- 连续系统与离散系统
- 仿真与仿真之间的区别
- 仿真与仿真之间的区别
- 仿真与仿真之间的区别(1)
- 仿真与仿真之间的区别(1)
- 仿真与模拟的区别(1)
- 仿真与模拟的区别
- ElectronJS 中的仿真
- ElectronJS 中的仿真(1)
- ElectronJS 中的仿真
- ElectronJS 中的仿真(1)
- 虚拟化和仿真的区别
- 虚拟化和仿真的区别(1)
- 建模与仿真-数据库(1)
- 建模与仿真-数据库
- 建模与仿真教程(1)
- 建模与仿真教程
- 建模与仿真-简介(1)
- 建模与仿真-简介
- 建模与仿真-连续
- 建模与仿真-连续(1)
- 讨论建模与仿真
- Python仿真建模简介
- Python仿真建模简介(1)
- 建模与仿真-有用的资源
- HMD 运动仿真 - C# (1)
- HMD 运动仿真 - C# 代码示例
- 多重仿真的统一控制物理 - C# (1)
- 多重仿真的统一控制物理 - C# 代码示例
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-23 04:14:39 🧑 作者: Mango
在离散系统中,系统状态的变化是不连续的,并且系统状态的每个变化都称为事件。离散系统仿真中使用的模型具有一组代表系统状态的数字,称为状态描述符。在本章中,我们还将学习排队仿真,这是离散事件仿真以及分时系统仿真中非常重要的方面。
以下是离散系统仿真行为的图形表示。
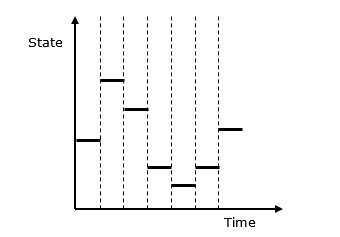
离散事件模拟─关键特征
离散事件模拟通常由以高级编程语言(例如Pascal,C++或任何专门的模拟语言)设计的软件执行。以下是五个关键功能-
-
实体-这些是诸如机器零件之类的真实元素的表示。
-
关系-意味着将实体链接在一起。
-
Simulation Executive-它负责控制提前时间和执行离散事件。
-
随机数发生器-它有助于模拟进入模拟模型的不同数据。
-
结果和统计信息-验证模型并提供性能指标。
时间图表示
每个系统都取决于时间参数。在图形表示中,它称为时钟时间或时间计数器,最初设置为零。时间基于以下两个因素进行更新-
-
时间分片-这是模型为每个事件定义的时间,直到不存在任何事件为止。
-
下一个事件-这是模型为下一个要执行的事件而不是时间间隔定义的事件。它比时间分片更有效。
排队系统的仿真
队列是系统中正在服务的所有实体与等待轮到的实体的组合。
参量
以下是排队系统中使用的参数列表。
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| λ | Denotes the arrival rate which is the number of arrivals per second |
| Ts | Denotes the mean service time for each arrival excluding the waiting time in the queue |
| σTs | Denotes the standard deviation of service time |
| ρ | Denotes the server time utilization, both when it was idle and busy |
| u | Denotes traffic intensity |
| r | Denotes the mean of items in the system |
| R | Denotes the total number of items in the system |
| Tr | Denotes the mean time of an item in the system |
| TR | Denotes the total time of an item in the system |
| σr | Denotes the standard deviation of r |
| σTr | Denotes the standard deviation of Tr |
| w | Denotes the mean number of items waiting in the queue |
| σw | Denotes the standard deviation of w |
| Tw | Denotes the mean waiting time of all items |
| Td | Denotes the mean waiting time of the items waiting in the queue |
| N | Denotes the number of servers in a system |
| mx(y) | Denotes the yth percentile which means the value of y below which x occurs y percent of the time |
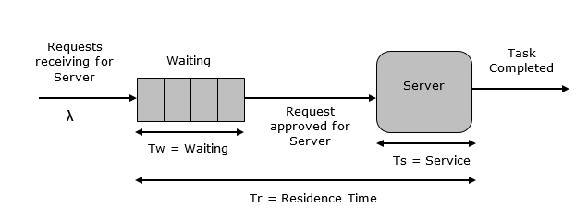
单服务器队列
如下图所示,这是最简单的排队系统。系统的中心元素是服务器,它为连接的设备或项目提供服务。如果服务器空闲,则项目请求向系统提供服务。然后,将立即为其提供服务,否则它将加入等待队列。服务器完成任务后,项目离开。
多服务器队列
顾名思义,该系统由多个服务器和一个用于所有项目的公共队列组成。当有任何项目请求服务器时,如果至少有一个服务器可用,则会对其进行分配。否则,队列开始开始,直到服务器空闲为止。在此系统中,我们假设所有服务器都是相同的,即为哪个项目选择了哪个服务器没有差异。
利用率是一个例外。假设N是相同的服务器,则ρ是每个服务器的利用率。将Nρ视为整个系统的利用率;那么最大利用率为N * 100% ,最大输入率为-
$λmax= \ frac {\ text {N}} {\ text {T} s} $

排队关系
下表显示了一些基本排队关系。
| General Terms | Single Server | Multi server |
|---|---|---|
| r = λTr Little’s formula | ρ = λTs | ρ = λTs/N |
| w = λTw Little’s formula | r = w + ρ | u = λTs = ρN |
| Tr = Tw + Ts | r = w + Nρ |
分时系统的仿真
分时系统的设计方式是,每个用户使用系统上共享的一小部分时间,从而导致多个用户同时共享系统。每个用户的切换速度如此之快,以至于每个用户都喜欢使用自己的系统。它基于CPU调度和多重编程的概念,通过在系统上同时执行多个作业,可以有效利用多种资源。
示例-SimOS仿真系统。
它是由斯坦福大学设计的,用于研究复杂的计算机硬件设计,分析应用程序性能以及研究操作系统。 SimOS包含对现代计算机系统的所有硬件组件的软件仿真,例如处理器,内存管理单元(MMU),高速缓存等。