写入文件的Java程序
Java中的Java FileWriter 类用于将面向字符的数据写入文件,因为此类是面向字符的类,因为它用于Java中的文件处理。
方法:在Java中有很多写入文件的方法,因为有很多类和方法可以实现如下目标:
- 使用writeString()方法
- 使用 FileWriter 类
- 使用 BufferedWriter 类
- 使用 FileOutputStream 类
方法一:使用writeString()方法
Java 11 版本支持此方法。此方法可以带四个参数。它们是文件路径、字符序列、字符集和选项。前两个参数对于此方法写入文件是必需的。它将字符写入文件的内容。它返回文件路径并且可以抛出四种类型的异常。最好在文件内容较短的情况下使用。
例子
它展示了使用 Files 类下的writeString()方法将数据写入文件。另一个类 Path 用于为文件名分配一个写入内容的路径。 Files 类有另一个名为readString()的方法来读取代码中使用的任何现有文件的内容,以检查内容是否正确写入文件。
Java
// Java Program to write into a file
// using writeString() method
// Importing java NIO package
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
// Importing class
import java.io.IOException;
// Class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
// Assign the content of the file
String text = "Welcome to geekforgeeks\nHappy Learning!";
// Define the file name of the file
Path fileName = Path.of("/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx");
// Write into the file
Files.writeString(fileName, text);
// Read the content of the file
String file_content = Files.readString(fileName);
// Print the content inside the file
System.out.println(file_content);
}
}Java
// Java Program to write into a file
// using FileWriterClass
// Importing java input/output classes
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
// Class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Content to be assigned to a file
// Custom input just for illustratinon purposes
String text
= "Computer Science Portal GeeksforGeeks";
// Try block to check if exception/s occurs
try {
// Create a FileWriter object
// to write in the file
FileWriter fWriter = new FileWriter(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx");
// Write into the file
// The content taken above inside the string
fWriter.write(text);
// Printing the contents of a file
System.out.println(text);
// Close the file writer object
fWriter.close();
// Display message to be printed on the console
// window after successful execution of the
// program
System.out.println(
"File is created successfully with the content.");
}
// Catch block to handle if exception occurs
catch (IOException e) {
// Print the exception
System.out.print(e.getMessage());
}
}
}Java
// Java Program to write into a File
// using BufferedWriter Class
// Importing java input output libraries
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
// Class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Assign the file content
// Custom contents taken as input to illustrate
String text
= "Computer Science Portal GeeksforGeks";
// Try block to check if exceptions occurs
try {
// Step 1: Create an object of BufferedWriter
BufferedWriter f_writer
= new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx"));
// Step 2: Write text(content) to file
f_writer.write(text);
// Step 3: Printing the content inside the file
// on the terminal/CMD
System.out.print(text);
// Step 4: Display message showcasing
// successful execution of the program
System.out.print(
"File is created successfully with the content.");
// Step 5: Close the BufferedWriter object
f_writer.close();
}
// Catch block to handle if exceptions occurs
catch (IOException e) {
// Print the exception
System.out.print(e.getMessage());
}
}
}Java
// Java Program to write into a file
// using FileOutputStream Class
// Importing java input output classes
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Assign the file content
String fileContent = "Welcome to geeksforgeeks";
// Try block to check if exception occurs
try {
// Step 1: Create an object of FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream outputStream
= new FileOutputStream("file.txt");
// Step 2: Store byte content from string
byte[] strToBytes = fileContent.getBytes();
// Step 3: Write into the file
outputStream.write(strToBytes);
// Print the success message (Optional)
System.out.print(
"File is created successfully with the content.");
// Step 4: Close the object
outputStream.close();
}
// Catch block to handle the exception
catch (IOException e) {
// Print the exception
System.out.print(e.getMessage());
}
}
}Welcome to geekforgeeks
Happy Learning!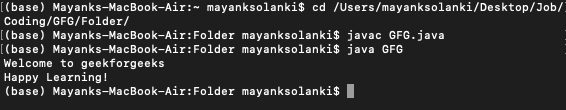
方法 2:使用 FileWriter 类
如果文件的内容很短,那么使用 FileWriter 类写入文件是另一个更好的选择。它还像 writeString() 方法一样将字符流写入文件的内容。此类的构造函数定义了默认字符编码和默认缓冲区大小(以字节为单位)。
例子
下面的示例演示如何使用 FileWriter 类将内容写入文件。它需要使用文件名创建 FileWriter 类的对象以写入文件。接下来,使用 write() 方法将文本变量的值写入文件中。如果在写入文件时发生任何错误,则会抛出 IO 异常,并从 catch 块打印错误消息。
Java
// Java Program to write into a file
// using FileWriterClass
// Importing java input/output classes
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
// Class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Content to be assigned to a file
// Custom input just for illustratinon purposes
String text
= "Computer Science Portal GeeksforGeeks";
// Try block to check if exception/s occurs
try {
// Create a FileWriter object
// to write in the file
FileWriter fWriter = new FileWriter(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx");
// Write into the file
// The content taken above inside the string
fWriter.write(text);
// Printing the contents of a file
System.out.println(text);
// Close the file writer object
fWriter.close();
// Display message to be printed on the console
// window after successful execution of the
// program
System.out.println(
"File is created successfully with the content.");
}
// Catch block to handle if exception occurs
catch (IOException e) {
// Print the exception
System.out.print(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
File is created successfully with the content.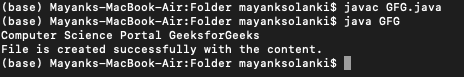
方法 3:使用 BufferedWriter 类
它用于将文本写入字符输出流。它有一个默认的缓冲区大小,但可以分配大缓冲区大小。它对于编写字符、字符串和数组很有用。如果不需要提示输出,最好将此类与任何用于将数据写入文件的编写器类一起包装。
例子
Java
// Java Program to write into a File
// using BufferedWriter Class
// Importing java input output libraries
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
// Class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Assign the file content
// Custom contents taken as input to illustrate
String text
= "Computer Science Portal GeeksforGeks";
// Try block to check if exceptions occurs
try {
// Step 1: Create an object of BufferedWriter
BufferedWriter f_writer
= new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx"));
// Step 2: Write text(content) to file
f_writer.write(text);
// Step 3: Printing the content inside the file
// on the terminal/CMD
System.out.print(text);
// Step 4: Display message showcasing
// successful execution of the program
System.out.print(
"File is created successfully with the content.");
// Step 5: Close the BufferedWriter object
f_writer.close();
}
// Catch block to handle if exceptions occurs
catch (IOException e) {
// Print the exception
System.out.print(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
File is created successfully with the content.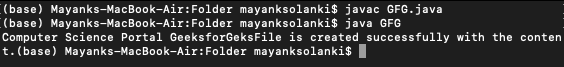
以下示例显示了使用 BufferedWriter 类写入文件。它还需要像 FileWriter 一样创建 BufferedWriter 类的对象来将内容写入文件。但是这个类通过使用大缓冲区大小来支持将大内容写入文件。
方法 4:使用 FileOutputStream 类
它用于将原始流数据写入文件。 FileWriter 和 BufferedWriter 类仅用于将文本写入文件,但可以使用 FileOutputStream 类写入二进制数据。
下面的示例显示了使用 FileOutputStream 类将数据写入文件。它还需要使用文件名创建类的对象以将数据写入文件。这里使用write()方法将字符串内容转换为写入文件的字节数组。
例子
Java
// Java Program to write into a file
// using FileOutputStream Class
// Importing java input output classes
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Assign the file content
String fileContent = "Welcome to geeksforgeeks";
// Try block to check if exception occurs
try {
// Step 1: Create an object of FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream outputStream
= new FileOutputStream("file.txt");
// Step 2: Store byte content from string
byte[] strToBytes = fileContent.getBytes();
// Step 3: Write into the file
outputStream.write(strToBytes);
// Print the success message (Optional)
System.out.print(
"File is created successfully with the content.");
// Step 4: Close the object
outputStream.close();
}
// Catch block to handle the exception
catch (IOException e) {
// Print the exception
System.out.print(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
File is created successfully with the content.