用于在链表中插入节点的 C 程序
我们在上一篇文章中介绍了链表。我们还创建了一个包含 3 个节点的简单链表并讨论了链表遍历。
这篇文章中讨论的所有程序都考虑了链表的以下表示。
C
// A linked list node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};C
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to
// the head of a list and an int, inserts a
// new node on the front of the list.
void push(struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// 1. Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// 2. put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make next of new node as head
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// 4. move the head to point to
// the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}C
// Given a node prev_node, insert a
// new node after the given prev_node
void insertAfter(struct Node* prev_node,
int new_data)
{
// 1. Check if the given prev_node
// is NULL
if (prev_node == NULL)
{
printf("the given previous node cannot be NULL");
return;
}
// 2. Allocate new node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// 3. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 4. Make next of new node as next
// of prev_node
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
// 5. Move the next of prev_node
// as new_node
prev_node->next = new_node;
}C
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to
// the head of a list and an int, appends a
// new node at the end
void append(struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// 1. Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Used in step 5
struct Node *last = *head_ref;
// 2. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. This new node is going to be the
// last node, so make next of it as NULL
new_node->next = NULL;
// 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make
// the new node as head
if (*head_ref == NULL)
{
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
// 5. Else traverse till the last node
while (last->next != NULL)
last = last->next;
// 6. Change the next of last node
last->next = new_node;
return;
}C
// A complete working C program to demonstrate
// all insertion methods on Linked List
#include
#include
// A linked list node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to
// the head of a list and an int, inserts a
// new node on the front of the list.
void push(struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// 1. Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// 2. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make next of new node as head
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// 4. move the head to point to
// the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Given a node prev_node, insert a
// new node after the given prev_node
void insertAfter(struct Node* prev_node,
int new_data)
{
// 1. Check if the given prev_node
// is NULL
if (prev_node == NULL)
{
printf("the given previous node cannot be NULL");
return;
}
// 2. Allocate new node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// 3. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 4. Make next of new node as next
// of prev_node
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
// 5. Move the next of prev_node
// as new_node
prev_node->next = new_node;
}
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to
// the head of a list and an int, appends a
// new node at the end
void append(struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// 1. Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Used in step 5
struct Node *last = *head_ref;
// 2. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. This new node is going to be the
// last node, so make next of it as NULL
new_node->next = NULL;
// 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make
// the new node as head
if (*head_ref == NULL)
{
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
// 5. Else traverse till the last node
while (last->next != NULL)
last = last->next;
// 6. Change the next of last node
last->next = new_node;
return;
}
// This function prints contents of the
// linked list starting from head
void printList(struct Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
printf(" %d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Start with the empty list
struct Node* head = NULL;
// Insert 6. So linked list
// becomes 6->NULL
append(&head, 6);
// Insert 7 at the beginning.
// So linked list becomes 7->6->NULL
push(&head, 7);
// Insert 1 at the beginning. So
// linked list becomes 1->7->6->NULL
push(&head, 1);
// Insert 4 at the end. So linked list
// becomes 1->7->6->4->NULL
append(&head, 4);
// Insert 8, after 7. So linked list
// becomes 1->7->8->6->4->NULL
insertAfter(head->next, 8);
printf("Created Linked list is: ");
printList(head);
return 0;
} 在这篇文章中,讨论了在链表中插入新节点的方法。可以通过三种方式添加节点
1)在链表的前面
2)在给定节点之后。
3)在链表的末尾。
在前面添加一个节点:(4步过程)
新节点总是添加在给定链表的头部之前。新添加的节点成为链表的新头。例如,如果给定的链表是 10->15->20->25,我们在前面添加一个项目 5,那么链表变为 5->10->15->20->25。让我们将添加到列表前面的函数称为 push()。 push() 必须接收指向头指针的指针,因为 push 必须更改头指针以指向新节点(请参阅this)
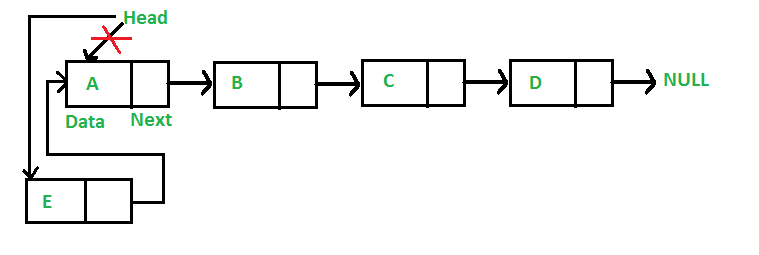
以下是在前面添加节点的 4 个步骤。
C
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to
// the head of a list and an int, inserts a
// new node on the front of the list.
void push(struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// 1. Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// 2. put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make next of new node as head
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// 4. move the head to point to
// the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
push() 的时间复杂度是 O(1),因为它做的工作量是恒定的。
在给定节点之后添加一个节点:(5个步骤)
我们得到一个指向节点的指针,新节点插入到给定节点之后。
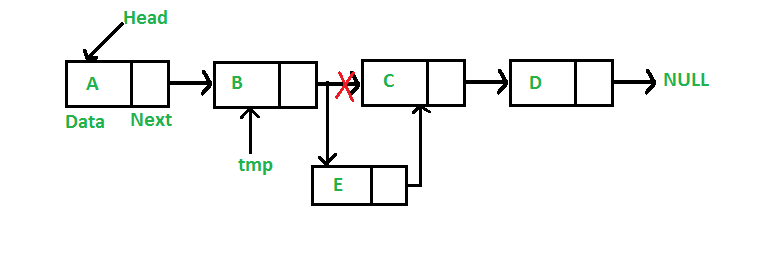
C
// Given a node prev_node, insert a
// new node after the given prev_node
void insertAfter(struct Node* prev_node,
int new_data)
{
// 1. Check if the given prev_node
// is NULL
if (prev_node == NULL)
{
printf("the given previous node cannot be NULL");
return;
}
// 2. Allocate new node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// 3. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 4. Make next of new node as next
// of prev_node
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
// 5. Move the next of prev_node
// as new_node
prev_node->next = new_node;
}
insertAfter() 的时间复杂度是 O(1),因为它做的工作量是恒定的。
最后添加一个节点:(6步过程)
新节点总是添加在给定链表的最后一个节点之后。例如,如果给定的链表是 5->10->15->20->25 并且我们在末尾添加了一个项目 30,那么链表变为 5->10->15->20->25- >30。
由于链接列表通常由其头部表示,因此我们必须遍历列表直到最后,然后将倒数第二个节点更改为新节点。
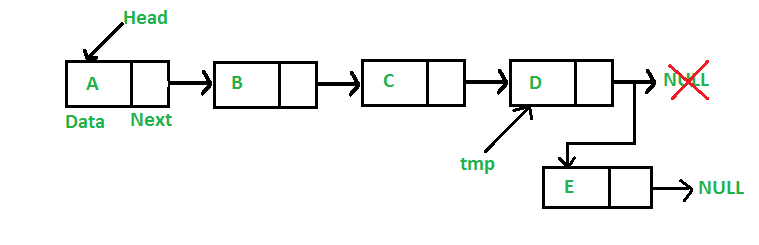
以下是最后添加节点的 6 个步骤。
C
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to
// the head of a list and an int, appends a
// new node at the end
void append(struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// 1. Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Used in step 5
struct Node *last = *head_ref;
// 2. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. This new node is going to be the
// last node, so make next of it as NULL
new_node->next = NULL;
// 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make
// the new node as head
if (*head_ref == NULL)
{
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
// 5. Else traverse till the last node
while (last->next != NULL)
last = last->next;
// 6. Change the next of last node
last->next = new_node;
return;
}
追加的时间复杂度是 O(n),其中 n 是链表中的节点数。由于从头到尾有一个循环,因此该函数执行 O(n) 工作。
通过保留一个指向链表尾部的额外指针,还可以优化此方法以在 O(1) 中工作。
下面是一个完整的程序,它使用上述所有方法来创建一个链表。
C
// A complete working C program to demonstrate
// all insertion methods on Linked List
#include
#include
// A linked list node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to
// the head of a list and an int, inserts a
// new node on the front of the list.
void push(struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// 1. Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// 2. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make next of new node as head
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// 4. move the head to point to
// the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Given a node prev_node, insert a
// new node after the given prev_node
void insertAfter(struct Node* prev_node,
int new_data)
{
// 1. Check if the given prev_node
// is NULL
if (prev_node == NULL)
{
printf("the given previous node cannot be NULL");
return;
}
// 2. Allocate new node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// 3. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 4. Make next of new node as next
// of prev_node
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
// 5. Move the next of prev_node
// as new_node
prev_node->next = new_node;
}
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to
// the head of a list and an int, appends a
// new node at the end
void append(struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// 1. Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Used in step 5
struct Node *last = *head_ref;
// 2. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. This new node is going to be the
// last node, so make next of it as NULL
new_node->next = NULL;
// 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make
// the new node as head
if (*head_ref == NULL)
{
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
// 5. Else traverse till the last node
while (last->next != NULL)
last = last->next;
// 6. Change the next of last node
last->next = new_node;
return;
}
// This function prints contents of the
// linked list starting from head
void printList(struct Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
printf(" %d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Start with the empty list
struct Node* head = NULL;
// Insert 6. So linked list
// becomes 6->NULL
append(&head, 6);
// Insert 7 at the beginning.
// So linked list becomes 7->6->NULL
push(&head, 7);
// Insert 1 at the beginning. So
// linked list becomes 1->7->6->NULL
push(&head, 1);
// Insert 4 at the end. So linked list
// becomes 1->7->6->4->NULL
append(&head, 4);
// Insert 8, after 7. So linked list
// becomes 1->7->8->6->4->NULL
insertAfter(head->next, 8);
printf("Created Linked list is: ");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
输出:
Created Linked list is: 1 7 8 6 4请参阅链表上的完整文章 |设置 2(插入节点)了解更多详情!