Java NIO 中的 AsynchronousFileChannel
Java.nio 包是在Java 1.4 版本中引入的。它允许我们并发处理不同的通道,因为它支持并发和多线程。异步文件通道 API 负责Java NIO 包,它定义在 NIO 通道包下。为了将 AsynchronousFileChannel API 导入我们的程序,请遵循以下语法:
句法:
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousFileChannel异步通道可供多个并发线程使用是安全的,因为该通道使文件操作能够异步执行,这与同步 I/O 操作不同,同步 I/O 操作在同步 I/O 操作中线程进入操作并等待请求完成。这是 asynchronousFileChannel 和 NIO 的 FileChannel 之间的唯一区别。
该请求首先由线程传递到操作系统的内核以在线程继续执行另一项工作时完成它。内核的工作完成后,它向线程发送信号,然后线程确认该信号并中断当前的工作,并根据需要在异步通道中处理 I/O 工作。
方法:
有两种实现并发的方法,如下所列。我们将通过示例详细了解上述两种方法。
- 未来对象
- 完成处理程序
方法一:未来对象
它返回一个Java.util.concurrent.Future 对象。有两种有用的方法来检索信息,这两种方法是——
- get() 方法:它返回异步处理的操作的状态,在此基础上可以决定其他任务的进一步执行。
- isDone() 方法:此方法将检查任务是否完成。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate AsynchronousFileChannel Class
// Via Future Object Approach
// Importing package
package com.java.nio;
// Importing required classes from java.nio package
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousFileChannel;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
// Main class
// FutureObjectExample
public class GFG {
// Method 1
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Calling the readFile() method that will run first
readFile();
}
// Method 2
// To read the file
private static void readFile()
throws IOException, InterruptedException,
ExecutionException
{
// Path of the file
String filePath
= "C:/users/Sir/Desktop/fileCopy.txt";
// First create the file and then specify its
// correct path
printFileContents(filePath);
Path path = Paths.get(filePath);
AsynchronousFileChannel channel
= AsynchronousFileChannel.open(
path, StandardOpenOption.READ);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(400);
Future result = channel.read(buffer, 0);
// Checking whether the task is been completed or
// not
while (!result.isDone()) {
System.out.println(
"The process of reading file is in progress asynchronously.");
}
// Print and display statements
System.out.println("Is the reading done? "
+ result.isDone());
System.out.println(
"The number of bytes read from file is "
+ result.get());
buffer.flip();
System.out.print("Buffer contents: ");
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.print((char)buffer.get());
}
System.out.println(" ");
// Closing the channels using close() method
buffer.clear();
channel.close();
}
// Method 3
// To print the contents of the file
private static void printFileContents(String path)
throws IOException
{
FileReader fr = new FileReader(path);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String textRead = br.readLine();
System.out.println("Content in the File: ");
while (textRead != null) {
// After reading all the text from the file it
// print the number of bytes in the file.
System.out.println(" " + textRead);
textRead = br.readLine();
}
// Closing the channels
// Closing the fr object
fr.close();
// Closing the br object
br.close();
}
} Java
// Java Program to Illustrate AsynchronousFileChannel Class
// Via Completion handler Approach
// Importing required classes from respective packages
package com.java.nio;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousFileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
// Main class
// CompletionHandler
public class GFG {
// Method 1
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Calling the writefile() method
writeFile();
}
// Method 2
// To write into a file
private static void writeFile() throws IOException
{
// Custom string
String input = "Content to be written to the file.";
System.out.println("Input string: " + input);
byte[] byteArray = input.getBytes();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(byteArray);
// Specifying path of File
Path path = Paths.get(
"C:/users/Sir/Desktop/fileCopy.txt");
AsynchronousFileChannel channel
= AsynchronousFileChannel.open(
path, StandardOpenOption
.WRITE); // calling the API
CompletionHandler handler
= new CompletionHandler() {
// Method 3
@Override
public void completed(Object result,
Object attachment)
{
System.out.println(
attachment + " completed and "
+ result + " bytes are written.");
}
// Method 4
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc,
Object attachment)
{
System.out.println(
attachment
+ " failed with exception:");
exc.printStackTrace();
}
};
channel.write(buffer, 0, "Async Task", handler);
// Closing the channel object tha we created earlier
// using close() method
channel.close();
printFileContents(path.toString());
}
// Method 5
// To print the fle contents
private static void printFileContents(String path)
throws IOException
{
FileReader fr = new FileReader(path);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String textRead = br.readLine();
System.out.println("File contents: ");
// Till there is some content in file
while (textRead != null) {
System.out.println(" " + textRead);
textRead = br.readLine();
}
// Closing the fr object
fr.close();
// Closing the br object
br.close();
}
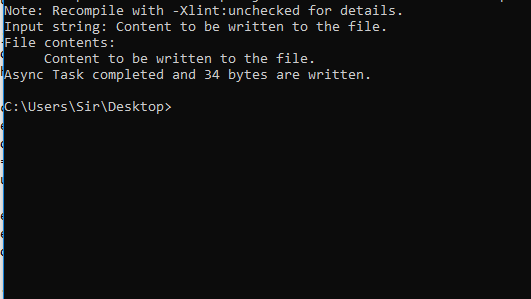
}输出:

方法 2:完成处理程序
对于这种方法,我们将使用 CompletionHandler 接口,它包含两个我们将要覆盖的有用方法。在这种情况下,将创建一个完成处理程序来使用异步 I/O 操作的结果,因为一旦任务完成,则只有处理程序具有执行的功能。
这两种方法如下:
- Completed() 方法:当 I/O 操作成功完成时调用此方法。
- failed() 方法:如果 I/O 操作失败,则调用此方法。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate AsynchronousFileChannel Class
// Via Completion handler Approach
// Importing required classes from respective packages
package com.java.nio;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousFileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
// Main class
// CompletionHandler
public class GFG {
// Method 1
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Calling the writefile() method
writeFile();
}
// Method 2
// To write into a file
private static void writeFile() throws IOException
{
// Custom string
String input = "Content to be written to the file.";
System.out.println("Input string: " + input);
byte[] byteArray = input.getBytes();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(byteArray);
// Specifying path of File
Path path = Paths.get(
"C:/users/Sir/Desktop/fileCopy.txt");
AsynchronousFileChannel channel
= AsynchronousFileChannel.open(
path, StandardOpenOption
.WRITE); // calling the API
CompletionHandler handler
= new CompletionHandler() {
// Method 3
@Override
public void completed(Object result,
Object attachment)
{
System.out.println(
attachment + " completed and "
+ result + " bytes are written.");
}
// Method 4
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc,
Object attachment)
{
System.out.println(
attachment
+ " failed with exception:");
exc.printStackTrace();
}
};
channel.write(buffer, 0, "Async Task", handler);
// Closing the channel object tha we created earlier
// using close() method
channel.close();
printFileContents(path.toString());
}
// Method 5
// To print the fle contents
private static void printFileContents(String path)
throws IOException
{
FileReader fr = new FileReader(path);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String textRead = br.readLine();
System.out.println("File contents: ");
// Till there is some content in file
while (textRead != null) {
System.out.println(" " + textRead);
textRead = br.readLine();
}
// Closing the fr object
fr.close();
// Closing the br object
br.close();
}
}
输出: