- Python中断并继续(1)
- Python中断并继续
- JavaScript |中断并继续(1)
- JavaScript |中断并继续
- 中断继续 - 无论代码示例
- 在 laravel 中中断并继续 - PHP (1)
- 在 laravel 中中断并继续 - PHP 代码示例
- 在Python中中断、继续和传递
- 在Python中中断、继续和传递(1)
- Python中的循环和控制语句(继续、中断和通过)(1)
- Python中的循环和控制语句(继续、中断和通过)
- javascript后中断循环(1)
- PowerShell继续和中断语句(1)
- PowerShell继续和中断语句
- ES6-循环
- ES6-循环(1)
- ES6 |循环
- ES6 |循环(1)
- tqdm 中断后继续 - Python (1)
- javascript代码示例后中断循环
- 如何在python中中断循环(1)
- tqdm 中断后继续 - Python 代码示例
- 如何在python代码示例中中断循环
- es6 中的循环 - Javascript (1)
- 中断输入循环 - Python (1)
- 继续 c++ (1)
- es6 中的循环 - Javascript 代码示例
- 中断(1)
- 中断(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-01 03:52:24 🧑 作者: Mango
ES6循环
编程语言中的循环语句有助于在条件评估为true时重复执行指令/功能集。循环是重复执行某些条件的理想方法。在循环中,重复称为迭代。
您可以在下图中看到循环的分类:
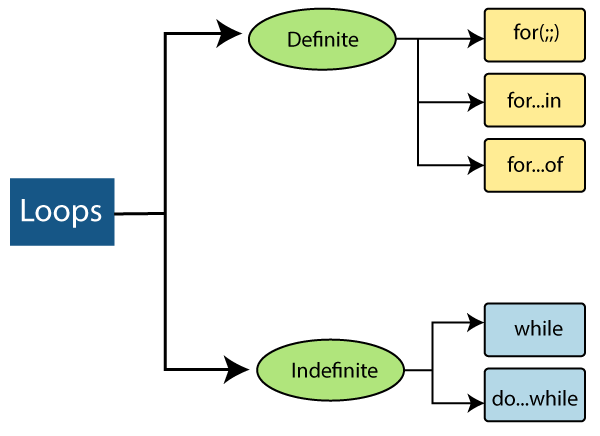
让我们尝试了解上图中的循环。
定环
确定循环具有确定/固定的迭代次数。在ES6中,下面列出了三种类型的定环:
| Definite Loop | Description |
|---|---|
| for( ; ; ) Loop | It executes the block of code for a definite number of times. |
| for…in Loop | It iterates through the properties of the object. |
| for…of loop | Unlike object literals, it iterates the iterables (arrays, string, etc.). |
让我们尝试详细说明上述循环。
for(;;)循环
for(;;)循环用于多次迭代程序的一部分。如果您有固定的迭代次数,则始终建议使用“ for”循环。
句法
for(initialization;condition;incr/decr){
//statement or code to be executed
}
“ for”循环包括一些定义如下的部分:
- 初始化:这是在循环开始时执行一次的初始条件。在这一部分中,我们将初始化变量,或者也可以将其用于已初始化的变量。这是一个可选语句。
- 条件:每次执行该循环以测试循环的条件。它继续执行循环,直到条件为假。它仅返回true或false的布尔值。这也是一个可选语句。
- 递增/递减:可以递增或递减变量的值,它也是可选语句。
- 语句:它表示循环的主体,每次在条件表达式为false之前都会执行。
流程图

例
在下面的“ for”循环的三个示例中,我们展示了简单的“ for”循环,具有多个表达式的“ for”循环和无限的“ for”循环。
- 表2通过使用for循环。
var i;
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
console.log("2 x "+ i +" =", 2*i);
}
输出量
2 x 1 = 2
2 x 2 = 4
2 x 3 = 6
2 x 4 = 8
2 x 5 = 10
2 x 6 = 12
2 x 7 = 14
2 x 8 = 16
2 x 9 = 18
2 x 10 = 20
- 具有多个表达式的for循环您可以使用逗号(,)运算符将多个赋值和最终表达式组合在单个for循环中。让我们尝试通过使用单个for循环来printFibonacci系列。
"use strict"
for(let temp, a = 0, b = 1; b<40; temp = a, a = b, b = a + temp)
console.log(b);
输出量
1
1
2
3
5
8
13
21
34
- 无限for循环的for循环无限给出如下的例子:
for(;;)
{
console.log("infinitive loop"); // It will print infinite times
}
输出量
infinite loop
infinite loop
infinite loop
infinite loop
infinite loop
infinite loop
infinite loop
infinite loop
infinite loop
infinite loop
infinite loop
infinite loop
.
.
.
.
infinite loop
要终止它,可以使用ctrl + c。
for…in循环
for…in循环类似于for循环,它循环访问对象的属性,即,当您需要访问对象的属性或键时,可以使用for…in循环。当您使用索引顺序不是必需的对象或字典时,这是一个更好的选择。
句法
for (variable_name in object_name) //Here in is the keyword
{
// statement or block to execute
}
在每次迭代中,都会将对象的一个属性分配给变量的名称,并且此循环一直进行到所有对象属性都被覆盖为止。
例
function Mobile(model_no){
this.Model = model_no;
this.Color = 'White';
this.RAM = '4GB';
}
var Samsung = new Mobile("Galaxy");
for(var props in Samsung)
{
console.log(props+ " : " +Samsung[props]);
}
输出量
Model : Galaxy
Color : White
RAM : 4GB
如果在对象的属性中传递函数,则此循环将在输出中为您提供完整的函数。您可以在以下代码中进行说明:
function Mobile(model_no){
this.Model = model_no;
this.Color = 'White';
this.RAM = '4GB';
this.Price = function price() // The loop will give you this function as it is written here.
{
console.log(this.model + "Price = Rs. 3300");
}
}
var Samsung = new Mobile("Galaxy");
for(var props in Samsung)
{
console.log(props+ " : " +Samsung[props]);
}
输出量
Model : Galaxy
Color : White
RAM : 4GB
Price : function price()
{
console.log(this.model + "Price = Rs. 3300");
}
因此,您还可以通过使用for … in循环来访问这些方法。
for…of循环
与对象字面量不同,此循环用于迭代可迭代对象(数组,字符串等)。
句法
for(variable_name of object_name) // Here of is a keyword
{
//statement or block to execute
}
在每次迭代中,将来自可迭代对象的一个属性分配给variable_name,并且循环持续到迭代结束。
例
var fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Mango', 'Orange'];
for(let value of fruits)
{
console.log(value);
}
/*
You can also write the above code like:
for(let value of ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Mango', 'Orange'])
{
console.log(value);
}
*/
输出量
Apple
Banana
Mango
Orange
不定循环
无限循环具有无限迭代。当循环内的迭代次数介于中间或未知时使用。
下面列出了两种类型的不确定循环:
| Indefinite Loops | Description |
|---|---|
| while Loop | It executes the instructions each time till the defined condition evaluates to true. |
| do…while Loop | It is similar to the while loop, but the key difference is that the do…while loop executes the loop at once irrespective of the terminator condition. |
让我们尝试详细说明上述循环。
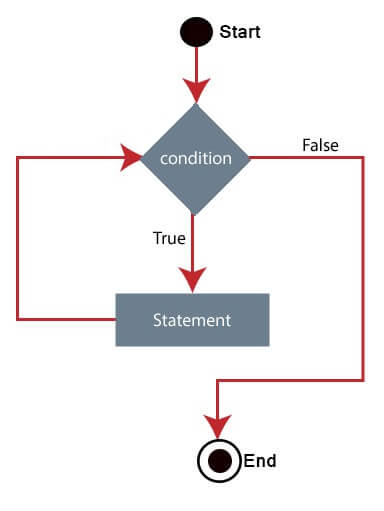
while循环
while循环是一个控制流语句,它允许根据给定的布尔条件重复执行代码。它由一个代码块和一个表达式/条件组成。
while循环在执行块之前检查表达式/条件;这就是为什么这种控制结构通常被称为预测试循环的原因。
句法
while (condition) {
statements;
}
流程图
例
var y = 0;
while (y < 4) {
console.log(y);
y++;
}
输出量
0
1
2
3
要记住的要点
- 在while循环中始终需要该条件,因为必须运行该循环。如果条件返回true,则循环将重新开始,但是如果返回false,则循环将停止。
- 如果条件始终为真,则循环永远不会结束。
do…while循环
这是一个控制流语句,至少执行一次代码块,然后将取决于条件是否循环重复执行该代码块。
do…while循环在执行完块后检查条件,这就是为什么此控制结构也称为后测试循环的原因。条件也可能总是评估为true,这将创建一个无限循环。
句法
do
{
// block of statements to be executed;
}
while (expression);
流程图

例
var count = 6, fact = 1;
do {
fact = fact * count--;
} while (count > 0);
console.log(fact);
输出量
720
如果使用while循环执行此示例,那么它将写为:
var count = 6, fact = 1;
while (count > 0)
{
fact = fact * count--;
}
console.log(fact);
输出量
720
上面两个示例之间的主要区别在于,仅当传递给条件的条件的值为真时才进入while循环。但是do … while循环只执行一次该语句,这是因为do … while循环的开始迭代不被视为布尔表达式。然后,对于进一步的迭代,while将检查条件并将控制从循环中取出。
循环控制语句
循环控制语句用于中断或控制执行流程。这些语句从正常顺序更改执行。 JavaScript为您提供了处理循环和switch语句的完整控件。
在某些情况下,您可能需要从循环中出来而不到达其底部。在某些情况下,您需要跳过部分代码并开始循环的进一步迭代。因此,为了在JavaScript中处理这种情况,我们有一个break和continue语句。
| Loop control statements | Description |
|---|---|
| The break statement | The break statement is used to bring the control of the program out from the loop. |
| The continue statement | It skips the subsequent statements of the current iteration and brings control of the program to the beginning of the loop. |
让我们尝试详细说明上述控制语句。
中断声明
它用于从循环中控制程序。您可以在循环内或switch语句中使用break语句。在循环中使用break语句会使程序退出循环。
句法
break;
例
var n = 1;
while(n<=7)
{
console.log("n="+n);
if(n==4)
{
break;
}
n++;
}
上面的代码将为1到7之间的数字范围printn的四个值。
当n的值为4时,由于break语句,循环强制控件退出循环。成功执行以上代码后,您将获得以下输出。
输出量
n=1
n=2
n=3
n=4
继续声明
与break语句不同,continue语句不会从循环中退出。它终止循环的当前迭代并开始下一个迭代。
句法
continue;
例
var n = 0;
while(n<=5)
{
n++;
if(n==3)
{
continue;
}
console.log("n = "+n);
}
上面的示例将显示n的值,但是如果n的值为3 ,它将跳过当前迭代。成功执行上述代码后,将获得以下输出。
输出量
n = 1
n = 2
n = 4
n = 5
n = 6
使用标签控制流量
标签不过是标识符,后跟冒号(:),并应用于代码块或语句。您可以使用标签休息一下,然后继续控制流程。
您不能在break and continue语句及其标签名称之间使用换行符。另外,标签名称和关联的循环之间不应有任何语句。
定义标签的语法
labelname:
Statement
labelname: JavaScript的任何标识符,不是保留字。
语句:这是一个JavaScript语句。
注意:在严格模式下,不能使用“ let”作为标签名称。因为let是保留的标识符,这将导致语法错误。
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
| Label with the break statement | It is used to exit from the loop or from the switch statement without using a label reference, but with label reference, it is used to jump out from any code block. |
| Label with continue statement | It is used to skip one iteration of the loop with or without using the label reference. |
带有break语句的标签
在不使用标签引用的情况下,可以仅使用中断从循环或从开关退出,但是在使用标签引用的情况下,可以使用中断从任何代码块跳出。
句法
break labelname;
例
var x, y;
loop1: //The first for statement is labeled as "loop1."
for (x = 1; x < 4; x++) {
loop2: //The second for statement is labelled as "loop2"
for (y = 1; y < 4; y++) {
if (x === 2 && y === 2) {
break loop1;
}
console.log('x = ' + x + ', y = ' + y);
}
}
输出量
x = 1, y = 1
x = 1, y = 2
x = 1, y = 3
x = 2, y = 1
带有继续声明的标签
continue语句仅可用于使用标签引用或不使用标签引用来跳过一个循环迭代。
句法
continue labelname;
例
var x, y;
loop1: //The first for statement is labelled as "loop1"
for (x = 1; x < 4; x++) {
loop2: //The second for statement is labelled as "loop2"
for (y = 1; y < 4; y++) {
if (x === 2 && y === 2) {
continue loop1;
}
console.log('x = ' + x + ', y = ' + y);
}
}
您可以在上述代码的以下输出中注意到,它同时跳过了“ x = 2,y = 2”和“ x = 2,y = 3”。
输出量
x = 1, y = 1
x = 1, y = 2
x = 1, y = 3
x = 2, y = 1
x = 3, y = 1
x = 3, y = 2
x = 3, y = 3
带标签的函数声明
在ECMAScript 6之前, LabeledStatement规范不允许将label语句与FunctionDeclaration关联。但是,标为FunctionDeclaration的是非严格代码中允许的扩展,并且大多数由ECMAScript浏览器托管的实现均支持该扩展。
但是在ECMAScript 2015(ES6)中, LabeledStatement的语法生成允许使用FunctionDeclaration作为LabeledItem,但是它包含一个错误规则,如果发生该错误,则会导致语法错误。
为了与Web浏览器兼容,该规则通过添加带下划线的文本进行了修改:
LabeledItem:功能声明
如果任何严格模式的源代码都匹配此规则,将导致语法错误。
从ECMAScript 2015开始,带标签的函数声明针对非严格代码进行了标准化:
L: function hello() {}
如果以严格模式编写以上代码,则将引发语法错误:
'use strict';
L: function hello() {}
// SyntaxError: In strict mode code, functions can only be declared at top level or inside a block.
不能在非严格模式或严格模式下标记生成器功能。
L: function* hello()
{
}
// SyntaxError: Generator Functions cannot be labelled