- Apache MXNet- Python API模块
- Apache MXNet- Python API模块(1)
- Apache MXNet- Python API符号
- Apache MXNet- Python API符号(1)
- Apache MXNet- Python API ndarray
- Apache MXNet- Python API ndarray(1)
- Apache MXNet教程
- Apache MXNet教程(1)
- Apache MXNet-简介
- Apache MXNet-简介(1)
- 讨论Apache MXNet(1)
- 讨论Apache MXNet
- Apache MXNet- Python软件包(1)
- Apache MXNet- Python软件包
- Apache MXNet-统一操作员API
- Apache MXNet-统一操作员API(1)
- Apache MXNet-NDArray(1)
- Apache MXNet-NDArray
- Apache MXNet-系统组件
- Apache MXNet-系统组件(1)
- Apache MXNet-有用的资源(1)
- Apache MXNet-有用的资源
- Apache MXNet-系统架构(1)
- Apache MXNet-系统架构
- Apache MXNet-Gluon(1)
- Apache MXNet-Gluon
- Apache MXNet-分布式培训
- Apache MXNet-分布式培训(1)
- Apache MXNet-KVStore和可视化
📅 最后修改于: 2020-12-10 04:54:01 🧑 作者: Mango
正如我们在前面的章节中已经讨论的那样,MXNet Gluon为DL项目提供了清晰,简洁和简单的API。它使Apache MXNet能够原型化,构建和训练DL模型,而不会丧失训练速度。
核心模块
让我们学习Apache MXNet Python应用程序编程接口(API)gluon的核心模块。
胶
Gluon在gluon.nn模块中提供了大量内置的NN层。这就是它被称为核心模块的原因。
方法及其参数
以下是mxnet.gluon.nn核心模块涵盖的一些重要方法及其参数-
| Methods and its Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| Activation(activation, **kwargs) | As name implies, this method applies an activation function to input. |
| AvgPool1D([pool_size, strides, padding, …]) | This is average pooling operation for temporal data. |
| AvgPool2D([pool_size, strides, padding, …]) | This is average pooling operation for spatial data. |
| AvgPool3D([pool_size, strides, padding, …]) | This is Average pooling operation for 3D data. The data can be spatial or spatio-temporal. |
| BatchNorm([axis, momentum, epsilon, center, …]) | It represents batch normalisation layer. |
| BatchNormReLU([axis, momentum, epsilon, …]) | It also represents batch normalisation layer but with Relu activation function. |
| Block([prefix, params]) | It gives the base class for all neural network layers and models. |
| Conv1D(channels, kernel_size[, strides, …]) | This method is used for 1-D convolution layer. For example, temporal convolution. |
| Conv1DTranspose(channels, kernel_size[, …]) | This method is used for Transposed 1D convolution layer. |
| Conv2D(channels, kernel_size[, strides, …]) | This method is used for 2D convolution layer. For example, spatial convolution over images). |
| Conv2DTranspose(channels, kernel_size[, …]) | This method is used for Transposed 2D convolution layer. |
| Conv3D(channels, kernel_size[, strides, …]) | This method is used for 3D convolution layer. For example, spatial convolution over volumes. |
| Conv3DTranspose(channels, kernel_size[, …]) | This method is used for Transposed 3D convolution layer. |
| Dense(units[, activation, use_bias, …]) | This method represents for your regular densely-connected NN layer. |
| Dropout(rate[, axes]) | As name implies, the method applies Dropout to the input. |
| ELU([alpha]) | This method is used for Exponential Linear Unit (ELU). |
| Embedding(input_dim, output_dim[, dtype, …]) | It turns non-negative integers into dense vectors of fixed size. |
| Flatten(**kwargs) | This method flattens the input to 2-D. |
| GELU(**kwargs) | This method is used for Gaussian Exponential Linear Unit (GELU). |
| GlobalAvgPool1D([layout]) | With the help of this method, we can do global average pooling operation for temporal data. |
| GlobalAvgPool2D([layout]) | With the help of this method, we can do global average pooling operation for spatial data. |
| GlobalAvgPool3D([layout]) | With the help of this method, we can do global average pooling operation for 3-D data. |
| GlobalMaxPool1D([layout]) | With the help of this method, we can do global max pooling operation for 1-D data. |
| GlobalMaxPool2D([layout]) | With the help of this method, we can do global max pooling operation for 2-D data. |
| GlobalMaxPool3D([layout]) | With the help of this method, we can do global max pooling operation for 3-D data. |
| GroupNorm([num_groups, epsilon, center, …]) | This method applies group normalization to the n-D input array. |
| HybridBlock([prefix, params]) | This method supports forwarding with both Symbol and NDArray. |
| HybridLambda(function[, prefix]) | With the help of this method we can wrap an operator or an expression as a HybridBlock object. |
| HybridSequential([prefix, params]) | It stacks HybridBlocks sequentially. |
| InstanceNorm([axis, epsilon, center, scale, …]) | This method applies instance normalisation to the n-D input array. |
实施实例
在下面的示例中,我们将使用Block(),它提供了所有神经网络层和模型的基类。
from mxnet.gluon import Block, nn
class Model(Block):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Model, self).__init__(**kwargs)
# use name_scope to give child Blocks appropriate names.
with self.name_scope():
self.dense0 = nn.Dense(20)
self.dense1 = nn.Dense(20)
def forward(self, x):
x = mx.nd.relu(self.dense0(x))
return mx.nd.relu(self.dense1(x))
model = Model()
model.initialize(ctx=mx.cpu(0))
model(mx.nd.zeros((5, 5), ctx=mx.cpu(0)))
输出
您将看到以下输出-
[[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
在下面的示例中,我们将使用HybridBlock()来支持Symbol和NDArray的转发。
import mxnet as mx
from mxnet.gluon import HybridBlock, nn
class Model(HybridBlock):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Model, self).__init__(**kwargs)
# use name_scope to give child Blocks appropriate names.
with self.name_scope():
self.dense0 = nn.Dense(20)
self.dense1 = nn.Dense(20)
def forward(self, x):
x = nd.relu(self.dense0(x))
return nd.relu(self.dense1(x))
model = Model()
model.initialize(ctx=mx.cpu(0))
model.hybridize()
model(mx.nd.zeros((5, 5), ctx=mx.cpu(0)))
输出
输出在下面提到-
[[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
胶体
Gluon在gluon.rnn模块中提供了大量内置的递归神经网络(RNN)层。这就是原因,它被称为核心模块。
方法及其参数
以下是mxnet.gluon.nn核心模块涵盖的一些重要方法及其参数:
| Methods and its Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| BidirectionalCell(l_cell, r_cell[, …]) | It is used for Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) cell. |
| DropoutCell(rate[, axes, prefix, params]) | This method will apply dropout on the given input. |
| GRU(hidden_size[, num_layers, layout, …]) | It applies a multi-layer gated recurrent unit (GRU) RNN to a given input sequence. |
| GRUCell(hidden_size[, …]) | It is used for Gated Rectified Unit (GRU) network cell. |
| HybridRecurrentCell([prefix, params]) | This method supports hybridize. |
| HybridSequentialRNNCell([prefix, params]) | With the help of this method we can sequentially stack multiple HybridRNN cells. |
| LSTM(hidden_size[, num_layers, layout, …])0 | It applies a multi-layer long short-term memory (LSTM) RNN to a given input sequence. |
| LSTMCell(hidden_size[, …]) | It is used for Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) network cell. |
| ModifierCell(base_cell) | It is the Base class for modifier cells. |
| RNN(hidden_size[, num_layers, activation, …]) | It applies a multi-layer Elman RNN with tanh or ReLU non-linearity to a given input sequence. |
| RNNCell(hidden_size[, activation, …]) | It is used for Elman RNN recurrent neural network cell. |
| RecurrentCell([prefix, params]) | It represents the abstract base class for RNN cells. |
| SequentialRNNCell([prefix, params]) | With the help of this method we can sequentially stack multiple RNN cells. |
| ZoneoutCell(base_cell[, zoneout_outputs, …]) | This method applies Zoneout on the base cell. |
实施实例
在下面的示例中,我们将使用GRU()将多层门控循环单元(GRU)RNN应用于给定的输入序列。
layer = mx.gluon.rnn.GRU(100, 3)
layer.initialize()
input_seq = mx.nd.random.uniform(shape=(5, 3, 10))
out_seq = layer(input_seq)
h0 = mx.nd.random.uniform(shape=(3, 3, 100))
out_seq, hn = layer(input_seq, h0)
out_seq
输出
这产生以下输出-
[[[ 1.50152072e-01 5.19012511e-01 1.02390535e-01 ... 4.35803324e-01
1.30406499e-01 3.30152437e-02]
[ 2.91542172e-01 1.02243155e-01 1.73325196e-01 ... 5.65296151e-02
1.76546033e-02 1.66693389e-01]
[ 2.22257316e-01 3.76294643e-01 2.11277917e-01 ... 2.28903517e-01
3.43954474e-01 1.52770668e-01]]
[[ 1.40634328e-01 2.93247789e-01 5.50393537e-02 ... 2.30207980e-01
6.61415309e-02 2.70989928e-02]
[ 1.11081995e-01 7.20834285e-02 1.08342394e-01 ... 2.28330195e-02
6.79589901e-03 1.25501186e-01]
[ 1.15944080e-01 2.41565228e-01 1.18612610e-01 ... 1.14908054e-01
1.61080107e-01 1.15969211e-01]]
………………………….
例
hn
输出
这产生以下输出-
[[[-6.08105101e-02 3.86217088e-02 6.64453954e-03 8.18805695e-02
3.85607071e-02 -1.36945639e-02 7.45836645e-03 -5.46515081e-03
9.49622393e-02 6.39371723e-02 -6.37890724e-03 3.82240303e-02
9.11015049e-02 -2.01375950e-02 -7.29381144e-02 6.93765879e-02
2.71829776e-02 -6.64435029e-02 -8.45306814e-02 -1.03075653e-01
6.72040805e-02 -7.06537142e-02 -3.93818803e-02 5.16211614e-03
-4.79770005e-02 1.10734522e-01 1.56721435e-02 -6.93409378e-03
1.16915874e-01 -7.95962065e-02 -3.06530762e-02 8.42394680e-02
7.60370195e-02 2.17055440e-01 9.85361822e-03 1.16660878e-01
4.08297703e-02 1.24978097e-02 8.25245082e-02 2.28673983e-02
-7.88266212e-02 -8.04114193e-02 9.28791538e-02 -5.70827350e-03
-4.46166918e-02 -6.41122833e-02 1.80885363e-02 -2.37745279e-03
4.37298454e-02 1.28888980e-01 -3.07202265e-02 2.50503756e-02
4.00907174e-02 3.37077095e-03 -1.78839862e-02 8.90695080e-02
6.30150884e-02 1.11416787e-01 2.12221760e-02 -1.13236710e-01
5.39616570e-02 7.80710578e-02 -2.28817668e-02 1.92073174e-02
………………………….
在下面的示例中,我们将使用LSTM()将LSTM(长期短期记忆)RNN应用于给定的输入序列。
layer = mx.gluon.rnn.LSTM(100, 3)
layer.initialize()
input_seq = mx.nd.random.uniform(shape=(5, 3, 10))
out_seq = layer(input_seq)
h0 = mx.nd.random.uniform(shape=(3, 3, 100))
c0 = mx.nd.random.uniform(shape=(3, 3, 100))
out_seq, hn = layer(input_seq,[h0,c0])
out_seq
输出
输出在下面提到-
[[[ 9.00025964e-02 3.96071747e-02 1.83841765e-01 ... 3.95872220e-02
1.25569820e-01 2.15555862e-01]
[ 1.55962542e-01 -3.10300849e-02 1.76772922e-01 ... 1.92474753e-01
2.30574399e-01 2.81707942e-02]
[ 7.83204585e-02 6.53361529e-03 1.27262697e-01 ... 9.97719541e-02
1.28254429e-01 7.55299702e-02]]
[[ 4.41036932e-02 1.35250352e-02 9.87644792e-02 ... 5.89378644e-03
5.23949116e-02 1.00922674e-01]
[ 8.59075040e-02 -1.67027581e-02 9.69351009e-02 ... 1.17763653e-01
9.71239135e-02 2.25218050e-02]
[ 4.34580036e-02 7.62207608e-04 6.37005866e-02 ... 6.14888743e-02
5.96345589e-02 4.72368896e-02]]
……………
例
hn
输出
运行代码时,您将看到以下输出-
[
[[[ 2.21408084e-02 1.42750628e-02 9.53067932e-03 -1.22849066e-02
1.78788435e-02 5.99269159e-02 5.65306023e-02 6.42553642e-02
6.56616641e-03 9.80876666e-03 -1.15729487e-02 5.98640442e-02
-7.21173314e-03 -2.78371759e-02 -1.90690923e-02 2.21447181e-02
8.38765781e-03 -1.38521893e-02 -9.06938594e-03 1.21346042e-02
6.06449470e-02 -3.77471633e-02 5.65885007e-02 6.63008019e-02
-7.34188128e-03 6.46054149e-02 3.19911093e-02 4.11194898e-02
4.43960279e-02 4.92892228e-02 1.74766723e-02 3.40303481e-02
-5.23341820e-03 2.68163737e-02 -9.43402853e-03 -4.11836170e-02
1.55221792e-02 -5.05655073e-02 4.24557598e-03 -3.40388380e-02
……………………
培训模块
Gluon的培训模块如下-
胶子损失
在mxnet.gluon.loss模块中, Gluon提供了预定义的损失函数。基本上,它具有训练神经网络的损失。这就是它被称为训练模块的原因。
方法及其参数
以下是mxnet.gluon.loss培训模块涵盖的一些重要方法及其参数:
| Methods and its Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| Loss(weight, batch_axis, **kwargs) | This acts as the base class for loss. |
| L2Loss([weight, batch_axis]) | It calculates the mean squared error (MSE) between label and prediction(pred). |
| L1Loss([weight, batch_axis]) | It calculates the mean absolute error (MAE) between label and pred. |
| SigmoidBinaryCrossEntropyLoss([…]) | This method is used for the cross-entropy loss for binary classification. |
| SigmoidBCELoss | This method is used for the cross-entropy loss for binary classification. |
| SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss([axis, …]) | It computes the softmax cross-entropy loss (CEL). |
| SoftmaxCELoss | It also computes the softmax cross entropy loss. |
| KLDivLoss([from_logits, axis, weight, …]) | It is used for the Kullback-Leibler divergence loss. |
| CTCLoss([layout, label_layout, weight]) | It is used for connectionist Temporal Classification Loss (TCL). |
| HuberLoss([rho, weight, batch_axis]) | It calculates smoothed L1 loss. The smoothed L1 loss will be equal to L1 loss if absolute error exceeds rho but is equal to L2 loss otherwise. |
| HingeLoss([margin, weight, batch_axis]) | This method calculates the hinge loss function often used in SVMs: |
| SquaredHingeLoss([margin, weight, batch_axis]) | This method calculates the soft-margin loss function used in SVMs: |
| LogisticLoss([weight, batch_axis, label_format]) | This method calculates the logistic loss. |
| TripletLoss([margin, weight, batch_axis]) | This method calculates triplet loss given three input tensors and a positive margin. |
| PoissonNLLLoss([weight, from_logits, …]) | The function calculates the Negative Log likelihood loss. |
| CosineEmbeddingLoss([weight, batch_axis, margin]) | The function computes the cosine distance between the vectors. |
| SDMLLoss([smoothing_parameter, weight, …]) | This method calculates Batchwise Smoothed Deep Metric Learning (SDML) Loss given two input tensors and a smoothing weight SDM Loss. It learns similarity between paired samples by using unpaired samples in the minibatch as potential negative examples. |
例
众所周知, mxnet.gluon.loss.loss将计算标签和预测(预测)之间的MSE(均方误差)。它是通过以下公式来完成的:
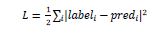
胶子参数
mxnet.gluon.parameter是一个保存参数的容器,即块的权重。
方法及其参数
以下是mxnet.gluon.parameter训练模块涵盖的一些重要方法及其参数-
| Methods and its Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| cast(dtype) | This method will cast data and gradient of this Parameter to a new data type. |
| data([ctx]) | This method will return a copy of this parameter on one context. |
| grad([ctx]) | This method will return a gradient buffer for this parameter on one context. |
| initialize([init, ctx, default_init, …]) | This method will initialize parameter and gradient arrays. |
| list_ctx() | This method will return a list of contexts this parameter is initialized on. |
| list_data() | This method will return copies of this parameter on all contexts. It will be done in the same order as creation. |
| list_grad() | This method will return gradient buffers on all contexts. This will be done in the same order as values(). |
| list_row_sparse_data(row_id) | This method will return copies of the ‘row_sparse’ parameter on all contexts. This will be done in the same order as creation. |
| reset_ctx(ctx) | This method will re-assign Parameter to other contexts. |
| row_sparse_data(row_id) | This method will return a copy of the ‘row_sparse’ parameter on the same context as row_id’s. |
| set_data(data) | This method will set this parameter’s value on all contexts. |
| var() | This method will return a symbol representing this parameter. |
| zero_grad() | This method will set the gradient buffer on all contexts to 0. |
实施实例
在下面的示例中,我们将使用initialize()方法初始化参数和渐变数组,如下所示:
weight = mx.gluon.Parameter('weight', shape=(2, 2))
weight.initialize(ctx=mx.cpu(0))
weight.data()
输出
输出在下面提到-
[[-0.0256899 0.06511251]
[-0.00243821 -0.00123186]]
例
weight.grad()
输出
输出如下-
[[0. 0.]
[0. 0.]]
例
weight.initialize(ctx=[mx.gpu(0), mx.gpu(1)])
weight.data(mx.gpu(0))
输出
您将看到以下输出-
[[-0.00873779 -0.02834515]
[ 0.05484822 -0.06206018]]
例
weight.data(mx.gpu(1))
输出
当执行上述代码时,您应该看到以下输出-
[[-0.00873779 -0.02834515]
[ 0.05484822 -0.06206018]]
胶子培训师
mxnet.gluon.trainer将优化器应用于一组参数。它应与autograd一起使用。
方法及其参数
以下是mxnet.gluon.trainer训练模块涵盖的一些重要方法及其参数-
| Methods and its Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| allreduce_grads() | This method will reduce the gradients from different contexts for each parameter (weight). |
| load_states(fname) | As name implies, this method will load trainer states. |
| save_states(fname) | As name implies, this method will save trainer states. |
| set_learning_rate(lr) | This method will set a new learning rate of the optimizer. |
| step(batch_size[, ignore_stale_grad]) | This method will make one step of parameter update. It should be called after autograd.backward() and outside of record() scope. |
| update(batch_size[, ignore_stale_grad]) | This method will also make one step of parameter update. It should be called after autograd.backward() and outside of record() scope and after trainer.update(). |
数据模块
下面解释了Gluon的数据模块-
胶子数据
Gluon在gluon.data模块中提供了大量内置数据集实用程序。这就是它被称为数据模块的原因。
类及其参数
以下是mxnet.gluon.data核心模块涵盖的一些重要方法及其参数。这些方法通常与数据集,采样和数据加载器有关。
| Methods and its Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| ArrayDataset(*args) | This method represents a dataset which combines two or more than two dataset-like objects. For example, Datasets, lists, arrays, etc. |
| BatchSampler(sampler, batch_size[, last_batch]) | This method wraps over another Sampler. Once wrapped it returns the mini batches of samples. |
| DataLoader(dataset[, batch_size, shuffle, …]) | Similar to BatchSampler but this method loads data from a dataset. Once loaded it returns the mini batches of data. |
| This represents the abstract dataset class. | |
| FilterSampler(fn, dataset) | This method represents the samples elements from a Dataset for which fn (function) returns True. |
| RandomSampler(length) | This method represents samples elements from [0, length) randomly without replacement. |
| RecordFileDataset(filename) | It represents a dataset wrapping over a RecordIO file. The extension of the file is .rec. |
| Sampler | This is the base class for samplers. |
| SequentialSampler(length[, start]) | It represents the sample elements from the set [start, start+length) sequentially. |
| It represents the sample elements from the set [start, start+length) sequentially. | This represents the simple Dataset wrapper especially for lists and arrays. |
实施实例
在下面的示例中,我们将使用gluon.data.BatchSampler() API,该API包装了另一个采样器。它返回小批样品。
import mxnet as mx
from mxnet.gluon import data
sampler = mx.gluon.data.SequentialSampler(15)
batch_sampler = mx.gluon.data.BatchSampler(sampler, 4, 'keep')
list(batch_sampler)
输出
输出在下面提到-
[[0, 1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6, 7], [8, 9, 10, 11], [12, 13, 14]]
gluon.data.vision.datasets
Gluon在gluon.data.vision.datasets模块中提供了大量预定义的视觉数据集功能。
类及其参数
MXNet为我们提供了有用且重要的数据集,其类和参数如下所示-
| Classes and its Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| MNIST([root, train, transform]) | This is a useful dataset providing us the handwritten digits. The url for MNIST dataset is http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist |
| FashionMNIST([root, train, transform]) | This dataset consists of Zalando’s article images consisting of fashion products. It is a drop-in replacement of original MNIST dataset. You can get this dataset from https://github.com/zalandoresearch/fashion-mnist |
| CIFAR10([root, train, transform]) | This is an image classification dataset from https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html. In this dataset each sample is an image with shape (32, 32, 3). |
| CIFAR100([root, fine_label, train, transform]) | This is CIFAR100 image classification dataset from https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html. It also has each sample is an image with shape (32, 32, 3). |
| ImageRecordDataset (filename[, flag, transform]) | This dataset is wrapping over a RecordIO file that contains images. In this each sample is an image with its corresponding label. |
| ImageFolderDataset (root[, flag, transform]) |
This is a dataset for loading image files that are stored in a folder structure. |
| ImageListDataset ([root, imglist, flag]) |
This is a dataset for loading image files that are specified by a list of entries. |
例
在下面的示例中,我们将展示ImageListDataset()的用法,该方法用于加载由条目列表指定的图像文件-
# written to text file *.lst
0 0 root/cat/0001.jpg
1 0 root/cat/xxxa.jpg
2 0 root/cat/yyyb.jpg
3 1 root/dog/123.jpg
4 1 root/dog/023.jpg
5 1 root/dog/wwww.jpg
# A pure list, each item is a list [imagelabel: float or list of float, imgpath]
[[0, root/cat/0001.jpg]
[0, root/cat/xxxa.jpg]
[0, root/cat/yyyb.jpg]
[1, root/dog/123.jpg]
[1, root/dog/023.jpg]
[1, root/dog/wwww.jpg]]
实用模块
Gluon中的实用程序模块如下-
gluon.utils
Gluon在gluon.utils模块中提供了大量内置的并行化实用程序优化器。它提供各种实用程序进行培训。这就是它被称为实用程序模块的原因。
功能及其参数
以下是此名为gluon.utils的实用程序模块中包含的函数及其参数–
| Functions and its Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| split_data(data, num_slice[, batch_axis, …]) | This function is usually use for data parallelism and each slice is sent to one device i.e. GPU. It splits an NDArray into num_slice slices along batch_axis. |
| split_and_load(data, ctx_list[, batch_axis, …]) | This function splits an NDArray into len(ctx_list) slices along batch_axis. The only difference from above split_data () function is that, it also loads each slice to one context in ctx_list. |
| clip_global_norm(arrays, max_norm[, …]) | The job of this function is to rescale NDArrays in such a way that the sum of their 2-norm is smaller than max_norm. |
| check_sha1(filename, sha1_hash) | This function will check whether the sha1 hash of the file content matches the expected hash or not. |
| download(url[, path, overwrite, sha1_hash, …]) | As name specifies, this function will download a given URL. |
| replace_file(src, dst) | This function will implement atomic os.replace. it will be done with Linux and OSX. |