Solidity – 合约基础
Solidity Contracts 就像任何其他面向对象编程语言中的类。它们牢固地包含数据作为状态变量和可以修改这些变量的函数。当在不同的实例(合约)上调用函数时,会发生 EVM函数调用,并且上下文会以无法访问状态变量的方式切换。任何事情发生都需要调用合约或其函数。合约的一些基本属性如下:
- Constructor:使用constructor关键字创建的特殊方法,合约创建时只调用一次。
- 状态变量:这些是用于存储合约状态的变量。
- 函数:函数用于通过修改状态变量来操纵合约的状态。
创建合同
以编程方式创建合约通常是使用 JavaScript API web3.js 完成的,它有一个内置函数web3.eth.Contract来创建合约。当一个合约被创建时,它的构造函数被执行,构造函数是一个可选的特殊方法,它使用构造函数关键字定义,每个合约执行一个。一旦构造函数被调用,合约的最终代码就会被添加到区块链中。
句法:
contract {
constructor() {
.......
}
// rest code
}
示例:在下面的示例中,创建了合约 Test来演示如何在 Solidity 中创建合约。
Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// how to create a contract
pragma solidity ^0.4.23;
// Creating a contract
contract Test {
// Declaring variable
string str;
// Defining a constructor
constructor(string str_in){
str = str_in;
}
// Defining a function to
// return value of variable 'str'
function str_out(
) public view returns(string memory){
return str;
}
}Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// visibility modifiers
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract contract_example {
// Declaring private
// state variable
uint private num1;
// Declaring public
// state variable
uint public num2;
// Declaring Internal
// state variable
string internal str;
// Defining a constructor
constructor() public {
num2 = 10;
}
// Defining a private function
function increment(
uint data1) private pure returns(
uint) { return data1 + 1; }
// Defining public functions
function updateValue(
uint data1) public { num1 = data1; }
function getValue(
) public view returns(
uint) { return num1; }
// Declaring public functions
function setStr(
string memory _str) public;
function getStr(
) public returns (string memory);
}
// Child contract inheriting
// from the parent contract
// 'contract_example'
contract derived_contract is contract_example{
// Defining public function of
// parent contract
function setStr(
string memory _str) public{
str = _str;
}
// Defining public function
// of parent contract
function getStr(
) public returns (
string memory){ return str; }
}
//External Contract
contract D {
// Defining a public function to create
// an object of child contract access the
// functions from child and parent contract
function readData(
) public payable returns(
string memory, uint) {
contract_example c
= new derived_contract();
c.setStr("GeeksForGeeks");
c.updateValue(16);
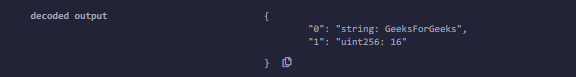
return (c.getStr(), c.getValue());
}
}输出 :
可见性修改器
Solidity 为函数和状态变量提供了四种类型的可见性。函数必须由四种可见性中的任何一种指定,但不允许使用外部状态变量。
- 外部:外部函数可以被其他合约通过交易调用。不能在内部调用外部函数。为了在合约中调用外部函数,使用this.function_name()方法。有时,当外部函数具有大量数据时,它们的效率会更高。
- 公共:公共函数或变量可以通过消息在外部或内部调用。对于公共静态变量,会在solidity中自动创建一个getter方法。
- 内部:这些函数或变量只能在内部访问,即在合约或派生合约中。
- 私有:这些函数或变量只能对定义它们的合约可见。派生合约也无法访问它们。
示例:在下面的示例中,创建了合约 contract_example以演示上面讨论的不同可见性修饰符。
坚固性
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// visibility modifiers
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract contract_example {
// Declaring private
// state variable
uint private num1;
// Declaring public
// state variable
uint public num2;
// Declaring Internal
// state variable
string internal str;
// Defining a constructor
constructor() public {
num2 = 10;
}
// Defining a private function
function increment(
uint data1) private pure returns(
uint) { return data1 + 1; }
// Defining public functions
function updateValue(
uint data1) public { num1 = data1; }
function getValue(
) public view returns(
uint) { return num1; }
// Declaring public functions
function setStr(
string memory _str) public;
function getStr(
) public returns (string memory);
}
// Child contract inheriting
// from the parent contract
// 'contract_example'
contract derived_contract is contract_example{
// Defining public function of
// parent contract
function setStr(
string memory _str) public{
str = _str;
}
// Defining public function
// of parent contract
function getStr(
) public returns (
string memory){ return str; }
}
//External Contract
contract D {
// Defining a public function to create
// an object of child contract access the
// functions from child and parent contract
function readData(
) public payable returns(
string memory, uint) {
contract_example c
= new derived_contract();
c.setStr("GeeksForGeeks");
c.updateValue(16);
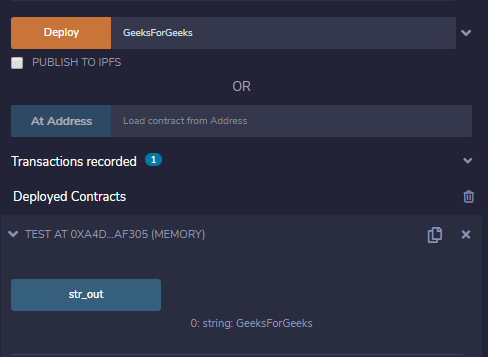
return (c.getStr(), c.getValue());
}
}
输出 :