强烈建议先阅读Van Emde Boas Tree上的先前文章。
删除步骤:
在这里,我们假设密钥已经存在于树中。
- 首先,我们检查是否只有一个键,然后将树的最大值和最小值指定为空值以删除键。
- 基本案例:如果树的Universe大小为2,则在仅存在一个键的上述条件为false之后,树中恰好存在两个键(在上述条件变为false之后),因此删除查询通过将树的最大值和最小值分配给树中存在的另一个键来设置键。
- 递归案例:
- 如果键是树的最小值,则找到树的下一个最小值,并将其分配为树的最小值,然后删除查询键。
- 现在查询关键字不存在于树中。我们将不得不更改树中的其余结构以完全消除密钥:
- 如果查询键的簇的最小值为空,那么我们也将从摘要中删除它。另外,如果键是树的最大值,则我们将找到新的最大值并将其分配为树的最大值。
- 否则,如果键是树的最大值,则找到新的最大值并将其分配为树的最大值。
以下是一系列图像,这些图像表示存在0、1、2个键的VEB树上的“删除键0查询”:
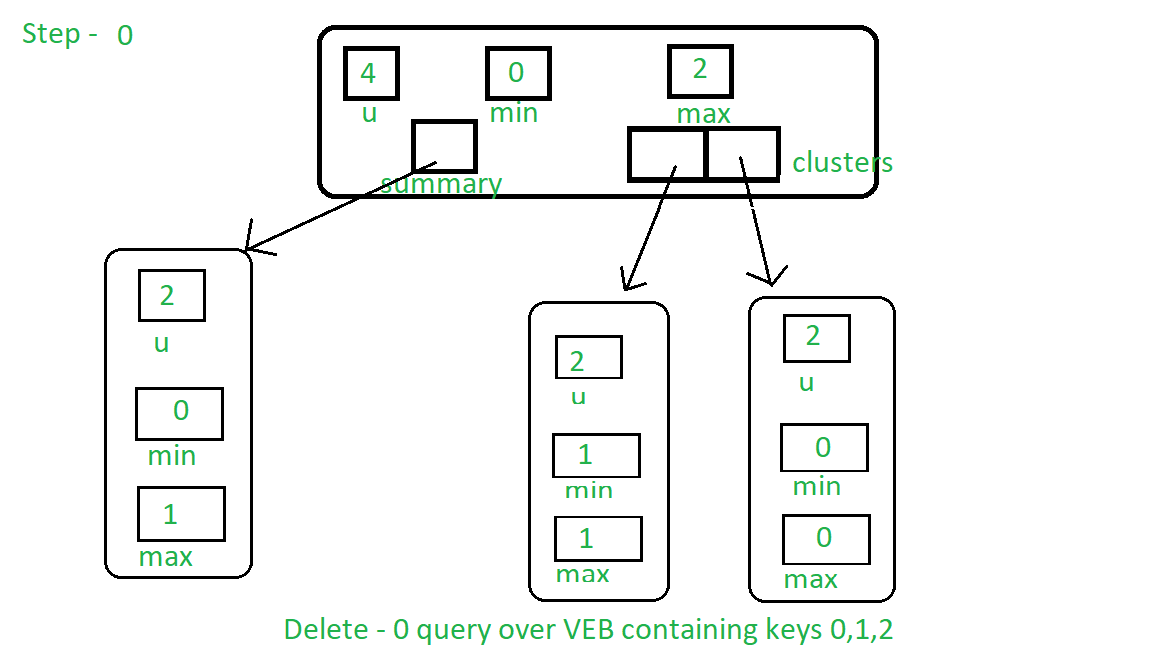
步骤1:由于0是树的最小值,它将满足算法其他部分的第一个条件。
首先,它找到下一个最大值1,并将其设置为最小值。 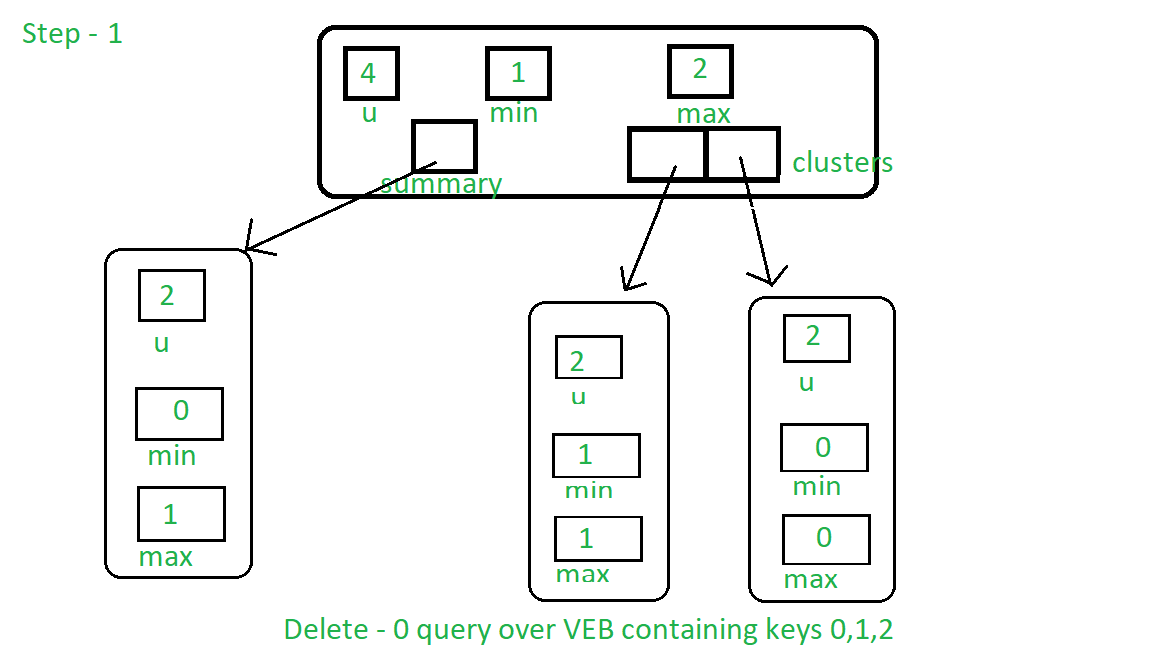
步骤2:现在它将从集群[0]中删除密钥1。 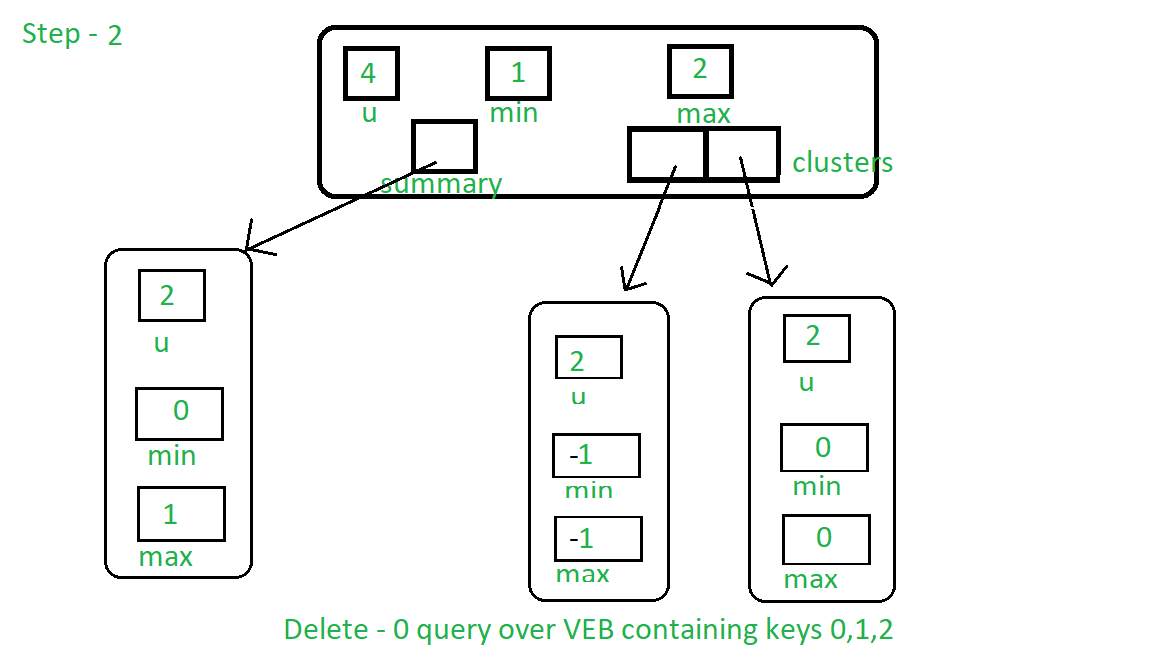
步骤3:下一个条件cluster [0]没有密钥,为true,因此也会从摘要中清除密钥。 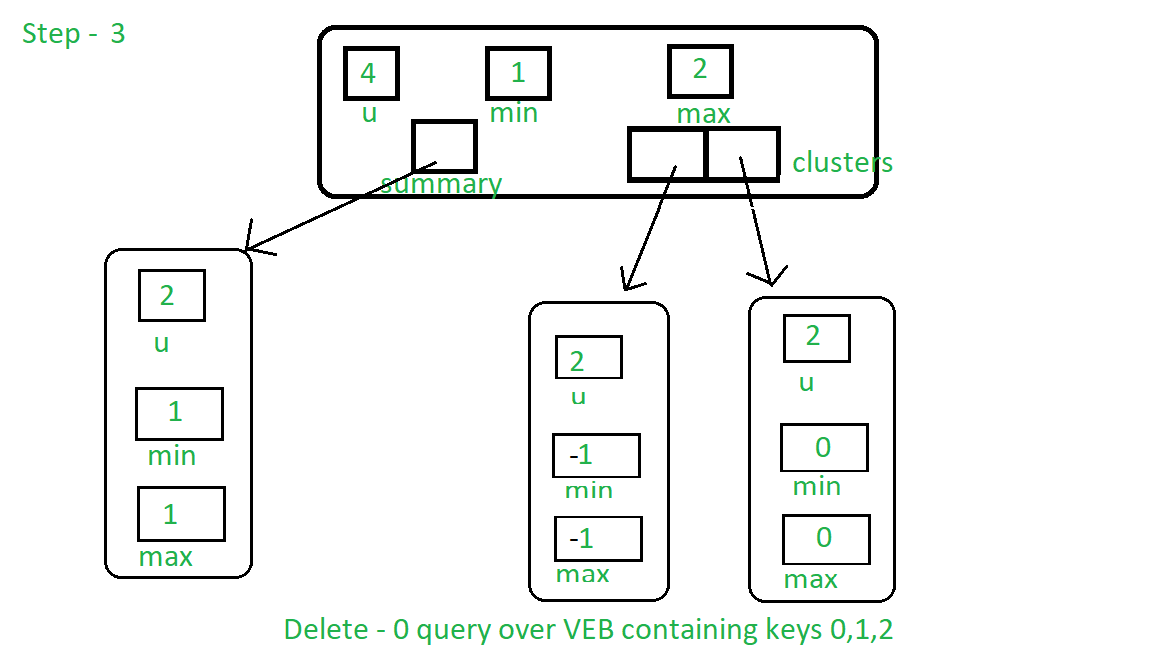
#include
using namespace std;
class Van_Emde_Boas {
public:
int universe_size;
int minimum;
int maximum;
Van_Emde_Boas* summary;
vector clusters;
// Function to return cluster numbers
// in which key is present
int high(int x)
{
int div = ceil(sqrt(universe_size));
return x / div;
}
// Function to return position of x in cluster
int low(int x)
{
int mod = ceil(sqrt(universe_size));
return x % mod;
}
// Function to return the index from
// cluster number and position
int generate_index(int x, int y)
{
int ru = ceil(sqrt(universe_size));
return x * ru + y;
}
// Constructor
Van_Emde_Boas(int size)
{
universe_size = size;
minimum = -1;
maximum = -1;
// Base case
if (size <= 2) {
summary = nullptr;
clusters = vector(0, nullptr);
}
else {
int no_clusters = ceil(sqrt(size));
// Assigning VEB(sqrt(u)) to summary
summary = new Van_Emde_Boas(no_clusters);
// Creating array of VEB Tree pointers of size sqrt(u)
clusters = vector(no_clusters, nullptr);
// Assigning VEB(sqrt(u)) to all its clusters
for (int i = 0; i < no_clusters; i++) {
clusters[i] = new Van_Emde_Boas(ceil(sqrt(size)));
}
}
}
};
// Function to return the minimum value
// from the tree if it exists
int VEB_minimum(Van_Emde_Boas* helper)
{
return (helper->minimum == -1 ? -1 : helper->minimum);
}
// Function to return the maximum value
// from the tree if it exists
int VEB_maximum(Van_Emde_Boas* helper)
{
return (helper->maximum == -1 ? -1 : helper->maximum);
}
// Function to insert a key in the tree
void insert(Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key)
{
// If no key is present in the tree
// then set both minimum and maximum
// to the key (Read the previous article
// for more understanding about it)
if (helper->minimum == -1) {
helper->minimum = key;
helper->maximum = key;
}
else {
if (key < helper->minimum) {
// If the key is less than the current minimum
// then swap it with the current minimum
// because this minimum is actually
// minimum of one of the internal cluster
// so as we go deeper into the Van Emde Boas
// we need to take that minimum to its real position
// This concept is similar to "Lazy Propagation"
swap(helper->minimum, key);
}
// Not base case then...
if (helper->universe_size > 2) {
// If no key is present in the cluster then insert key into
// both cluster and summary
if (VEB_minimum(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]) == -1) {
insert(helper->summary, helper->high(key));
// Sets the minimum and maximum of cluster to the key
// as no other keys are present we will stop at this level
// we are not going deeper into the structure like
// Lazy Propagation
helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]->minimum = helper->low(key);
helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]->maximum = helper->low(key);
}
else {
// If there are other elements in the tree then recursively
// go deeper into the structure to set attributes accordingly
insert(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)], helper->low(key));
}
}
// Sets the key as maximum it is greater than current maximum
if (key > helper->maximum) {
helper->maximum = key;
}
}
}
// Function that returns true if the
// key is present in the tree
bool isMember(Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key)
{
// If universe_size is less than the key
// then we can not search the key so returns
// false
if (helper->universe_size < key) {
return false;
}
// If at any point of our traversal
// of the tree if the key is the minimum
// or the maximum of the subtree, then
// the key is present so returns true
if (helper->minimum == key || helper->maximum == key) {
return true;
}
else {
// If after attending above condition,
// if the size of the tree is 2 then
// the present key must be
// maximum or minimum of the tree if it
// is not then it returns false becuase key
// can not be present in the sub tree
if (helper->universe_size == 2) {
return false;
}
else {
// Recursive call over the cluster
// in which the key can be present
// and also pass the new position of the key
// i.e., low(key)
return isMember(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)],
helper->low(key));
}
}
}
// Function to find the successor of the given key
int VEB_successor(Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key)
{
// Base case: If key is 0 and its successor
// is present then return 1 else return null
if (helper->universe_size == 2) {
if (key == 0 && helper->maximum == 1) {
return 1;
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
// If key is less then minimum then return minimum
// because it will be successor of the key
else if (helper->minimum != -1 && key < helper->minimum) {
return helper->minimum;
}
else {
// Find successor inside the cluster of the key
// First find the maximum in the cluster
int max_incluster = VEB_maximum(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]);
int offset{ 0 }, succ_cluster{ 0 };
// If there is any key( maximum!=-1 ) present in the cluster then find
// the successor inside of the cluster
if (max_incluster != -1 && helper->low(key) < max_incluster) {
offset = VEB_successor(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)],
helper->low(key));
return helper->generate_index(helper->high(key), offset);
}
// Otherwise look for the next cluster with at least one key present
else {
succ_cluster = VEB_successor(helper->summary, helper->high(key));
// If there is no cluster with any key present
// in summary then return null
if (succ_cluster == -1) {
return -1;
}
// Find minimum in successor cluster which will
// be the successor of the key
else {
offset = VEB_minimum(helper->clusters[succ_cluster]);
return helper->generate_index(succ_cluster, offset);
}
}
}
}
// Function to find the predecessor of the given key
int VEB_predecessor(Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key)
{
// Base case: If the key is 1 and it's predecessor
// is present then return 0 else return null
if (helper->universe_size == 2) {
if (key == 1 && helper->minimum == 0) {
return 0;
}
else
return -1;
}
// If the key is greater than maximum of the tree then
// return key as it will be the predecessor of the key
else if (helper->maximum != -1 && key > helper->maximum) {
return helper->maximum;
}
else {
// Find predecessor in the cluster of the key
// First find minimum in the key to check whether any key
// is present in the cluster
int min_incluster = VEB_minimum(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]);
int offset{ 0 }, pred_cluster{ 0 };
// If any key is present in the cluster then find predecessor in
// the cluster
if (min_incluster != -1 && helper->low(key) > min_incluster) {
offset = VEB_predecessor(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)],
helper->low(key));
return helper->generate_index(helper->high(key), offset);
}
// Otherwise look for predecessor in the summary which
// returns the index of predecessor cluster with any key present
else {
pred_cluster = VEB_predecessor(helper->summary, helper->high(key));
// If no predecessor cluster then...
if (pred_cluster == -1) {
// Special case which is due to lazy propagation
if (helper->minimum != -1 && key > helper->minimum) {
return helper->minimum;
}
else
return -1;
}
// Otherwise find maximum in the predecessor cluster
else {
offset = VEB_maximum(helper->clusters[pred_cluster]);
return helper->generate_index(pred_cluster, offset);
}
}
}
}
// Function to delete a key from the tree
// assuming that the key is present
void VEB_delete(Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key)
{
// If only one key is present, it means
// that it is the key we want to delete
// Same condition as key == max && key == min
if (helper->maximum == helper->minimum) {
helper->minimum = -1;
helper->maximum = -1;
}
// Base case: If the above condition is not true
// i.e. the tree has more than two keys
// and if its size is two than a tree has exactly two keys.
// We simply delete it by assigning it to another
// present key value
else if (helper->universe_size == 2) {
if (key == 0) {
helper->minimum = 1;
}
else {
helper->minimum = 0;
}
helper->maximum = helper->minimum;
}
else {
// As we are doing something similar to lazy propagation
// we will basically find next bigger key
// and assign it as minimum
if (key == helper->minimum) {
int first_cluster = VEB_minimum(helper->summary);
key
= helper->generate_index(first_cluster,
VEB_minimum(helper->clusters[first_cluster]));
helper->minimum = key;
}
// Now we delete the key
VEB_delete(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)],
helper->low(key));
// After deleting the key, rest of the improvements
// If the minimum in the cluster of the key is -1
// then we have to delete it from the summary to
// eliminate the key completely
if (VEB_minimum(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]) == -1) {
VEB_delete(helper->summary, helper->high(key));
// After the above condition, if the key
// is maximum of the tree then...
if (key == helper->maximum) {
int max_insummary = VEB_maximum(helper->summary);
// If the max value of the summary is null
// then only one key is present so
// assign min. to max.
if (max_insummary == -1) {
helper->maximum = helper->minimum;
}
else {
// Assign global maximum of the tree, after deleting
// our query-key
helper->maximum
= helper->generate_index(max_insummary,
VEB_maximum(helper->clusters[max_insummary]));
}
}
}
// Simply find the new maximum key and
// set the maximum of the tree
// to the new maximum
else if (key == helper->maximum) {
helper->maximum
= helper->generate_index(helper->high(key),
VEB_maximum(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]));
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Van_Emde_Boas* end = new Van_Emde_Boas(8);
// Inserting Keys
insert(end, 1);
insert(end, 0);
insert(end, 2);
insert(end, 4);
// Before deletion
cout << isMember(end, 2) << endl;
cout << VEB_predecessor(end, 4) << " "
<< VEB_successor(end, 1) << endl;
// Delete only if the key is present
if (isMember(end, 2))
VEB_delete(end, 2);
// After deletion
cout << isMember(end, 2) << endl;
cout << VEB_predecessor(end, 4) << " "
<< VEB_successor(end, 1) << endl;
}
输出:
1
2 2
0
1 4