反向树路径
给定一棵树和节点数据,任务是反转到该特定节点的路径。
例子:
Input:
7
/ \
6 5
/ \ / \
4 3 2 1
Data = 4
Output: Inorder of tree
7 6 3 4 2 5 1
Input:
7
/ \
6 5
/ \ / \
4 3 2 1
Data = 2
Output : Inorder of tree
4 6 3 2 7 5 1这个想法是使用地图来明智地存储路径级别。
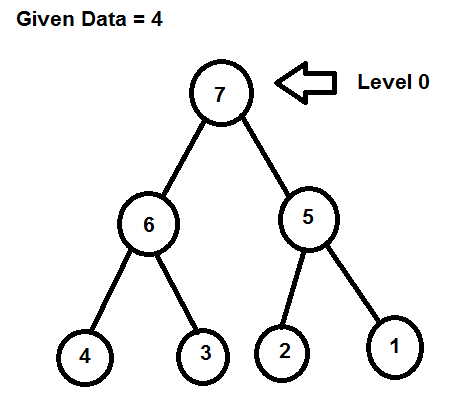
找到节点路径并将其存储在地图中
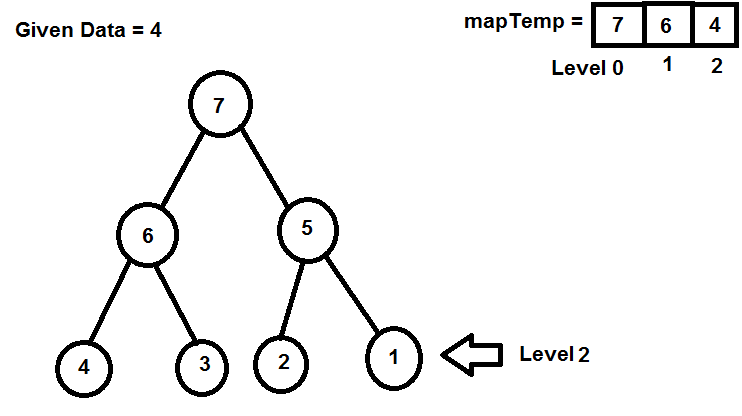
路径是
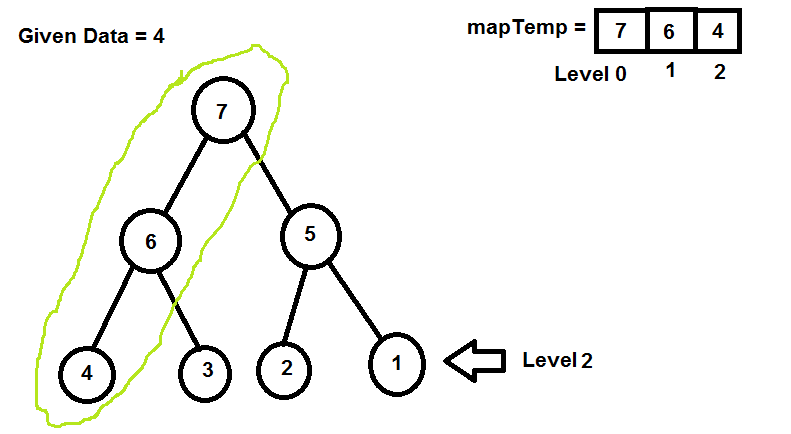
用地图 nextPos 索引值替换位置
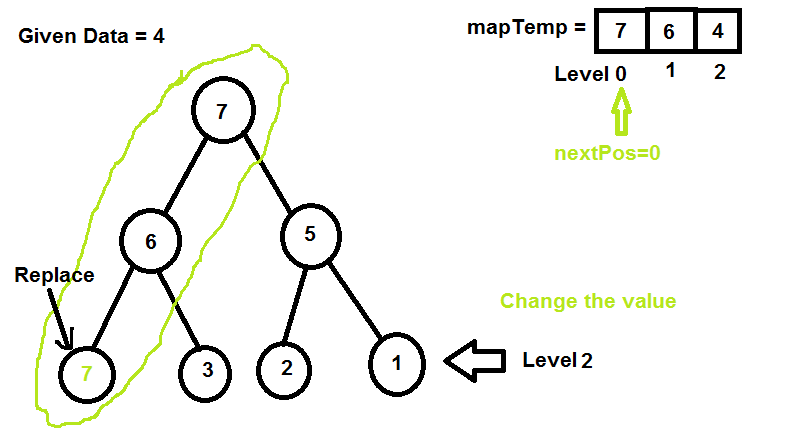
增加 nextpos 索引并替换下一个值

增加 nextpos 索引并替换下一个值
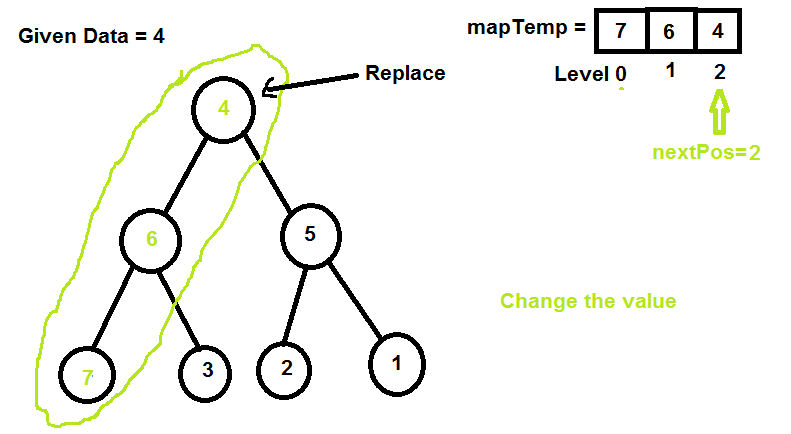
让我们理解代码:
C++
// C++ program to Reverse Tree path
#include
using namespace std;
// A Binary Tree Node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// 'data' is input. We need to reverse path from
// root to data.
// 'level' is current level.
// 'temp' that stores path nodes.
// 'nextpos' used to pick next item for reversing.
Node* reverseTreePathUtil(Node* root, int data,
map& temp, int level, int& nextpos)
{
// return NULL if root NULL
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
// Final condition
// if the node is found then
if (data == root->data) {
// store the value in it's level
temp[level] = root->data;
// change the root value with the current
// next element of the map
root->data = temp[nextpos];
// increment in k for the next element
nextpos++;
return root;
}
// store the data in particular level
temp[level] = root->data;
// We go to right only when left does not
// contain given data. This way we make sure
// that correct path node is stored in temp[]
Node *left, *right;
left = reverseTreePathUtil(root->left, data, temp,
level + 1, nextpos);
if (left == NULL)
right = reverseTreePathUtil(root->right, data,
temp, level + 1, nextpos);
// If current node is part of the path,
// then do reversing.
if (left || right) {
root->data = temp[nextpos];
nextpos++;
return (left ? left : right);
}
// return NULL if not element found
return NULL;
}
// Reverse Tree path
void reverseTreePath(Node* root, int data)
{
// store per level data
map temp;
// it is for replacing the data
int nextpos = 0;
// reverse tree path
reverseTreePathUtil(root, data, temp, 0, nextpos);
}
// INORDER
void inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root != NULL) {
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->data << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
}
// Utility function to create a new tree node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us create binary tree shown in above diagram
Node* root = newNode(7);
root->left = newNode(6);
root->right = newNode(5);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(3);
root->right->left = newNode(2);
root->right->right = newNode(1);
/* 7
/ \
6 5
/ \ / \
4 3 2 1 */
int data = 4;
// Reverse Tree Path
reverseTreePath(root, data);
// Traverse inorder
inorder(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to Reverse Tree path
import java.util.*;
class solution
{
// A Binary Tree Node
static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
};
//class for int values
static class INT {
int data;
};
// 'data' is input. We need to reverse path from
// root to data.
// 'level' is current level.
// 'temp' that stores path nodes.
// 'nextpos' used to pick next item for reversing.
static Node reverseTreePathUtil(Node root, int data,
Map temp, int level, INT nextpos)
{
// return null if root null
if (root == null)
return null;
// Final condition
// if the node is found then
if (data == root.data) {
// store the value in it's level
temp.put(level,root.data);
// change the root value with the current
// next element of the map
root.data = temp.get(nextpos.data);
// increment in k for the next element
nextpos.data++;
return root;
}
// store the data in particular level
temp.put(level,root.data);
// We go to right only when left does not
// contain given data. This way we make sure
// that correct path node is stored in temp[]
Node left, right=null;
left = reverseTreePathUtil(root.left, data, temp,
level + 1, nextpos);
if (left == null)
right = reverseTreePathUtil(root.right, data,
temp, level + 1, nextpos);
// If current node is part of the path,
// then do reversing.
if (left!=null || right!=null) {
root.data = temp.get(nextpos.data);
nextpos.data++;
return (left!=null ? left : right);
}
// return null if not element found
return null;
}
// Reverse Tree path
static void reverseTreePath(Node root, int data)
{
// store per level data
Map< Integer, Integer> temp= new HashMap< Integer, Integer>();
// it is for replacing the data
INT nextpos=new INT();
nextpos.data = 0;
// reverse tree path
reverseTreePathUtil(root, data, temp, 0, nextpos);
}
// INORDER
static void inorder(Node root)
{
if (root != null) {
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print( root.data + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
}
// Utility function to create a new tree node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Let us create binary tree shown in above diagram
Node root = newNode(7);
root.left = newNode(6);
root.right = newNode(5);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(3);
root.right.left = newNode(2);
root.right.right = newNode(1);
/* 7
/ \
6 5
/ \ / \
4 3 2 1 */
int data = 4;
// Reverse Tree Path
reverseTreePath(root, data);
// Traverse inorder
inorder(root);
}
}
//contributed by Arnab Kundu Python3
# Python3 program to Reverse Tree path
# A Binary Tree Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# 'data' is input. We need to reverse path from
# root to data.
# 'level' is current level.
# 'temp' that stores path nodes.
# 'nextpos' used to pick next item for reversing.
def reverseTreePathUtil(root, data,temp, level, nextpos):
# return None if root None
if (root == None):
return None, temp, nextpos;
# Final condition
# if the node is found then
if (data == root.data):
# store the value in it's level
temp[level] = root.data;
# change the root value with the current
# next element of the map
root.data = temp[nextpos];
# increment in k for the next element
nextpos += 1
return root, temp, nextpos;
# store the data in particular level
temp[level] = root.data;
# We go to right only when left does not
# contain given data. This way we make sure
# that correct path node is stored in temp[]
right = None
left, temp, nextpos = reverseTreePathUtil(root.left, data, temp,
level + 1, nextpos);
if (left == None):
right, temp, nextpos = reverseTreePathUtil(root.right, data,
temp, level + 1, nextpos);
# If current node is part of the path,
# then do reversing.
if (left or right):
root.data = temp[nextpos];
nextpos += 1
return (left if left != None else right), temp, nextpos;
# return None if not element found
return None, temp, nextpos;
# Reverse Tree path
def reverseTreePath(root, data):
# store per level data
temp = dict()
# it is for replacing the data
nextpos = 0;
# reverse tree path
reverseTreePathUtil(root, data, temp, 0, nextpos);
# INORDER
def inorder(root):
if (root != None):
inorder(root.left);
print(root.data, end = ' ')
inorder(root.right);
# Utility function to create a new tree node
def newNode(data):
temp = Node(data)
return temp;
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Let us create binary tree shown in above diagram
root = newNode(7);
root.left = newNode(6);
root.right = newNode(5);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(3);
root.right.left = newNode(2);
root.right.right = newNode(1);
''' 7
/ \
6 5
/ \ / \
4 3 2 1 '''
data = 4;
# Reverse Tree Path
reverseTreePath(root, data);
# Traverse inorder
inorder(root);
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56.C#
// C# program to Reverse Tree path
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// A Binary Tree Node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
}
//class for int values
public class INT
{
public int data;
}
// 'data' is input. We need to reverse
// path from root to data.
// 'level' is current level.
// 'temp' that stores path nodes.
// 'nextpos' used to pick next item for reversing.
public static Node reverseTreePathUtil(Node root, int data,
IDictionary temp,
int level, INT nextpos)
{
// return null if root null
if (root == null)
{
return null;
}
// Final condition
// if the node is found then
if (data == root.data)
{
// store the value in it's level
temp[level] = root.data;
// change the root value with the
// current next element of the map
root.data = temp[nextpos.data];
// increment in k for the next element
nextpos.data++;
return root;
}
// store the data in particular level
temp[level] = root.data;
// We go to right only when left does not
// contain given data. This way we make sure
// that correct path node is stored in temp[]
Node left, right = null;
left = reverseTreePathUtil(root.left, data, temp,
level + 1, nextpos);
if (left == null)
{
right = reverseTreePathUtil(root.right, data, temp,
level + 1, nextpos);
}
// If current node is part of the path,
// then do reversing.
if (left != null || right != null)
{
root.data = temp[nextpos.data];
nextpos.data++;
return (left != null ? left : right);
}
// return null if not element found
return null;
}
// Reverse Tree path
public static void reverseTreePath(Node root,
int data)
{
// store per level data
IDictionary temp = new Dictionary();
// it is for replacing the data
INT nextpos = new INT();
nextpos.data = 0;
// reverse tree path
reverseTreePathUtil(root, data,
temp, 0, nextpos);
}
// INORDER
public static void inorder(Node root)
{
if (root != null)
{
inorder(root.left);
Console.Write(root.data + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
}
// Utility function to create
// a new tree node
public static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Let us create binary tree
// shown in above diagram
Node root = newNode(7);
root.left = newNode(6);
root.right = newNode(5);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(3);
root.right.left = newNode(2);
root.right.right = newNode(1);
/* 7
/ \
6 5
/ \ / \
4 3 2 1 */
int data = 4;
// Reverse Tree Path
reverseTreePath(root, data);
// Traverse inorder
inorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13 Javascript
C++
// CPP program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
#define nl "\n"
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int value) { data = value; }
};
// Function to print inorder
// traversal of the tree
void inorder(Node* temp)
{
if (temp == NULL)
return;
inorder(temp->left);
cout << temp->data << " ";
inorder(temp->right);
}
// Utility function to track
// root to leaf paths
void reverseTreePathUtil(Node* root, vector path,
int pathLen, int key)
{
// Check if root is null then return
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Store the node in path array
path[pathLen] = root;
pathLen++;
// Check if we find the node upto
// which path needs to be
// reversed
if (root->data == key) {
// Current path array contains
// the path which needs
// to be reversed
int i = 0, j = pathLen - 1;
// Swap the data of two nodes
while (i < j) {
int temp = path[i]->data;
path[i]->data = path[j]->data;
path[j]->data = temp;
i++;
j--;
}
}
// Check if the node is a
// leaf node then return
if (!root->left and !root->right)
return;
// Call utility function for
// left and right subtree
// recursively
reverseTreePathUtil(root->left, path,
pathLen, key);
reverseTreePathUtil(root->right, path,
pathLen, key);
}
// Function to reverse tree path
void reverseTreePath(Node* root, int key)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Initialize a vector to store paths
vector path(50, NULL);
reverseTreePathUtil(root, path, 0, key);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* root = new Node(7);
root->left = new Node(6);
root->right = new Node(5);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(3);
root->right->left = new Node(2);
root->right->right = new Node(1);
/* 7
/ \
6 5
/ \ / \
4 3 2 1 */
int key = 4;
reverseTreePath(root, key);
inorder(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int value)
{ this.data = value; }
};
// Function to print inorder
// traversal of the tree
static void inorder(Node temp)
{
if (temp == null)
return;
inorder(temp.left);
System.out.print(temp.data+" ");
inorder(temp.right);
}
// Utility function to track
// root to leaf paths
static void reverseTreePathUtil(Node root, ArrayList path,
int pathLen, int key)
{
// Check if root is null then return
if (root == null)
return;
// Store the node in path array
path.set(pathLen, root);
pathLen++;
// Check if we find the node upto
// which path needs to be
// reversed
if (root.data == key) {
// Current path array contains
// the path which needs
// to be reversed
int i = 0, j = pathLen - 1;
// Swap the data of two nodes
while (i < j)
{
int temp = path.get(i).data;
path.get(i).data = path.get(j).data;
path.get(j).data = temp;
i++;
j--;
}
}
// Check if the node is a
// leaf node then return
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return;
// Call utility function for
// left and right subtree
// recursively
reverseTreePathUtil(root.left, path,
pathLen, key);
reverseTreePathUtil(root.right, path,
pathLen, key);
}
// Function to reverse tree path
static void reverseTreePath(Node root, int key)
{
if (root == null)
return;
// Initialize a vector to store paths
ArrayList path = new ArrayList();
for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++)
{
path.add(null);
}
reverseTreePathUtil(root, path, 0, key);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String []args)
{
Node root = new Node(7);
root.left = new Node(6);
root.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(2);
root.right.right = new Node(1);
/* 7
/ \
6 5
/ \ / \
4 3 2 1 */
int key = 4;
reverseTreePath(root, key);
inorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76. Python3
# Python program for the above approach
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data;
self.left = None;
self.right = None;
# Function to prinorder
# traversal of the tree
def inorder(temp):
if (temp == None):
return;
inorder(temp.left);
print(temp.data, end=" ");
inorder(temp.right);
# Utility function to track
# root to leaf paths
def reverseTreePathUtil(root, path, pathLen, key):
# Check if root is None then return
if (root == None):
return;
# Store the Node in path array
path[pathLen] = root;
pathLen+=1;
# Check if we find the Node upto
# which path needs to be
# reversed
if (root.data == key):
# Current path array contains
# the path which needs
# to be reversed
i = 0;
j = pathLen - 1;
# Swap the data of two Nodes
while (i < j):
temp = path[i].data;
path[i].data = path[j].data;
path[j].data = temp;
i += 1;
j -= 1;
# Check if the Node is a
# leaf Node then return
if (root.left == None and root.right == None):
return;
# Call utility function for
# left and right subtree
# recursively
reverseTreePathUtil(root.left, path, pathLen, key);
reverseTreePathUtil(root.right, path, pathLen, key);
# Function to reverse tree path
def reverseTreePath(root, key):
if (root == None):
return;
# Initialize a vector to store paths
path = [None for i in range(50)];
reverseTreePathUtil(root, path, 0, key);
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(7);
root.left = Node(6);
root.right = Node(5);
root.left.left = Node(4);
root.left.right = Node(3);
root.right.left = Node(2);
root.right.right = Node(1);
'''
* 7 / \ 6 5 / \ / \ 4 3 2 1
'''
key = 4;
reverseTreePath(root, key);
inorder(root);
# This code is contributed by umadevi9616C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int value)
{ this.data = value; }
};
// Function to print inorder
// traversal of the tree
static void inorder(Node temp)
{
if (temp == null)
return;
inorder(temp.left);
Console.Write(temp.data+" ");
inorder(temp.right);
}
// Utility function to track
// root to leaf paths
static void reverseTreePathUtil(Node root, List path,
int pathLen, int key)
{
// Check if root is null then return
if (root == null)
return;
// Store the node in path array
path[pathLen]= root;
pathLen++;
// Check if we find the node upto
// which path needs to be
// reversed
if (root.data == key) {
// Current path array contains
// the path which needs
// to be reversed
int i = 0, j = pathLen - 1;
// Swap the data of two nodes
while (i < j)
{
int temp = path[i].data;
path[i].data = path[j].data;
path[j].data = temp;
i++;
j--;
}
}
// Check if the node is a
// leaf node then return
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return;
// Call utility function for
// left and right subtree
// recursively
reverseTreePathUtil(root.left, path,
pathLen, key);
reverseTreePathUtil(root.right, path,
pathLen, key);
}
// Function to reverse tree path
static void reverseTreePath(Node root, int key)
{
if (root == null)
return;
// Initialize a vector to store paths
List path = new List();
for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++)
{
path.Add(null);
}
reverseTreePathUtil(root, path, 0, key);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = new Node(7);
root.left = new Node(6);
root.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(2);
root.right.right = new Node(1);
/* 7
/ \
6 5
/ \ / \
4 3 2 1 */
int key = 4;
reverseTreePath(root, key);
inorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616 Javascript
输出
7 6 3 4 2 5 1 另一种方法:
使用打印所有从根到叶路径的概念。这个想法是跟踪从根到要反转路径的特定节点的路径,一旦我们得到该特定节点,我们只需反转这些节点的数据。
在这里,我们不仅会尝试跟踪叶子路径的所有根节点,还会检查我们需要反转路径的节点。
使用向量来存储每条路径。
一旦我们得到需要反转路径的节点,我们使用一种简单的算法来反转在存储在向量中的跟随路径中找到的节点的数据。
上述方法的实现如下:
C++
// CPP program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
#define nl "\n"
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int value) { data = value; }
};
// Function to print inorder
// traversal of the tree
void inorder(Node* temp)
{
if (temp == NULL)
return;
inorder(temp->left);
cout << temp->data << " ";
inorder(temp->right);
}
// Utility function to track
// root to leaf paths
void reverseTreePathUtil(Node* root, vector path,
int pathLen, int key)
{
// Check if root is null then return
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Store the node in path array
path[pathLen] = root;
pathLen++;
// Check if we find the node upto
// which path needs to be
// reversed
if (root->data == key) {
// Current path array contains
// the path which needs
// to be reversed
int i = 0, j = pathLen - 1;
// Swap the data of two nodes
while (i < j) {
int temp = path[i]->data;
path[i]->data = path[j]->data;
path[j]->data = temp;
i++;
j--;
}
}
// Check if the node is a
// leaf node then return
if (!root->left and !root->right)
return;
// Call utility function for
// left and right subtree
// recursively
reverseTreePathUtil(root->left, path,
pathLen, key);
reverseTreePathUtil(root->right, path,
pathLen, key);
}
// Function to reverse tree path
void reverseTreePath(Node* root, int key)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Initialize a vector to store paths
vector path(50, NULL);
reverseTreePathUtil(root, path, 0, key);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* root = new Node(7);
root->left = new Node(6);
root->right = new Node(5);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(3);
root->right->left = new Node(2);
root->right->right = new Node(1);
/* 7
/ \
6 5
/ \ / \
4 3 2 1 */
int key = 4;
reverseTreePath(root, key);
inorder(root);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int value)
{ this.data = value; }
};
// Function to print inorder
// traversal of the tree
static void inorder(Node temp)
{
if (temp == null)
return;
inorder(temp.left);
System.out.print(temp.data+" ");
inorder(temp.right);
}
// Utility function to track
// root to leaf paths
static void reverseTreePathUtil(Node root, ArrayList path,
int pathLen, int key)
{
// Check if root is null then return
if (root == null)
return;
// Store the node in path array
path.set(pathLen, root);
pathLen++;
// Check if we find the node upto
// which path needs to be
// reversed
if (root.data == key) {
// Current path array contains
// the path which needs
// to be reversed
int i = 0, j = pathLen - 1;
// Swap the data of two nodes
while (i < j)
{
int temp = path.get(i).data;
path.get(i).data = path.get(j).data;
path.get(j).data = temp;
i++;
j--;
}
}
// Check if the node is a
// leaf node then return
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return;
// Call utility function for
// left and right subtree
// recursively
reverseTreePathUtil(root.left, path,
pathLen, key);
reverseTreePathUtil(root.right, path,
pathLen, key);
}
// Function to reverse tree path
static void reverseTreePath(Node root, int key)
{
if (root == null)
return;
// Initialize a vector to store paths
ArrayList path = new ArrayList();
for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++)
{
path.add(null);
}
reverseTreePathUtil(root, path, 0, key);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String []args)
{
Node root = new Node(7);
root.left = new Node(6);
root.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(2);
root.right.right = new Node(1);
/* 7
/ \
6 5
/ \ / \
4 3 2 1 */
int key = 4;
reverseTreePath(root, key);
inorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76.
Python3
# Python program for the above approach
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data;
self.left = None;
self.right = None;
# Function to prinorder
# traversal of the tree
def inorder(temp):
if (temp == None):
return;
inorder(temp.left);
print(temp.data, end=" ");
inorder(temp.right);
# Utility function to track
# root to leaf paths
def reverseTreePathUtil(root, path, pathLen, key):
# Check if root is None then return
if (root == None):
return;
# Store the Node in path array
path[pathLen] = root;
pathLen+=1;
# Check if we find the Node upto
# which path needs to be
# reversed
if (root.data == key):
# Current path array contains
# the path which needs
# to be reversed
i = 0;
j = pathLen - 1;
# Swap the data of two Nodes
while (i < j):
temp = path[i].data;
path[i].data = path[j].data;
path[j].data = temp;
i += 1;
j -= 1;
# Check if the Node is a
# leaf Node then return
if (root.left == None and root.right == None):
return;
# Call utility function for
# left and right subtree
# recursively
reverseTreePathUtil(root.left, path, pathLen, key);
reverseTreePathUtil(root.right, path, pathLen, key);
# Function to reverse tree path
def reverseTreePath(root, key):
if (root == None):
return;
# Initialize a vector to store paths
path = [None for i in range(50)];
reverseTreePathUtil(root, path, 0, key);
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(7);
root.left = Node(6);
root.right = Node(5);
root.left.left = Node(4);
root.left.right = Node(3);
root.right.left = Node(2);
root.right.right = Node(1);
'''
* 7 / \ 6 5 / \ / \ 4 3 2 1
'''
key = 4;
reverseTreePath(root, key);
inorder(root);
# This code is contributed by umadevi9616
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int value)
{ this.data = value; }
};
// Function to print inorder
// traversal of the tree
static void inorder(Node temp)
{
if (temp == null)
return;
inorder(temp.left);
Console.Write(temp.data+" ");
inorder(temp.right);
}
// Utility function to track
// root to leaf paths
static void reverseTreePathUtil(Node root, List path,
int pathLen, int key)
{
// Check if root is null then return
if (root == null)
return;
// Store the node in path array
path[pathLen]= root;
pathLen++;
// Check if we find the node upto
// which path needs to be
// reversed
if (root.data == key) {
// Current path array contains
// the path which needs
// to be reversed
int i = 0, j = pathLen - 1;
// Swap the data of two nodes
while (i < j)
{
int temp = path[i].data;
path[i].data = path[j].data;
path[j].data = temp;
i++;
j--;
}
}
// Check if the node is a
// leaf node then return
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return;
// Call utility function for
// left and right subtree
// recursively
reverseTreePathUtil(root.left, path,
pathLen, key);
reverseTreePathUtil(root.right, path,
pathLen, key);
}
// Function to reverse tree path
static void reverseTreePath(Node root, int key)
{
if (root == null)
return;
// Initialize a vector to store paths
List path = new List();
for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++)
{
path.Add(null);
}
reverseTreePathUtil(root, path, 0, key);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = new Node(7);
root.left = new Node(6);
root.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(2);
root.right.right = new Node(1);
/* 7
/ \
6 5
/ \ / \
4 3 2 1 */
int key = 4;
reverseTreePath(root, key);
inorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
Javascript
输出
7 6 3 4 2 5 1 时间复杂度: O(N)
空间复杂度: O(N)