;
do {
node = new TreeNode(preorder[pre]);
if (root == null) {
root = node;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
if (set.contains(stack.peek())) {
set.remove(stack.peek());
stack.pop().right = node;
}
else {
stack.peek().left = node;
}
}
stack.push(node);
} while (preorder[pre++] != inorder[in] && pre < preorder.length);
node = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty() && in < inorder.length &&
stack.peek().val == inorder[in]) {
node = stack.pop();
in++;
}
if (node != null) {
set.add(node);
stack.push(node);
}
}
return root;
}
// Function to print tree in Inorder
void printInorder(TreeNode node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
System.out.print(node.val + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
// driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
int in[] = new int[] { 9, 8, 4, 2, 10, 5, 10, 1, 6, 3, 13, 12, 7 };
int pre[] = new int[] { 1, 2, 4, 8, 9, 5, 10, 10, 3, 6, 7, 12, 13 };
int len = in.length;
TreeNode root = tree.buildTree(pre, in);
tree.printInorder(root);
}
} Python3
# Python3 program to construct a tree using
# inorder and preorder traversal
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
s = set()
st = []
# Function to build tree using given traversal
def buildTree(preorder, inorder, n):
root = None;
pre = 0
in_t = 0
while pre < n:
node = None;
while True:
node = TreeNode(preorder[pre])
if (root == None):
root = node;
if (len(st) > 0):
if (st[-1] in s):
s.discard(st[-1]);
st[-1].right = node;
st.pop();
else:
st[-1].left = node;
st.append(node);
if pre>=n or preorder[pre] == inorder[in_t]:
pre += 1
break
pre += 1
node = None;
while (len(st) > 0 and in_t < n and st[-1].val == inorder[in_t]):
node = st[-1];
st.pop();
in_t += 1
if (node != None):
s.add(node);
st.append(node);
return root;
# Function to print tree in_t Inorder
def printInorder( node):
if (node == None):
return;
''' first recur on left child '''
printInorder(node.left);
''' then print data of node '''
print(node.val, end=" ");
''' now recur on right child '''
printInorder(node.right);
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
in_t = [ 9, 8, 4, 2, 10, 5, 10, 1, 6, 3, 13, 12, 7 ]
pre = [ 1, 2, 4, 8, 9, 5, 10, 10, 3, 6, 7, 12, 13 ]
l = len(in_t)
root = buildTree(pre, in_t, l);
printInorder(root);
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56.C#
// C# program to construct a tree
// using inorder and preorder traversal
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class TreeNode
{
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
class GFG
{
static HashSet set = new HashSet();
static Stack stack = new Stack();
// Function to build tree using given traversal
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder)
{
TreeNode root = null;
for (int pre = 0, iN = 0; pre < preorder.Length;)
{
TreeNode node = null;
do {
node = new TreeNode(preorder[pre]);
if (root == null)
{
root = node;
}
if (stack.Count != 0)
{
if (set.Contains(stack.Peek()))
{
set.Remove(stack.Peek());
stack.Pop().right = node;
}
else
{
stack.Peek().left = node;
}
}
stack.Push(node);
} while (preorder[pre++] != inorder[iN] &&
pre < preorder.Length);
node = null;
while (stack.Count != 0 && iN < inorder.Length &&
stack.Peek().val == inorder[iN])
{
node = stack.Pop();
iN++;
}
if (node != null)
{
set.Add(node);
stack.Push(node);
}
}
return root;
}
// Function to print tree in Inorder
void printInorder(TreeNode node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
Console.Write(node.val + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
GFG tree = new GFG();
int []iN = new int[] { 9, 8, 4, 2, 10, 5, 10,
1, 6, 3, 13, 12, 7 };
int []pre = new int[] { 1, 2, 4, 8, 9, 5, 10,
10, 3, 6, 7, 12, 13 };
int len = iN.Length;
TreeNode root = tree.buildTree(pre, iN);
tree.printInorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Javascript
Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is
D B E A F C时间复杂度: O(n^2) 。最坏的情况发生在树左倾斜时。最坏情况的前序和中序遍历示例是 {A, B, C, D} 和 {D, C, B, A}。
有效的方法:
我们可以使用散列(C++ 中的 unordered_map 或Java中的 HashMap)来优化上述解决方案。我们将中序遍历的索引存储在哈希表中。这样搜索就可以在 O(1) 时间内完成。
C++
/* C++ program to construct tree using inorder
and preorder traversals */
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct Node {
char data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
struct Node* newNode(char data)
{
struct Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Recursive function to construct binary of size
len from Inorder traversal in[] and Preorder traversal
pre[]. Initial values of inStrt and inEnd should be
0 and len -1. The function doesn't do any error
checking for cases where inorder and preorder
do not form a tree */
struct Node* buildTree(char in[], char pre[], int inStrt,
int inEnd, unordered_map& mp)
{
static int preIndex = 0;
if (inStrt > inEnd)
return NULL;
/* Pick current node from Preorder traversal using preIndex
and increment preIndex */
char curr = pre[preIndex++];
struct Node* tNode = newNode(curr);
/* If this node has no children then return */
if (inStrt == inEnd)
return tNode;
/* Else find the index of this node in Inorder traversal */
int inIndex = mp[curr];
/* Using index in Inorder traversal, construct left and
right subtress */
tNode->left = buildTree(in, pre, inStrt, inIndex - 1, mp);
tNode->right = buildTree(in, pre, inIndex + 1, inEnd, mp);
return tNode;
}
// This function mainly creates an unordered_map, then
// calls buildTree()
struct Node* buldTreeWrap(char in[], char pre[], int len)
{
// Store indexes of all items so that we
// we can quickly find later
unordered_map mp;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
mp[in[i]] = i;
return buildTree(in, pre, 0, len - 1, mp);
}
/* This function is here just to test buildTree() */
void printInorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
printInorder(node->left);
printf("%c ", node->data);
printInorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
char in[] = { 'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C' };
char pre[] = { 'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F' };
int len = sizeof(in) / sizeof(in[0]);
struct Node* root = buldTreeWrap(in, pre, len);
/* Let us test the built tree by printing
Inorder traversal */
printf("Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is \n");
printInorder(root);
}
Java
/* Java program to construct tree using inorder
and preorder traversals */
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class Node
{
char data;
Node left,right;
Node(char item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class Tree
{
public static Node root;
// Store indexes of all items so that we
// we can quickly find later
static HashMap mp = new HashMap<>();
static int preIndex = 0;
/* Recursive function to construct binary of size
len from Inorder traversal in[] and Preorder traversal
pre[]. Initial values of inStrt and inEnd should be
0 and len -1. The function doesn't do any error
checking for cases where inorder and preorder
do not form a tree */
public static Node buildTree(char[] in, char[] pre, int inStrt, int inEnd)
{
if(inStrt > inEnd)
{
return null;
}
/* Pick current node from Preorder traversal using preIndex
and increment preIndex */
char curr = pre[preIndex++];
Node tNode;
tNode = new Node(curr);
/* If this node has no children then return */
if (inStrt == inEnd)
{
return tNode;
}
/* Else find the index of this node in Inorder traversal */
int inIndex = mp.get(curr);
/* Using index in Inorder traversal, construct left and
right subtress */
tNode.left = buildTree(in, pre, inStrt, inIndex - 1);
tNode.right = buildTree(in, pre, inIndex + 1, inEnd);
return tNode;
}
// This function mainly creates an unordered_map, then
// calls buildTree()
public static Node buldTreeWrap(char[] in, char[] pre, int len)
{
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
mp.put(in[i], i);
}
return buildTree(in, pre, 0, len - 1);
}
/* This function is here just to test buildTree() */
static void printInorder(Node node)
{
if(node == null)
{
return;
}
printInorder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
printInorder(node.right);
}
/* Driver code */
public static void main (String[] args)
{
char[] in = {'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C'};
char[] pre = {'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F'};
int len = in.length;
Tree.root=buldTreeWrap(in, pre, len);
/* Let us test the built tree by printing
Inorder traversal */
System.out.println("Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is");
printInorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
Python3
# Python3 program to construct tree using inorder
# and preorder traversals
# A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
# and a pointer to right child
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Recursive function to construct binary of size
# len from Inorder traversal in[] and Preorder traversal
# pre[]. Initial values of inStrt and inEnd should be
# 0 and len -1. The function doesn't do any error
# checking for cases where inorder and preorder
# do not form a tree
def buildTree(inn, pre, inStrt, inEnd):
global preIndex, mp
if (inStrt > inEnd):
return None
# Pick current node from Preorder traversal
# using preIndex and increment preIndex
curr = pre[preIndex]
preIndex += 1
tNode = Node(curr)
# If this node has no children then return
if (inStrt == inEnd):
return tNode
# Else find the index of this
# node in Inorder traversal
inIndex = mp[curr]
# Using index in Inorder traversal,
# construct left and right subtress
tNode.left = buildTree(inn, pre, inStrt,
inIndex - 1)
tNode.right = buildTree(inn, pre, inIndex + 1,
inEnd)
return tNode
# This function mainly creates an
# unordered_map, then calls buildTree()
def buldTreeWrap(inn, pre, lenn):
global mp
# Store indexes of all items so that we
# we can quickly find later
# unordered_map mp;
for i in range(lenn):
mp[inn[i]] = i
return buildTree(inn, pre, 0, lenn - 1)
# This function is here just to test buildTree()
def prInorder(node):
if (node == None):
return
prInorder(node.left)
print(node.data, end = " ")
prInorder(node.right)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
mp = {}
preIndex = 0
inn = [ 'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C' ]
pre = [ 'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F' ]
lenn = len(inn)
root = buldTreeWrap(inn, pre,lenn)
# Let us test the built tree by printing
# Inorder traversal
print("Inorder traversal of "
"the constructed tree is")
prInorder(root)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
/* C# program to construct tree using inorder
and preorder traversals */
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
public class Node
{
public char data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(char d)
{
data = d;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class Tree
{
public static Node root;
// Store indexes of all items so that we
// we can quickly find later
static Dictionary mp = new Dictionary();
static int preIndex = 0;
/* Recursive function to construct binary of size
len from Inorder traversal in[] and Preorder traversal
pre[]. Initial values of inStrt and inEnd should be
0 and len -1. The function doesn't do any error
checking for cases where inorder and preorder
do not form a tree */
static Node buildTree(char[] In, char[] pre,
int inStrt, int inEnd)
{
if(inStrt > inEnd)
{
return null;
}
/* Pick current node from Preorder traversal using preIndex
and increment preIndex */
char curr = pre[preIndex++];
Node tNode;
tNode = new Node(curr);
/* If this node has no children then return */
if(inStrt == inEnd)
{
return tNode;
}
/* Else find the index of this node in Inorder traversal */
int inIndex = mp[curr];
/* Using index in Inorder traversal, construct left and
right subtress */
tNode.left = buildTree(In, pre, inStrt, inIndex - 1);
tNode.right = buildTree(In, pre, inIndex + 1, inEnd);
return tNode;
}
// This function mainly creates an unordered_map, then
// calls buildTree()
public static Node buldTreeWrap(char[] In, char[] pre, int len)
{
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
mp.Add(In[i], i);
}
return buildTree(In, pre, 0, len - 1);
}
/* This function is here just to test buildTree() */
static void printInorder(Node node)
{
if(node == null)
{
return;
}
printInorder(node.left);
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
printInorder(node.right);
}
/* Driver code */
static public void Main (){
char[] In = {'D', 'B', 'E', 'A', 'F', 'C'};
char[] pre = {'A', 'B', 'D', 'E', 'C', 'F'};
int len = In.Length;
Tree.root = buldTreeWrap(In, pre, len);
/* Let us test the built tree by printing
Inorder traversal */
Console.WriteLine("Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is");
printInorder(Tree.root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127
Inorder traversal of the constructed tree is
D B E A F C时间复杂度: O(n)另一种方法:
使用 InOrder 遍历是 Left-Root-Right 而 PreOrder 遍历是 Root-Left-Right 的事实。此外,PreOrder 遍历中的第一个节点始终是根节点,而 InOrder 遍历中的第一个节点是树中最左边的节点。
维护两个数据结构:Stack(存储我们在遍历 PreOrder 数组时访问的路径)和 Set(维护预期下一个右子树所在的节点)。
1. 执行以下操作,直到到达最左边的节点。
继续从 PreOrder 遍历创建节点
如果堆栈的最顶层元素不在集合中,则将创建的节点链接到堆栈最顶层元素(如果有)的左子节点,而不弹出该元素。
否则将创建的节点链接到堆栈最顶层元素的右子节点。从集合和堆栈中删除堆栈的最顶部元素。
将节点推送到堆栈。
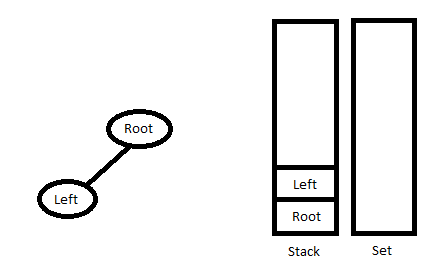
2. 继续从堆栈中弹出节点,直到堆栈为空,或者堆栈的最顶部元素与 InOrder 遍历的当前元素比较。循环结束后,将最后一个节点推回堆栈和集合中。
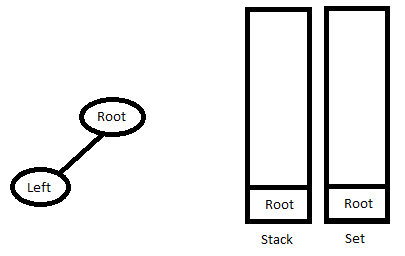
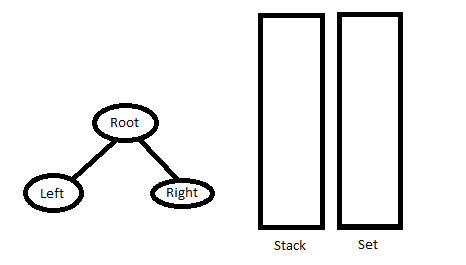
3. 转到步骤 1。
C++
// C++ program to construct a tree using
// inorder and preorder traversal
#include
using namespace std;
class TreeNode
{
public:
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
};
set s;
stack st;
// Function to build tree using given traversal
TreeNode* buildTree(int preorder[], int inorder[],int n)
{
TreeNode* root = NULL;
for (int pre = 0, in = 0; pre < n;)
{
TreeNode* node = NULL;
do
{
node = new TreeNode(preorder[pre]);
if (root == NULL)
{
root = node;
}
if (st.size() > 0)
{
if (s.find(st.top()) != s.end())
{
s.erase(st.top());
st.top()->right = node;
st.pop();
}
else
{
st.top()->left = node;
}
}
st.push(node);
} while (preorder[pre++] != inorder[in] && pre < n);
node = NULL;
while (st.size() > 0 && in < n &&
st.top()->val == inorder[in])
{
node = st.top();
st.pop();
in++;
}
if (node != NULL)
{
s.insert(node);
st.push(node);
}
}
return root;
}
// Function to print tree in Inorder
void printInorder(TreeNode* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print the data of node */
cout << node->val << " ";
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node->right);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int in[] = { 9, 8, 4, 2, 10, 5, 10, 1, 6, 3, 13, 12, 7 };
int pre[] = { 1, 2, 4, 8, 9, 5, 10, 10, 3, 6, 7, 12, 13 };
int len = sizeof(in)/sizeof(int);
TreeNode *root = buildTree(pre, in, len);
printInorder(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Java
// Java program to construct a tree using inorder and preorder traversal
import java.util.*;
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
class BinaryTree {
static Set set = new HashSet<>();
static Stack stack = new Stack<>();
// Function to build tree using given traversal
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder)
{
TreeNode root = null;
for (int pre = 0, in = 0; pre < preorder.length;) {
TreeNode node = null;
do {
node = new TreeNode(preorder[pre]);
if (root == null) {
root = node;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
if (set.contains(stack.peek())) {
set.remove(stack.peek());
stack.pop().right = node;
}
else {
stack.peek().left = node;
}
}
stack.push(node);
} while (preorder[pre++] != inorder[in] && pre < preorder.length);
node = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty() && in < inorder.length &&
stack.peek().val == inorder[in]) {
node = stack.pop();
in++;
}
if (node != null) {
set.add(node);
stack.push(node);
}
}
return root;
}
// Function to print tree in Inorder
void printInorder(TreeNode node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
System.out.print(node.val + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
// driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
int in[] = new int[] { 9, 8, 4, 2, 10, 5, 10, 1, 6, 3, 13, 12, 7 };
int pre[] = new int[] { 1, 2, 4, 8, 9, 5, 10, 10, 3, 6, 7, 12, 13 };
int len = in.length;
TreeNode root = tree.buildTree(pre, in);
tree.printInorder(root);
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program to construct a tree using
# inorder and preorder traversal
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
s = set()
st = []
# Function to build tree using given traversal
def buildTree(preorder, inorder, n):
root = None;
pre = 0
in_t = 0
while pre < n:
node = None;
while True:
node = TreeNode(preorder[pre])
if (root == None):
root = node;
if (len(st) > 0):
if (st[-1] in s):
s.discard(st[-1]);
st[-1].right = node;
st.pop();
else:
st[-1].left = node;
st.append(node);
if pre>=n or preorder[pre] == inorder[in_t]:
pre += 1
break
pre += 1
node = None;
while (len(st) > 0 and in_t < n and st[-1].val == inorder[in_t]):
node = st[-1];
st.pop();
in_t += 1
if (node != None):
s.add(node);
st.append(node);
return root;
# Function to print tree in_t Inorder
def printInorder( node):
if (node == None):
return;
''' first recur on left child '''
printInorder(node.left);
''' then print data of node '''
print(node.val, end=" ");
''' now recur on right child '''
printInorder(node.right);
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
in_t = [ 9, 8, 4, 2, 10, 5, 10, 1, 6, 3, 13, 12, 7 ]
pre = [ 1, 2, 4, 8, 9, 5, 10, 10, 3, 6, 7, 12, 13 ]
l = len(in_t)
root = buildTree(pre, in_t, l);
printInorder(root);
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56.
C#
// C# program to construct a tree
// using inorder and preorder traversal
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class TreeNode
{
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
class GFG
{
static HashSet set = new HashSet();
static Stack stack = new Stack();
// Function to build tree using given traversal
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder)
{
TreeNode root = null;
for (int pre = 0, iN = 0; pre < preorder.Length;)
{
TreeNode node = null;
do {
node = new TreeNode(preorder[pre]);
if (root == null)
{
root = node;
}
if (stack.Count != 0)
{
if (set.Contains(stack.Peek()))
{
set.Remove(stack.Peek());
stack.Pop().right = node;
}
else
{
stack.Peek().left = node;
}
}
stack.Push(node);
} while (preorder[pre++] != inorder[iN] &&
pre < preorder.Length);
node = null;
while (stack.Count != 0 && iN < inorder.Length &&
stack.Peek().val == inorder[iN])
{
node = stack.Pop();
iN++;
}
if (node != null)
{
set.Add(node);
stack.Push(node);
}
}
return root;
}
// Function to print tree in Inorder
void printInorder(TreeNode node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
Console.Write(node.val + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
GFG tree = new GFG();
int []iN = new int[] { 9, 8, 4, 2, 10, 5, 10,
1, 6, 3, 13, 12, 7 };
int []pre = new int[] { 1, 2, 4, 8, 9, 5, 10,
10, 3, 6, 7, 12, 13 };
int len = iN.Length;
TreeNode root = tree.buildTree(pre, iN);
tree.printInorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
9 8 4 2 10 5 10 1 6 3 13 12 7从后序和中序构造二叉树