用户有存储机器。它有一层用于数据存储,另一层用于高速缓存。用户已在第一层中存储了一个长度为N的数组。
当CPU需要数据时,它将立即在高速缓存中检查是否有数据。如果存在数据,则导致CACHE HITS ,否则导致CACHE MISS ,即数据不在高速缓存中,因此它从主内存中检索数据并将数据块插入高速缓存层。

出现的问题是:机器将块加载到高速缓存层需要多少次,即确定CACHE MISS的数量?
例子 –
让我们假设一个数组,并用A0,A1,…,AN表示它的元素?
现在,用户希望将该数组的某些元素加载到缓存中。

机器将数组装入大小为B的块中:
假设块大小为4。
1 2 3 4位于第1块中,5 6 7 8位于第2块中,而9,10位于第3块中。
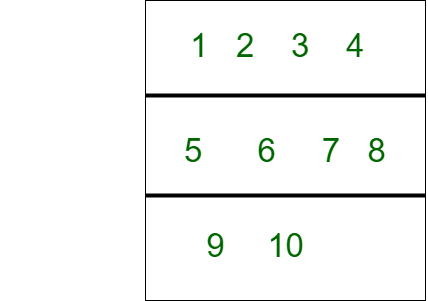
A0,A1,…,AB? 1个块AB,AB + 1,…,A2B? 1形成另一个块,依此类推。最后一块可能包含少于用户数组的B个元素。
一次最多只能包含一个块。每当用户尝试访问元素Ai时,机器都会检查Ai所在的块是否已在高速缓存中,如果不是,则将该块加载到高速缓存层中,以便它可以快速访问其中的任何数据。
但是,一旦用户尝试访问缓存中当前加载的块之外的元素,就会从缓存中删除以前加载到缓存中的块,因为计算机会加载一个包含正在访问的元素的新块。
例子 –
用户具有要按此顺序访问的元素Ax1,Ax2,…,AxM序列。最初,缓存为空。我们需要找出机器将一个块加载到缓存层中需要多少次。
输入格式:
- 每个测试用例的第一行包含三个以空格分隔的整数N,B和M。
- 第二行包含M个以空格分隔的整数x1,x2,…,xM。
输入 :
5 3 3
0 3 4输出 :
2解释 :
机器将元素[A0,A1,A2]存储在一个块中,并将[A3,A4]存储在另一个块中。访问A0时,将装载块[A0,A1,A2]。然后,访问A3从缓存中删除先前的块并加载块[A3,A4]。最后,当用户访问A4时,由于当前已将包含A4的块加载到缓存中,因此不会加载新块。
方法 :
- 最初发生高速缓存未命中是因为高速缓存层为空,我们找到了下一个乘数和起始元素。
- 获取用户值并找到下一个乘数,该乘数可被块大小整除。
- 查找当前块的起始元素。
- 如果用户值大于下一个乘数且小于起始元素,则发生高速缓存未命中。
执行 :
C++
// C++ program to implement Cache Miss
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the next multiplier
int findnextmultiplier(int i, int b)
{
for (int j = i; j <= i * b; j++) {
if (j % b == 0)
return j;
}
}
// Function to find the cache miss
int ans(int n, int b, int m, int user[])
{
// Initially cache miss occurs
int start, cacheMiss = 1, nextmultiplier;
// Find next multiplier for ith user and start
nextmultiplier= findnextmultiplier(user[0] + 1, b);
start = nextmultiplier - b + 1;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
// If ith user is greater than nextmultiplier or lesser
// than start then cache miss occurs
if (user[i] + 1 > nextmultiplier || user[i] + 1 < start) {
cacheMiss++;
nextmultiplier= findnextmultiplier(user[i] + 1, b);
start = nextmultiplier - b + 1;
}
}
// Printing cache miss
cout << cacheMiss << endl;
return 0;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n=5, b=3, m=3;
int user[3] = {0, 3, 4};
ans(n, b, m, user);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to implement Cache Hits
public class Main
{
// Function to find the next multiplier
public static int findnextmultiplier(int i, int b)
{
for (int j = i; j <= i * b; j++)
{
if (j % b == 0)
return j;
}
return 0;
}
// Function to find the cache hits
public static int ans(int n, int b, int m, int user[])
{
// Initially cache hit occurs
int start, ch = 1, nextmultiplier;
// Find next multiplier for ith user and start
nextmultiplier= findnextmultiplier(user[0] + 1, b);
start = nextmultiplier - b + 1;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
{
// If ith user is greater than nextmultiplier or lesser
// than start then cache hit occurs
if (user[i] + 1 > nextmultiplier || user[i] + 1 < start)
{
ch++;
nextmultiplier= findnextmultiplier(user[i] + 1, b);
start = nextmultiplier - b + 1;
}
}
// Printing cache hits
System.out.println(ch);
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n=5, b=3, m=3;
int user[] = {0, 3, 4};
ans(n, b, m, user);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07Python3
# Python3 program to implement Cache Hits
# Function to find the next multiplier
def findnextmultiplier(i, b):
for j in range(i, (i * b) + 1):
if (j % b == 0):
return j
# Function to find the cache hits
def ans(n, b, m, user):
# Initially cache hit occurs
ch = 1
# Find next multiplier for ith user and start
nextmultiplier = findnextmultiplier(user[0] + 1, b)
start = nextmultiplier - b + 1
for i in range(1, m):
# If ith user is greater than nextmultiplier
# or lesser than start then cache hit occurs
if (user[i] + 1 > nextmultiplier or
user[i] + 1 < start):
ch += 1
nextmultiplier = findnextmultiplier(
user[i] + 1, b)
start = nextmultiplier - b + 1
# Printing cache hits
print(ch)
# Driver code
n = 5
b = 3
m = 3
user = [ 0, 3, 4 ]
ans(n, b, m, user)
# This code is contributed by rag2127C#
// C# program to implement Cache Hits
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to find the next multiplier
static int findnextmultiplier(int i, int b)
{
for(int j = i; j <= i * b; j++)
{
if (j % b == 0)
return j;
}
return 0;
}
// Function to find the cache hits
static int ans(int n, int b, int m, int[] user)
{
// Initially cache hit occurs
int start, ch = 1, nextmultiplier;
// Find next multiplier for ith user and start
nextmultiplier = findnextmultiplier(
user[0] + 1, b);
start = nextmultiplier - b + 1;
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++)
{
// If ith user is greater than nextmultiplier
// or lesser than start then cache hit occurs
if (user[i] + 1 > nextmultiplier ||
user[i] + 1 < start)
{
ch++;
nextmultiplier = findnextmultiplier(
user[i] + 1, b);
start = nextmultiplier - b + 1;
}
}
// Printing cache hits
Console.WriteLine(ch);
return 0;
}
// Driver Code
static void Main()
{
int n = 5, b = 3, m = 3;
int[] user = { 0, 3, 4 };
ans(n, b, m, user);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019Javascript
输出 :
2时间复杂度: O(m)
辅助空间: O(1)