通过应用软件架构模式开发android应用程序始终是开发人员的首选。架构模式为项目文件提供了模块化,并确保所有代码都包含在单元测试中。它使开发人员将来可以轻松完成维护软件和扩展应用程序功能的任务。 MVC(模型-视图-演示者)和MVP(模型-视图-演示者) 是两个 开发人员中最流行的android体系结构。
模型-视图-控制器(MVC)模式
MVC模式建议将代码分为3个部分。在创建应用程序的类/文件时,开发人员必须将其分类为以下三层之一:
型号:此组件存储应用程序数据。它不具备有关接口的知识。该模型负责处理域逻辑(实际业务规则)以及与数据库和网络层的通信。
视图:这是UI(用户界面)层,其中包含在屏幕上可见的组件。此外,它提供了存储在模型中的数据的可视化,并向用户提供了交互。
控制器:此组件建立视图与模型之间的关系。它包含核心应用程序逻辑,并通知用户行为并根据需要更新模型。

模型—视图—演示器(MVP)模式
MVP模式克服了MVC的挑战,并提供了一种构造项目代码的简便方法。 MVP之所以被广泛接受,是因为它提供了模块化,可测试性以及更干净和可维护的代码库。它由以下三个组件组成:
型号:用于存储数据的层。它负责处理域逻辑(实际业务规则)以及与数据库和网络层的通信。
查看: UI(用户界面)层。它提供数据的可视化并跟踪用户的操作,以便通知Presenter。
演示者:从模型中获取数据并应用UI逻辑来决定要显示的内容。它管理视图的状态,并根据用户从视图中输入的通知执行操作。
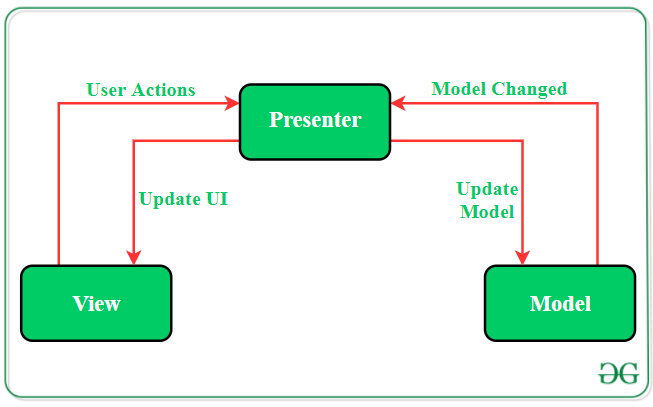
MVC和MVP设计模式之间的主要区别
|
MVC(Model View Controller) |
MVP(Model View Presenter |
|---|---|
| One of the oldest software architecture | Developed as the second iteration of software architecture which is advance from MVC. |
| UI(View) and data-access mechanism(Model) are tightly coupled. | The View is loosely coupled to the Model. |
| Controller and View layer falls in the same activity/fragment | Communication between View-Presenter and Presenter-Model happens via an interface. |
| User inputs are handled by Controller which instructs the model for further operations. | User inputs are handled by View which instructs the presenter to call appropriate functions. |
| The many-to-one relationship exists between Controller and View as one Controller can select different View based upon required operations. | The one-to-one relationship exists between Presenter and View as one Presenter class manages one View at a time. |
| The Controller is the overall in charge as it creates the appropriate View and interacts with the Model according to the user’s request. | The View is the overall in charge in this schema as View call methods of Presenter which further directs Model. |
| Limited support to Unit Testing | Unit Testing is highly supported. |
想要一个节奏更快,更具竞争性的环境来学习Android的基础知识吗?
单击此处前往由我们的专家精心策划的指南,以使您立即做好行业准备!