- groovy 到 int - Groovy (1)
- groovy 到 int - Groovy 代码示例
- Groovy-方法
- Groovy-方法(1)
- groovy 中的数组(1)
- groovy 拆分字符串 - Groovy (1)
- Groovy-字符串
- Groovy-字符串(1)
- groovy 拆分字符串 - Groovy 代码示例
- Groovy-文件I / O
- Groovy-文件I O(1)
- Groovy-列表(1)
- Groovy-列表
- groovy - 任何代码示例
- groovy 代码示例中的数组
- Python和 Groovy 的区别
- Python和 Groovy 的区别(1)
- groovy 简单字符串模板 - Groovy 代码示例
- Groovy-循环(1)
- Groovy-循环
- Groovy-变量(1)
- Groovy-变量
- Groovy-范围(1)
- Groovy-范围
- groovy random uuid - Groovy (1)
- Groovy-JSON(1)
- Groovy-JSON
- Groovy-数据库
- Groovy 和Java 的区别(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-04 06:38:47 🧑 作者: Mango
在Groovy中,数字实际上表示为对象的数字,所有数字都是Integer类的实例。为了使对象执行某项操作,我们需要调用其类中声明的方法之一。
Groovy支持整数和浮点数。
- 整数是不包含小数的值。
- 浮点数是一个十进制值,其中包括一个十进制小数。
Groovy中的数字示例如下所示-
Integer x = 5;
Float y = 1.25;
其中x是Integer类型, y是浮点型。
常规中将数字定义为对象的原因通常是因为需要对数字执行运算。在原始类型上提供类的概念称为包装器类。
默认情况下,Groovy中提供了以下包装器类。
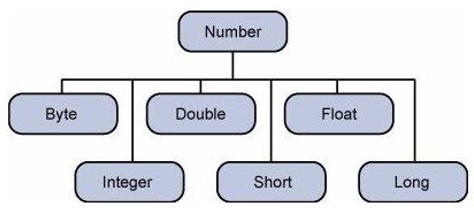
包装类的对象包含或包装其各自的原始数据类型。将原始数据类型转换为对象的过程称为装箱,而编译器会注意这一点。将对象转换回其对应的原始类型的过程称为拆箱。
例
以下是装箱和拆箱的示例-
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
Integer x = 5,y = 10,z = 0;
// The the values of 5,10 and 0 are boxed into Integer types
// The values of x and y are unboxed and the addition is performed
z = x+y;
println(z);
}
}
上面程序的输出为15。在上面的示例中,首先将5、10和0的值分别装箱到Integer变量x,y和z中。然后,在执行x和y的加法运算时,会将值从其Integer类型中拆箱。
编号方法
由于Groovy中的数字表示为类,因此以下是可用方法的列表。
| S.No. | Methods & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | xxxValue()
This method takes on the Number as the parameter and returns a primitive type based on the method which is invoked. |
| 2 | compareTo()
The compareTo method is to use compare one number against another. This is useful if you want to compare the value of numbers. |
| 3 | equals()
The method determines whether the Number object that invokes the method is equal to the object that is passed as argument. |
| 4 | valueOf()
The valueOf method returns the relevant Number Object holding the value of the argument passed. |
| 5 | toString()
The method is used to get a String object representing the value of the Number Object. |
| 6 | parseInt()
This method is used to get the primitive data type of a certain String. parseXxx() is a static method and can have one argument or two. |
| 7 | abs()
The method gives the absolute value of the argument. The argument can be int, float, long, double, short, byte. |
| 8 | ceil()
The method ceil gives the smallest integer that is greater than or equal to the argument. |
| 9 | floor()
The method floor gives the largest integer that is less than or equal to the argument. |
| 10 | rint()
The method rint returns the integer that is closest in value to the argument. |
| 11 | round()
The method round returns the closest long or int, as given by the methods return type. |
| 12 | min()
The method gives the smaller of the two arguments. The argument can be int, float, long, double. |
| 13 | max()
The method gives the maximum of the two arguments. The argument can be int, float, long, double. |
| 14 | exp()
The method returns the base of the natural logarithms, e, to the power of the argument. |
| 15 | log()
The method returns the natural logarithm of the argument. |
| 16 | pow()
The method returns the value of the first argument raised to the power of the second argument. |
| 17 | sqrt()
The method returns the square root of the argument. |
| 18 | sin()
The method returns the sine of the specified double value. |
| 19 | cos()
The method returns the cosine of the specified double value. |
| 20 | tan()
The method returns the tangent of the specified double value. |
| 21 | asin()
The method returns the arcsine of the specified double value. |
| 22 | acos()
The method returns the arccosine of the specified double value. |
| 23 | atan()
The method returns the arctangent of the specified double value. |
| 24 | atan2()
The method Converts rectangular coordinates (x, y) to polar coordinate (r, theta) and returns theta. |
| 25 | toDegrees()
The method converts the argument value to degrees. |
| 26 | radian()
The method converts the argument value to radians. |
| 27 | random()
The method is used to generate a random number between 0.0 and 1.0. The range is: 0.0 =< Math.random < 1.0. Different ranges can be achieved by using arithmetic. |